An Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a personal retirement savings plan that offers tax advantages for retirement savings in the United States. On the other hand, an annuity is a financial product that pays out a fixed stream of payments to an individual, primarily used as an income stream for retirees. Combining these two concepts, an annuity in an IRA is a financial strategy where an IRA is used to invest in an annuity, thus creating a more predictable income stream in retirement. This strategy has gained popularity among those seeking a steady income during their retirement years. However, the practicality of this option depends largely on the individual's financial circumstances, retirement goals, and risk tolerance. By combining an annuity with an IRA, you have the potential to impact your retirement income and financial security significantly. This strategy offers the advantage of a predictable income stream, providing stability during retirement. Traditional IRAs are tax-deferred accounts where contributions may be tax-deductible. The money invested in the IRA grows tax-deferred until withdrawn. When you purchase an annuity within a traditional IRA, the payments from the annuity are taxed as ordinary income when withdrawn. This setup can be beneficial if you expect to be in a lower tax bracket in retirement than you are during your working years. Moreover, combining the tax-deferred growth of a traditional IRA with an annuity's regular payments can help create a reliable source of income in retirement. In a Roth IRA, contributions are made after taxes, meaning withdrawals during retirement are typically tax-free. When an annuity is held in a Roth IRA, this extends to the payouts from the annuity. Hence, an annuity in a Roth IRA can provide a stream of tax-free income in retirement, a significant benefit for those concerned about future tax rates. This arrangement also provides more flexibility as Roth IRAs do not have required minimum distributions (RMDs), allowing the annuity to grow as long as desired. A Simplified Employee Pension IRA (SEP-IRA) is an IRA for self-employed individuals and small business owners. A SEP-IRA can also hold an annuity, offering tax-deferred growth on your contributions. The advantage of a SEP-IRA is that it has higher contribution limits than a traditional or Roth IRA, allowing for a larger investment in the annuity. However, like a traditional IRA, withdrawals from the annuity will be taxed as ordinary income. A Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE-IRA) is a retirement plan for small businesses. Like other IRAs, an annuity can be purchased within a SIMPLE IRA. A SIMPLE IRA offers tax-deferred growth and, like the SEP-IRA, has higher contribution limits than a traditional or Roth IRA. This means you could invest more money in an annuity. However, the withdrawals from the annuity are taxed as ordinary income. Evaluate your financial goals, risk tolerance, and retirement needs to determine the most suitable annuity type for you. Fixed Annuities: Offer a guaranteed rate of return and a stable income stream. These are suitable for individuals with low-risk tolerance. Variable Annuities: Linked to the performance of the investment portfolio or sub-accounts they are invested in, offering potentially higher returns with higher risk. Indexed Annuities: A hybrid, where returns are tied to a market index with a guaranteed minimum return but capped maximum return. Consider factors such as: Financial Strength: Look for companies with high ratings from rating agencies such as A.M. Best, S&P, and Moody's. Reputation: Assess customer satisfaction ratings and read reviews to evaluate their customer service and reliability. Annuity Features and Fees: Compare the different annuity products, additional features or riders offered, and associated costs to find the most value. The actual purchase process involves transferring funds from your IRA to the insurance company. This should be a trustee-to-trustee transfer to avoid tax penalties. Steps include: Request for Transfer: Contact your IRA custodian to initiate the fund transfer