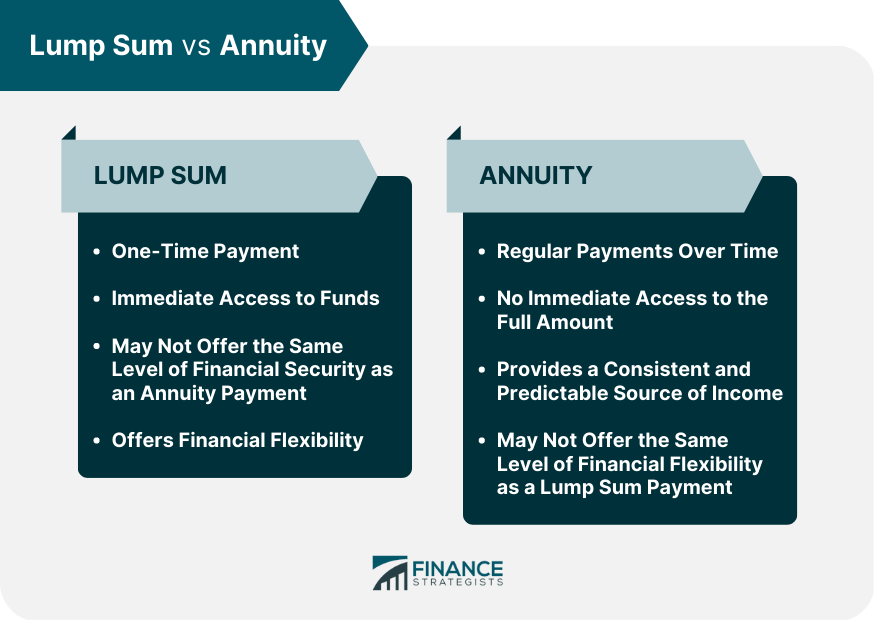
A lump sum payment is a one-time, usually large, payment made to an individual. This can come in the form of an inheritance, legal settlement, or lottery win. The recipient of a lump sum payment gains access to the full amount of the payment immediately. An annuity payment, on the other hand, is a series of regular payments made to an individual over a period of time. This can be in the form of a retirement pension, a structured settlement, or a lottery win. The recipient of an annuity payment receives regular payments over a set period of time, typically ranging from a few years to a lifetime. There are pros and cons to each option. A lump sum payment can provide immediate access to funds, which can be used to pay off debt, make large purchases, or invest in other areas. However, if not invested wisely, the lump sum payment can quickly diminish in value. An annuity payment, while providing a more consistent and predictable source of income, may not offer the same level of financial flexibility as a lump sum payment. Deciding between Lump Sum and Annuity? Click here. These factors are essential to consider as they can impact the amount of money received, financial security, and overall investment returns: For individuals who are younger and have a longer life expectancy, taking a lump sum payment may be a better option, as they have more time to invest and potentially grow their money. For older individuals, an annuity may be more attractive, as they can rely on a steady stream of income for the rest of their life. For those who need a large sum of money immediately to pay off debt or make a significant purchase, a lump sum payment may be the better option. For individuals who have a stable source of income but are concerned about having enough money in retirement, an annuity payment may be more attractive. A lump sum payment can provide more investment flexibility and the opportunity for higher returns but comes with greater risk. An annuity payment, while less risky, may not provide the same level of investment flexibility or the potential for high returns. A lump sum payment may result in a higher tax bill initially, but may also offer more tax planning opportunities in the future. An annuity payment, on the other hand, may result in lower taxes overall but also offer fewer tax planning opportunities. A lump sum payment can provide more flexibility when it comes to leaving an inheritance or making charitable donations. An annuity payment, while providing a consistent source of income, may not offer the same level of flexibility when it comes to estate planning. To help illustrate the decision-making process between a lump sum payment and an annuity payment, here are some real-life scenarios: Imagine you are the lucky winner of a lottery jackpot. You are faced with the decision of choosing between a lump sum payment of $10 million or an annuity payment of $500,000 annually for 20 years. If you are young and have a longer life expectancy, the lump sum payment may be the better option, as you have more time to invest and grow your money. However, if you are older and concerned about having a steady stream of income in retirement, the annuity payment may be more attractive. Additionally, if you have a high-risk tolerance and a solid investment plan, the lump sum payment may provide the opportunity for greater returns. Assume that you are approaching retirement age and have saved $1 million for retirement. You can choose to receive either a lump sum payment or an annuity payment of $3,000 per month for the remainder of your life. If you are concerned about having a steady stream of income in retirement, the annuity payment may be the better option. However, if you have a high-risk tolerance and a solid investment plan, the lump sum payment may be a better option in terms of anticipated returns.. Additionally, if you have specific financial goals, such as paying off debt or making a large purchase, the lump sum payment may be more attractive. Suppose you are the recipient of a $1 million legal settlement. You have the option of taking a lump sum payment or an annuity payment of $5,000 per month for the next 16 years. If you have a stable source of income and are concerned about having a consistent stream of income for the coming years, the annuity payment may be the better option. However, if you have specific financial goals or investment opportunities, the lump sum payment may be more attractive. Additionally, if you have concerns about the stability of the annuity provider, the lump sum payment may be a safer option. Investment strategies for a lump sum payment and an annuity payment can vary significantly. For a lump sum payment, investing in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other assets can provide the potential for higher returns. However, this comes with greater risk, and it is important to have a solid investment plan and risk management strategy in place. For an annuity payment, there are several options, including immediate annuities, variable annuities, and fixed annuities. Fixed annuities provide a set payment over a period of time, while variable annuities offer the potential for higher returns but also come with greater risk. Immediate annuities provide a guaranteed income stream for life but offer less investment flexibility. When faced with the decision of receiving a lump sum payment or an annuity payment, it is important to consider a range of factors, including age, income needs, investment goals, tax implications, and estate planning considerations. There are pros and cons to each option, and the best choice will depend on the individual's unique circumstances and financial goals. Investment strategies for a lump sum payment and an annuity payment can also vary significantly, and it is important to have a solid investment plan and risk management strategy in place. Ultimately, whether choosing a lump sum payment or an annuity payment, it is important to seek the advice of a financial professional and to carefully consider all available options before making a decision that can have a significant impact on your financial future.Lump Sum vs Annuity
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between a Lump Sum and Annuity
Age and Life Expectancy
Income Needs
Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
Tax Implications
Estate Planning Considerations

Real-Life Scenarios for Lump Sum vs Annuity
Scenario 1: Lottery Winnings
Scenario 2: Retirement Savings
Scenario 3: Legal Settlement
Investment Strategies for Lump Sum vs Annuity
Final Thoughts
Lump Sum vs Annuity FAQs
A lump sum payment is a one-time payment, while an annuity payment is a series of regular payments made over a period of time.
Age and life expectancy, income needs, investment goals, and risk tolerance, tax implications, and estate planning considerations are factors to consider.
The answer depends on the individual's unique circumstances and financial goals. Each option has pros and cons, and the best choice will depend on a range of factors, including age, income needs, investment goals, tax implications, and estate planning considerations.
Investment strategies for a lump sum payment can include investing in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other assets. In contrast, investment strategies for an annuity payment can include fixed annuities, variable annuities, and immediate annuities.
Yes, it is important to seek the advice of a financial professional and to carefully consider all available options before making a decision that can have a significant impact on your financial future.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











