Retirement annuities are long-term financial contracts provided by insurance companies that offer a steady stream of income during retirement. They function as a form of insurance against outliving one's retirement savings and provide financial stability in the later years of life. The primary goal of retirement annuities is to provide a secure and stable income source during retirement, ensuring financial security and peace of mind. They also serve as an essential tool for diversifying one's retirement income sources and mitigating the risk of market fluctuations. There are several types of annuities for retirement, each with unique features and benefits. These include immediate annuities, deferred annuities, fixed annuities, variable annuities, and indexed annuities. Immediate annuities are contracts that begin paying out a predetermined income stream immediately after the purchase. The annuitant makes a lump-sum payment to the insurance company, and in return, the company guarantees a fixed income for a specified period or for the annuitant's lifetime. Immediate annuities offer the advantage of generating income right away, which can be beneficial for those who need financial support as soon as they retire. This type of annuity can provide a guaranteed income for the annuitant's life or a specified period, ensuring financial stability. However, the downside of immediate annuities is their lack of liquidity, as the initial investment is locked in the annuity. Furthermore, there is no potential for capital appreciation, meaning the annuitant will not benefit from any increase in the value of the underlying assets. Deferred annuities are contracts that accumulate funds over a specified period before starting to pay out income. The annuitant makes either a lump-sum payment or a series of payments during the accumulation phase, and the funds grow tax-deferred until the payout phase begins. Deferred annuities allow for tax-deferred growth, enabling the annuitant to accumulate wealth over time without paying taxes on gains until the payout phase begins. Additionally, these annuities offer flexible contribution options, making it easier for individuals to adapt their investment strategy as needed. On the other hand, deferred annuities do not provide immediate income, which can be a drawback for those who need financial support upon retirement. There is also the potential for surrender charges if the annuitant decides to withdraw funds early, which can be a significant disadvantage. Fixed annuities are contracts that provide a guaranteed fixed interest rate during the accumulation phase and a predetermined income stream during the payout phase. They offer a safe and predictable return on investment. Fixed annuities provide the benefit of a guaranteed interest rate, offering a predictable and stable return on investment. This feature makes fixed annuities an attractive option for conservative investors or those who want a steady income stream during retirement. However, the downside of fixed annuities is their limited potential for growth, as the interest rate is fixed and may not keep pace with inflation. As a result, the annuitant's purchasing power might erode over time, leading to a reduced standard of living in retirement. Variable annuities are contracts that allow the annuitant to invest in a variety of investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. The income generated during the payout phase depends on the performance of the underlying investments. Variable annuities offer the potential for higher returns due to the flexibility of investing in a range of investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. This feature can be attractive to those looking to maximize their retirement income through capital appreciation. However, variable annuities come with higher fees compared to other annuity types, as they include management fees and other charges associated with the underlying investments. Moreover, the investment risk associated with variable annuities can result in losses if the investments perform poorly, impacting the annuitant's retirement income. Indexed annuities are contracts that link the performance of the annuity to a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. The annuity's return depends on the performance of the index, but it usually includes a guaranteed minimum return to protect against market downturns. Indexed annuities can provide the potential for higher returns by linking the annuity's performance to a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. This feature allows the annuitant to benefit from market gains while offering some protection against market downturns through a guaranteed minimum return. However, indexed annuities often have a cap on returns, limiting the potential gains during periods of strong market performance. Additionally, the complexity of indexed annuities can make it difficult for some investors to understand the product fully and make informed decisions. Consider your long-term financial objectives and risk appetite before choosing an annuity. Assess whether you need immediate income, guaranteed returns, or growth potential. Annuities offer various payout options, including life-only, joint and survivor, and period-certain annuities. Consider the best option based on your individual needs and financial situation. Annuities may come with various fees and charges, such as surrender charges, management fees, and mortality and expense risk charges. Be sure to understand and compare these costs before making a decision. Annuities offer tax-deferred growth, but the income generated during the payout phase is taxable. Understand the tax implications of different annuity types and consult a tax professional for guidance. Inflation can erode the purchasing power of your annuity income. Consider annuities with features that help protect against inflation, such as cost-of-living adjustments or inflation-linked returns. Choose an annuity provider with a strong financial rating and reputation to ensure the long-term stability and security of your investment. Retirement annuities serve as an important tool for diversifying income sources during retirement, providing a stable income stream alongside other income sources such as Social Security, pensions, and investments. Annuities can help protect against the risk of outliving one's savings by providing a guaranteed lifetime income, ensuring financial security in retirement. Retirement annuities offer a predictable and steady income stream, providing financial stability and peace of mind during retirement. Annuities can help preserve the principal of your investment, protecting your retirement savings from market fluctuations and downturns. Social Security is a government-run program that provides a source of retirement income based on your work history and earnings. Pensions are employer-sponsored retirement plans that provide a guaranteed income during retirement, based on factors such as years of service and salary. IRAs are tax-advantaged investment accounts that allow individuals to save for retirement independently of their employer. 401(k) plans are employer-sponsored retirement savings plans that offer tax advantages and the potential for employer matching contributions. Investing in dividend-paying stocks can provide a source of income during retirement through regular dividend payments. Bonds are fixed-income securities that pay interest over a fixed period, offering a predictable income stream during retirement. Investing in real estate, either through direct property ownership or real estate investment trusts (REITs), can generate rental income and potential capital appreciation during retirement. Mutual funds and ETFs offer diversified investment options, providing potential income and growth during retirement. Retirement annuities are long-term contracts offered by insurance companies that provide a guaranteed income stream during retirement, protecting against the risk of outliving savings. There are various types of annuities, including immediate, deferred, fixed, variable, and indexed annuities, each with unique features and benefits. Factors to consider when choosing a retirement annuity include financial goals, payout options, fees and charges, tax implications, inflation protection, and the financial strength of the annuity provider. Retirement annuities play a crucial role in retirement planning by diversifying income sources, protecting against longevity risk, ensuring a steady income stream, and preserving principal. Alternatives to retirement annuities include Social Security, pensions, IRAs, 401(k) plans, dividend-paying stocks, bonds, real estate, mutual funds, and ETFs. Consult with a financial advisor, insurance broker, or retirement planning professional to help navigate the complex world of retirement annuities and ensure you make informed decisions that align with your financial objectives and retirement needs.What Are Retirement Annuities?
