Annuity death benefits are payouts provided to the beneficiaries of an annuity contract upon the death of the annuitant (the person who receives income from the annuity). These benefits offer financial protection and a source of income to the annuitant's loved ones in the event of their passing. The primary purpose of annuity death benefits is to provide financial security and support to the annuitant's beneficiaries. These benefits ensure that the annuitant's investment in the annuity is not lost and can be passed on to their loved ones. There are various types of annuities, such as fixed, variable, and indexed, each with different features and death benefit options. Understanding the different types of annuity death benefits is crucial to making informed decisions when purchasing an annuity. The standard death benefit is the most basic and common type of annuity death benefit. Upon the death of the annuitant, the beneficiary receives the greater of the annuity's account value or the total premiums paid into the annuity. Beneficiaries can choose from several payout options, such as a lump-sum payment, periodic payments over a specified period, or lifetime income payments. An enhanced death benefit offers additional features and guarantees to the standard death benefit, such as a guaranteed growth rate on the account value or a stepped-up death benefit based on the annuity's highest account value on a specified anniversary date. Payout Options Like the standard death benefit, beneficiaries can choose from various payout options, including lump-sum, periodic, or lifetime income payments. A return of premium death benefit guarantees that the beneficiary will receive at least the total amount of premiums paid into the annuity, regardless of the annuity's account value at the time of the annuitant's death. Payout options for the return of premium death benefits are similar to those of the standard and enhanced death benefits, allowing beneficiaries to choose from lump-sum payments, periodic payments, or lifetime income payments. The age of the annuitant at the time of purchasing the annuity can influence the death benefit amount, as older annuitants may have lower death benefits due to a shorter expected lifespan. The annuitant's health status can also impact the death benefit amount, as those with serious health conditions may receive lower death benefits or be denied coverage altogether. The choice of primary and contingent beneficiaries can affect the distribution of annuity death benefits, as different beneficiaries may have different rights and payout options. Annuity contract provisions, such as optional riders and exclusions, can influence annuity death benefits' amount and payout options. For variable and indexed annuities, the investment performance of the underlying assets can significantly impact the annuity's account value and, consequently, the death benefit amount. If beneficiaries choose to receive a lump-sum distribution of annuity death benefits, the earnings portion of the payment is generally subject to federal income tax. For non-qualified annuities, the earnings portion of the death benefit payments is taxable as ordinary income to the beneficiary. The principal, or original investment, is not subject to income tax. The entire death benefit payment is typically subject to federal income tax for qualified annuities, such as those held in an IRA or other retirement accounts. State income tax treatment of annuity death benefits varies depending on the state's tax laws. Beneficiaries should consult with a tax professional to understand the specific state tax implications. Annuity death benefits may be subject to estate taxes, depending on the size of the annuitant's estate and applicable estate tax laws. Proper estate planning can help minimize or avoid estate tax liabilities. Annuity death benefits provide financial security to the annuitant's beneficiaries, ensuring they receive a source of income or a lump-sum payment upon their death. Annuity death benefits offer tax deferral benefits, as the earnings within the annuity grow tax-deferred until they are distributed to the beneficiary. Annuity death benefits offer flexibility in payout options, allowing beneficiaries to choose a payment structure that best suits their financial needs. Annuity death benefits can have tax implications for the beneficiary, as the earnings portion of the benefit is generally subject to federal income tax. The annuitant may have limited control over the underlying investments for variable and indexed annuities, which can impact the account value and death benefit amount. Annuities often come with fees and charges, such as surrender charges, management fees, and rider costs, which can reduce the overall value of the annuity and death benefits overall value. When choosing the right annuity death benefit option, it is essential to assess the financial needs of the annuitant and their beneficiaries, considering factors such as income replacement, debt repayment, and future financial goals. The annuitant should evaluate their investment risk tolerance when selecting an annuity with death benefits, as different annuity types and investment options come with varying levels of risk. Before purchasing an annuity, comparing different annuity products and death benefit options is crucial to find the most suitable product that aligns with the annuitant's financial goals and risk tolerance. Consulting a financial professional like an insurance broker can help the annuitant navigate the complexities of annuity death benefits and make informed decisions tailored to their specific financial situation. Annuity death benefits provide financial security and support to the beneficiaries of the annuity contract upon the annuitant's death. Annuity death benefits play a significant role in overall financial planning, providing a source of income or a lump-sum payment to beneficiaries upon the annuitant's death. By considering the various factors affecting annuity death benefits, weighing the pros and cons, and consulting with an insurance broker, annuitants can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and provide a secure financial future for their beneficiaries. What Are Annuity Death Benefits?