process. Provide them with the details about the insurance company and the annuity product. Fund Transfer: The IRA custodian will facilitate the direct transfer of funds to the insurance company. Purchase Confirmation: Once the transfer is complete, you'll receive a confirmation from the insurance company, and your annuity contract will start. It's advisable to involve a financial advisor throughout this process. They can provide valuable insights, clarify doubts, and ensure your choices align with your long-term financial objectives. Remember, every step towards purchasing annuities with IRA funds should be carefully considered, given its potential impact on your financial stability in retirement. Insurance companies play a critical role in the annuity transaction. They not only provide the annuity product, but they also guarantee the payouts of the annuity. This is why selecting an insurance company that is financially stable and has a strong reputation in the industry is crucial. When buying an annuity with IRA funds, it's important to consider factors such as interest rates, fees, and associated charges. The return on an annuity often depends on interest rates, so you should understand how current rates compare to historical averages. Additionally, annuities can come with various fees and charges, such as management fees, surrender charges, and mortality and expense risk charges, which can affect the net return of your investment. Tax-deferred growth is one of the main tax advantages of an annuity in an IRA. This means that the earnings from the annuity are taxed once they are withdrawn. This allows the investment to grow faster than it would in a taxable account, as the money that would have gone towards taxes remains invested. It's also crucial to understand the withdrawal rules and potential penalties associated with annuities in IRAs. For traditional, SEP, and SIMPLE IRAs, withdrawals before age 59½ may be subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty and regular income tax. On the other hand, Roth IRAs allow for tax-free and penalty-free withdrawals of contributions at any time, but earnings may be subject to taxes and penalties if withdrawn before age 59½ and before the account is five years old. Traditional, SEP and SIMPLE IRAs require minimum distributions once the account owner reaches age 72. These RMDs also apply to annuities within these IRAs. Failure to take the RMD can result in a significant tax penalty—50% of the amount that should have been withdrawn. However, Roth IRAs do not have RMDs during the owner's lifetime, providing more flexibility for those with annuities in Roth IRAs. Annuities in an IRA can provide a steady stream of income during retirement. Depending on the type of annuity purchased, this could be a fixed amount or vary based on underlying investments' performance. This income can supplement other retirement income sources such as Social Security or pensions. Several factors can affect annuity payouts. These include the amount invested in the annuity, the annuity's interest rate, the age at which the annuity payments begin, the number of years the payments are guaranteed to be made (the "period certain"), and whether the annuity is intended for one or two people. There are several payout options for annuities. These include the income for a guaranteed period (period certain), lifetime payments for the annuitant only (life only), lifetime payments that continue for a spouse after the annuitant's death (joint and survivor), and lifetime payments with a guaranteed total payout (life with cash refund). While annuities can offer predictable income, they can also come with various fees and charges. These can include administrative fees, mortality, and expense risk charges, surrender charges, and investment management fees. High fees can significantly reduce the return on your investment. Annuity payments are typically guaranteed by the insurance company that issues the annuity. Therefore, there is a risk that if the insurance company becomes insolvent, it may be unable to make the promised payments. This risk can be mitigated by choosing an insurance