What Are Deferred Income Annuities?
Deferred income annuities (DIAs) are a type of annuity contract designed to provide individuals with a guaranteed income stream, starting at a predetermined point in the future.
They are a popular choice for those seeking financial security in retirement, as they offer protection against outliving one's savings.
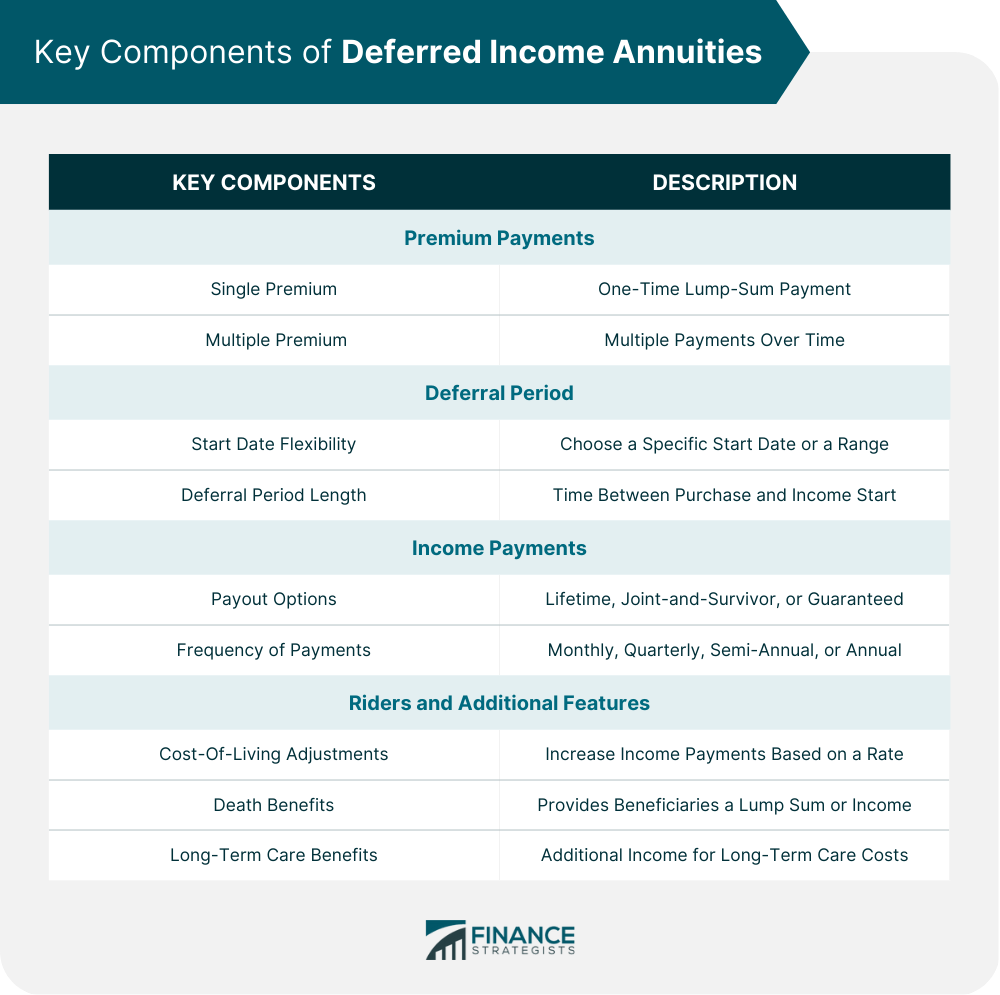
Key Components of Deferred Income Annuities
Premium Payments
Single Premium. A single premium deferred income annuity (SPDIA) involves making a one-time, lump-sum payment to an insurance company in exchange for a guaranteed income stream starting at a future date.
Multiple Premiums. With a flexible premium deferred income annuity (FPDIA), individuals can make multiple payments over time, allowing for a more manageable approach to funding their future income.
Deferral Period
Start Date Flexibility. The deferral period is the time between the purchase of the annuity and the start of the income payments. Policyholders can choose a specific start date or a range of dates, providing flexibility in retirement planning.