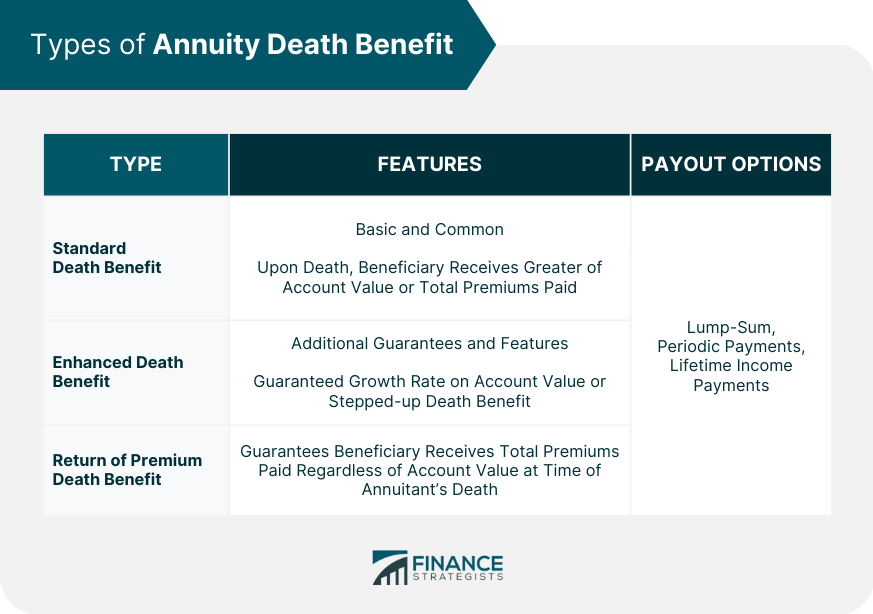
Types of Annuity Death Benefits
Standard Death Benefit
Features
Payout Options
Enhanced Death Benefit
Features
Return of Premium Death Benefit
Features
Payout Options
Factors Affecting Annuity Death Benefits
Age of Annuitant
Health of Annuitant
Beneficiary Designations
Annuity Contract Provisions
Investment Performance
Tax Implications of Annuity Death Benefits
Federal Income Tax
Lump-Sum Distribution
Non-Qualified Annuity
Qualified Annuity
State Income Tax
Estate Tax Considerations
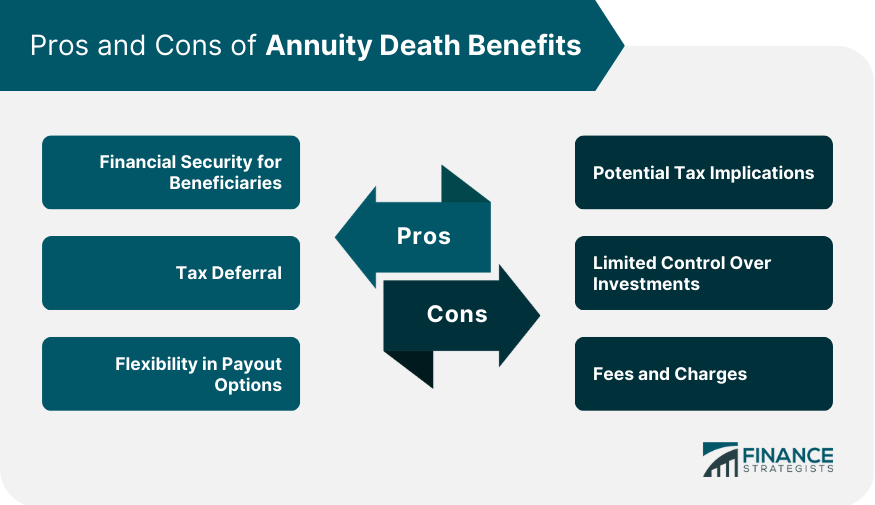
Pros and Cons of Annuity Death Benefits
Advantages
Financial Security for Beneficiaries
Tax Deferral
Flexibility in Payout Options
Disadvantages
Potential Tax Implications
Limited Control Over Investments
Fees and Charges
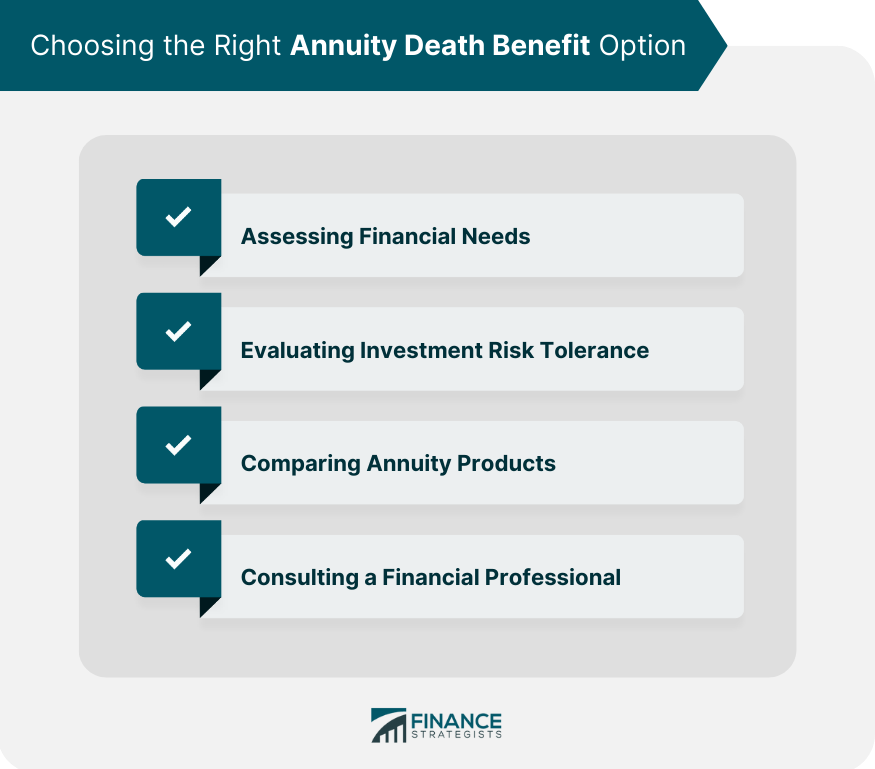
Choosing the Right Annuity Death Benefit Option
Assessing Financial Needs
Evaluating Investment Risk Tolerance
Comparing Annuity Products
Consulting a Financial Professional
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of annuity death benefits, including standard, enhanced, and return of premium death benefits, is crucial to making informed decisions when purchasing an annuity.
Factors that can affect annuity death benefits include the age and health of the annuitant, beneficiary designations, annuity contract provisions, and investment performance.
Annuity death benefits offer advantages, such as financial security for beneficiaries, tax deferral, and flexibility in payout options, but also have potential disadvantages, such as potential tax implications, limited control over investments, and fees and charges.
Annuity Death Benefits FAQs