company with a high financial strength rating and by diversifying investments across different companies. Surrender charges are fees that are assessed if you withdraw funds from an annuity before a specified period. These charges can be significant and can reduce your return. In addition, as mentioned earlier, early withdrawals from an IRA before age 59½ may be subject to a 10% penalty. Mutual funds pool money from many investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They can provide diversification and professional management but also have fees and potential tax implications. ETFs are similar to mutual funds but are traded on stock exchanges. They offer diversification and typically have lower fees than mutual funds. Due to their unique structure, ETFs can also be more tax-efficient than mutual funds. Individual bonds and stocks can also be alternatives to an IRA's annuities. While they may require more active management and can be more volatile, they offer the potential for higher returns. Deciding if an annuity in an IRA is right for you requires weighing the pros and cons. The predictable income stream, tax-deferred growth, and potential for a lifetime income can be attractive benefits. However, the fees, potential early withdrawal penalties, and the risk of insurer insolvency are significant considerations. Your personal financial goals and retirement plans play a crucial role in deciding whether an annuity in an IRA is suitable. An annuity might be a good option if you value steady, predictable income and are concerned about outliving your savings. Conversely, you prefer other investment options if you are willing to assume more risk for potentially higher returns or want more flexibility. An insurance broker or financial advisor can provide valuable guidance in decision-making. They can help you understand your options, evaluate different annuity products, and choose a strategy that aligns with your retirement goals and risk tolerance.What Is Annuity in an IRA?
Annuities Within Different IRA Types
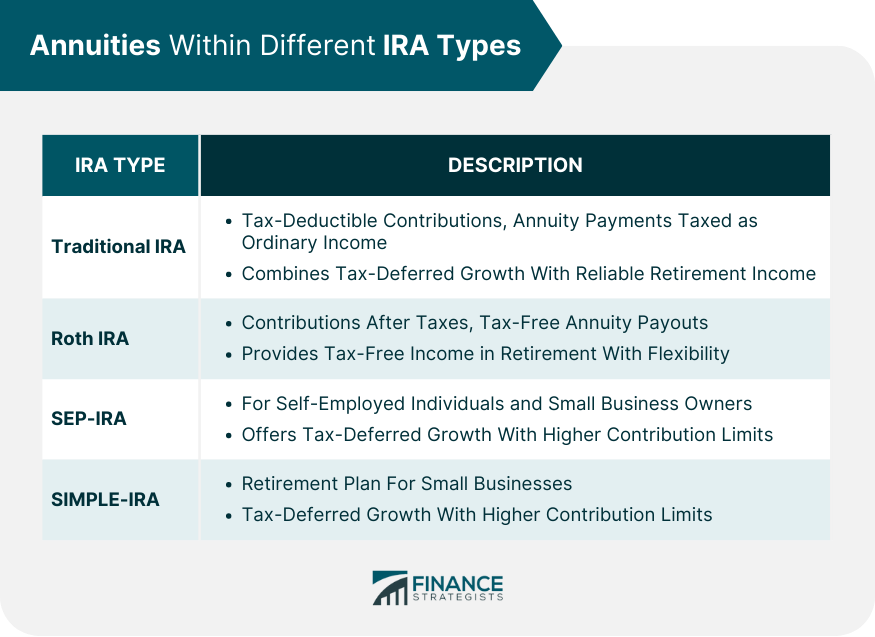
Traditional IRA
Roth IRA
SEP-IRA
SIMPLE-IRA
Steps in Purchasing Annuities
Decide on Type of Annuity
Choose the Right Insurance Company
Transfer Funds
Consult a Financial Advisor

Role of Insurance Companies
Interest Rates, Fees, and Charges
Tax Considerations for Annuities in an IRA
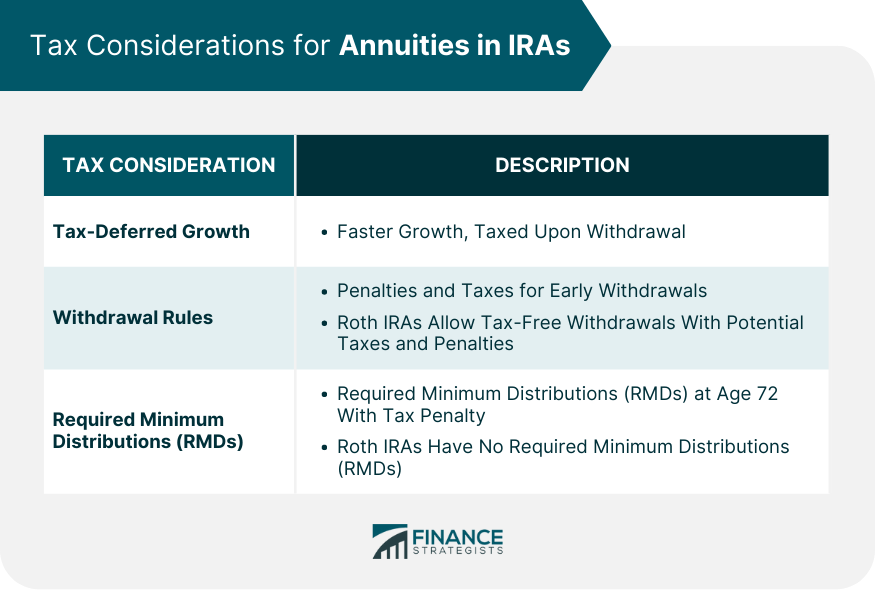
Tax-Deferred Growth
Withdrawal Rules and Penalties
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
Annuities and IRA at Retirement
How Annuities Provide Income During Retirement
Factors Affecting Annuity Payouts
Annuity Payout Options
Potential Risks and Downsides of Annuities in an IRA
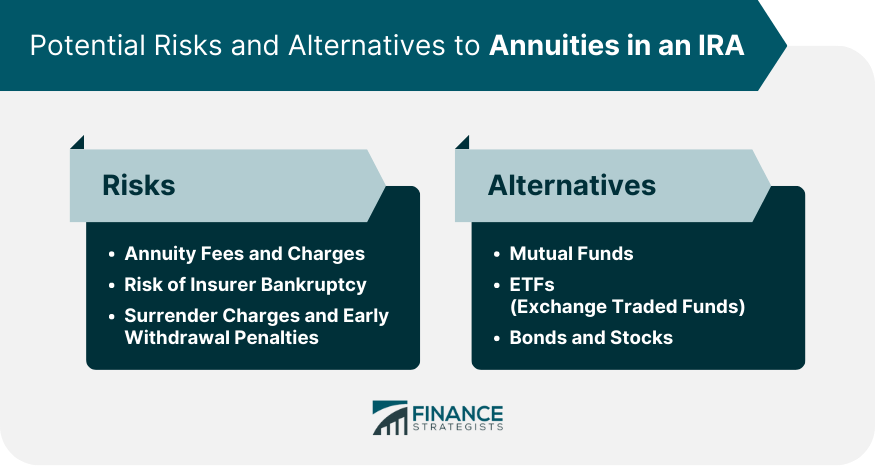
Annuity Fees and Charges
Risk of Insurer Bankruptcy
Surrender Charges and Early Withdrawal Penalties
Alternatives to Annuities in an IRA
Mutual Funds
ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds)
Bonds and Stocks
Conclusion
Annuity in IRA FAQs
"Annuity in an IRA" refers to the strategy of using an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) to invest in an annuity, creating a consistent income stream during retirement.
Incorporating an annuity into an IRA provides a reliable income source, potential tax advantages, and the opportunity for long-term growth within a tax-advantaged retirement account.
Directly transferring an existing annuity into an IRA is not possible. However, funds from an existing annuity can be used to contribute to an IRA, subject to IRS regulations and contribution limits.
The tax implications depend on the specific annuity and IRA type. Withdrawals from a traditional IRA with an annuity are generally taxable as income, while withdrawals from a Roth IRA with an annuity may be tax-free during retirement.
Before including an annuity in an IRA, important considerations include retirement goals, risk tolerance, annuity fees, surrender charges, and potential tax consequences. Seeking guidance from a financial advisor can help evaluate if this strategy aligns with financial objectives.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