Deferral Period Length. The length of the deferral period can vary, but longer deferral periods typically result in higher income payments, as the insurance company has more time to invest the premiums before beginning income payouts.
Income Payments
Payout Options. Income payments can be structured in various ways, including lifetime income, joint-and-survivor income (for couples), or a guaranteed period certain (e.g., 10, 15, or 20 years).
Frequency of Payments. Policyholders can choose the frequency of income payments, with options such as monthly, quarterly, semi-annual, or annual payments.
Riders and Additional Features
Cost-of-Living Adjustments. To help protect against inflation, some DIAs offer cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs), which increase income payments based on a specified rate or index.
Death Benefits. A death benefit rider can provide a lump-sum payment or continued income to beneficiaries if the annuitant dies before or during the income phase.
Long-Term Care Benefits. A long-term care rider can provide additional income to cover long-term care expenses, such as nursing home or home health care costs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Deferred Income Annuity
Financial Goals and Retirement Planning
Individuals should assess their financial goals, anticipated expenses, and desired retirement lifestyle when determining whether a DIA is appropriate for their needs.
Risk Tolerance and Investment Horizon
DIAs can provide a level of certainty and protection against market volatility, making them suitable for conservative investors or those with a shorter investment horizon.
Inflation and Interest Rate Considerations
The impact of inflation and interest rates on the purchasing power of future income payments should be considered when choosing a DIA, as higher inflation and interest rates can erode the real value of the income stream.
Tax Implications
DIAs offer tax-deferred growth, but income payments are taxed as ordinary income. Understanding the tax implications of DIAs can help individuals make more informed decisions.
Insurance Company's Financial Strength
Selecting a financially stable insurance company with a strong credit rating is essential, as the company's ability to meet its contractual obligations will impact the security of the annuity income.

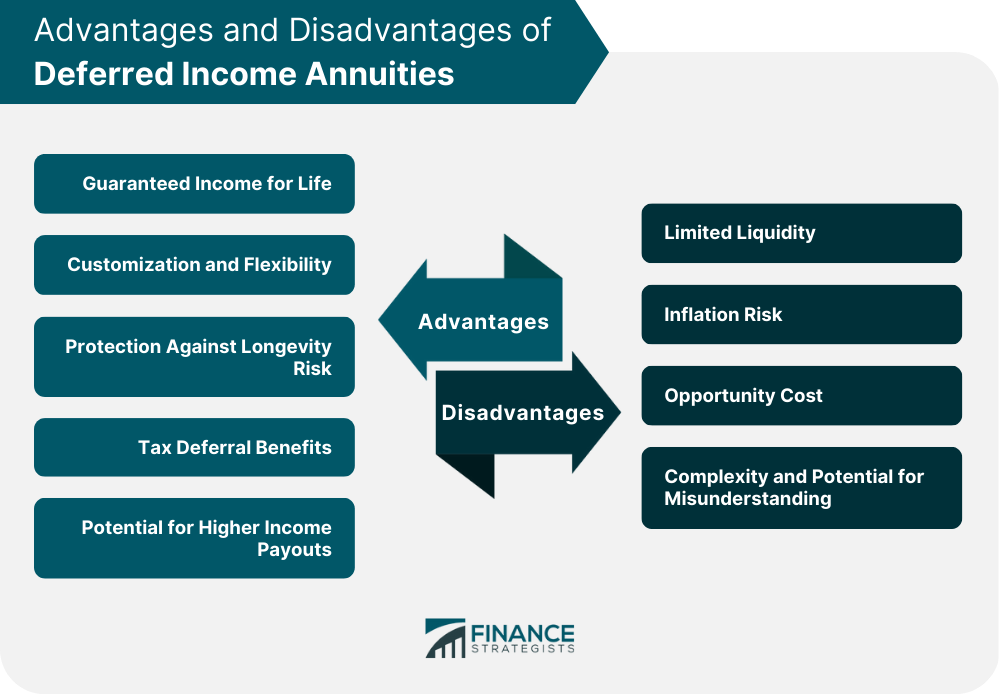
Advantages of Deferred Income Annuities
Guaranteed Income for Life
DIAs provide a guaranteed income stream for life or a specified period, reducing the risk of outliving one's savings.