Annuity death benefits are payouts provided to beneficiaries upon the death of the annuitant, offering financial protection and a source of income to the annuitant's loved ones. They are important for ensuring that the annuitant's investment in the annuity is passed on to their beneficiaries, providing financial security and support.
The three main types of annuity death benefits are standard, enhanced, and return of premium death benefits. Standard death benefits typically pay the greater of the annuity's account value or total premiums paid. Enhanced death benefits offer additional features, such as guaranteed growth rates or stepped-up benefits. Return of premium death benefits guarantees that beneficiaries receive at least the total amount of premiums paid, regardless of the annuity's account value.
Factors affecting annuity death benefits include the age and health of the annuitant, beneficiary designations, annuity contract provisions, and investment performance. These factors can influence the death benefit amount, payout options, and overall value of the annuity.
Annuity death benefits are subject to federal and state income taxes and potential estate taxes. For federal income tax purposes, the earnings portion of the death benefit payments is generally taxable as ordinary income. State income tax treatment varies depending on state laws. Annuity death benefits may also be subject to estate taxes, depending on the size of the annuitant's estate and applicable laws.
To choose the right annuity death benefits option, assess your financial needs and the needs of your beneficiaries, evaluate your investment risk tolerance, compare different annuity products and death benefit options, and consult a financial professional. This process will help you make informed decisions tailored to your specific financial situation and goals, ensuring that your annuity death benefits provide a secure financial future for your beneficiaries.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