Customization and Flexibility
Policyholders can customize their DIA by choosing the deferral period, payout options, frequency of payments, and additional riders to meet their unique needs and financial goals.
Protection Against Longevity Risk
With increased life expectancies, the risk of outliving one's retirement savings is a significant concern. DIAs help mitigate this risk by providing a guaranteed income stream for life or a specified period.
Tax Deferral Benefits
Deferred income annuities allow for tax-deferred growth of the premium payments, potentially resulting in more significant income payments in the future. However, it's important to note that the income payments will be taxed as ordinary income when received.
Potential for Higher Income Payouts
Longer deferral periods can result in higher income payments, as the insurance company has more time to invest the premiums before beginning income payouts.
Disadvantages and Potential Drawbacks of Deferred Income Annuities
Limited Liquidity
Once purchased, DIAs typically offer limited or no liquidity, meaning policyholders cannot easily access the funds invested in the annuity before the income phase begins.
Inflation Risk
Fixed income payments from a DIA may not keep pace with inflation, resulting in a decrease in purchasing power over time. Choosing a DIA with a cost-of-living adjustment can help mitigate this risk.
Opportunity Cost
Investing in a DIA may result in opportunity cost or lower potential returns compared to other investment options, such as equities or bonds, especially during periods of strong market performance.
Complexity and Potential for Misunderstanding
DIAs can be complex products with various features, riders, and fees, making it essential for individuals to fully understand the terms and conditions before purchasing.
Strategies for Incorporating Deferred Income Annuities in Retirement Planning
Diversification and Asset Allocation
Including a DIA as part of a diversified portfolio can provide a stable income stream, reducing the impact of market volatility on retirement income because of the distribution of different assets across a portfolio.
Laddering Annuities
Purchasing multiple DIAs with staggered start dates can provide a strategy for addressing changing income needs and managing interest rate risk in retirement.
Combining With Other Retirement Income Sources
Integrating DIAs with other retirement income sources, such as Social Security, pensions, and investment portfolios, can create a comprehensive and diversified retirement income plan.
Regulation and Oversight of Deferred Income Annuities
State Insurance Departments
DIAs are regulated at the state level by state insurance departments, which enforce compliance with insurance laws and protect consumers.
National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC)
The NAIC is a U.S. regulatory support organization that establishes model laws and regulations for insurance products, including annuities, and helps coordinate state insurance regulation efforts.
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA)
FINRA is a self-regulatory organization that oversees broker-dealers and registered representatives who sell annuities, ensuring compliance with securities laws and promoting investor protection.
Final Thoughts
Deferred income annuities are an attractive option for those seeking a guaranteed income stream in retirement, providing protection against longevity risk and market volatility.
However, as with any financial product, it's important to consider the advantages, disadvantages, and potential risks before making a decision.
Factors such as financial goals, risk tolerance, inflation and interest rate considerations, and the insurance companies' financial strength should all be taken into account.
Incorporating a DIA into a diversified retirement income plan and seeking the advice of a trusted insurance broker can help ensure a more secure and comfortable retirement.
If you're considering purchasing a deferred income annuity, it's essential to work with a knowledgeable insurance broker who can help guide you through the decision-making process and ensure that you fully understand the terms and conditions of the product.
By seeking the advice of an insurance professional, you can make a more informed decision and feel more confident about your retirement income plan.
Deferred Income Annuities FAQs
A deferred income annuity (DIA) is a type of annuity contract that offers a guaranteed income stream starting at a predetermined point in the future.
Deferred income annuities provide a guaranteed income stream for life, protection against longevity risk, customization and flexibility, tax-deferred growth, and potential for higher income payouts.
Potential drawbacks of deferred income annuities include limited liquidity, inflation risk, opportunity cost, complexity, and potential for misunderstanding.
When choosing a deferred income annuity, it's essential to consider factors such as financial goals, risk tolerance, inflation and interest rate considerations, tax implications, and the insurance company's financial strength.
Yes, it's highly recommended to seek the advice of a knowledgeable insurance broker before purchasing a deferred income annuity. An insurance professional can help guide you through the decision-making process, ensure that you fully understand the terms and conditions of the product, and help you make a more informed decision.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