Types of Retirement Annuities
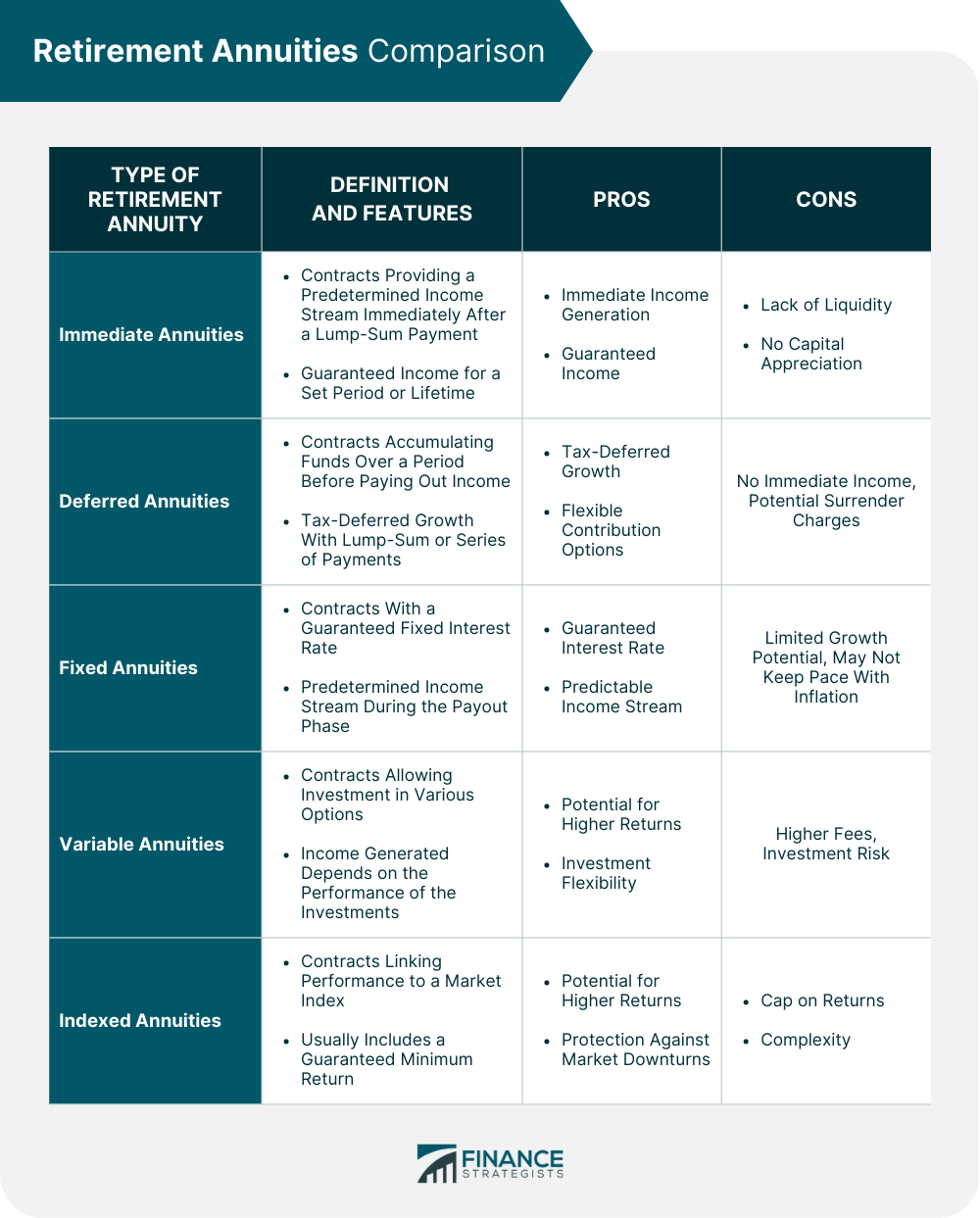
Immediate Annuities
Deferred Annuities
Fixed Annuities
Variable Annuities
Indexed Annuities
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Retirement Annuity
Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
Payout Options
Fees and Charges
Tax Implications
Inflation Protection
Financial Strength of the Annuity Provider

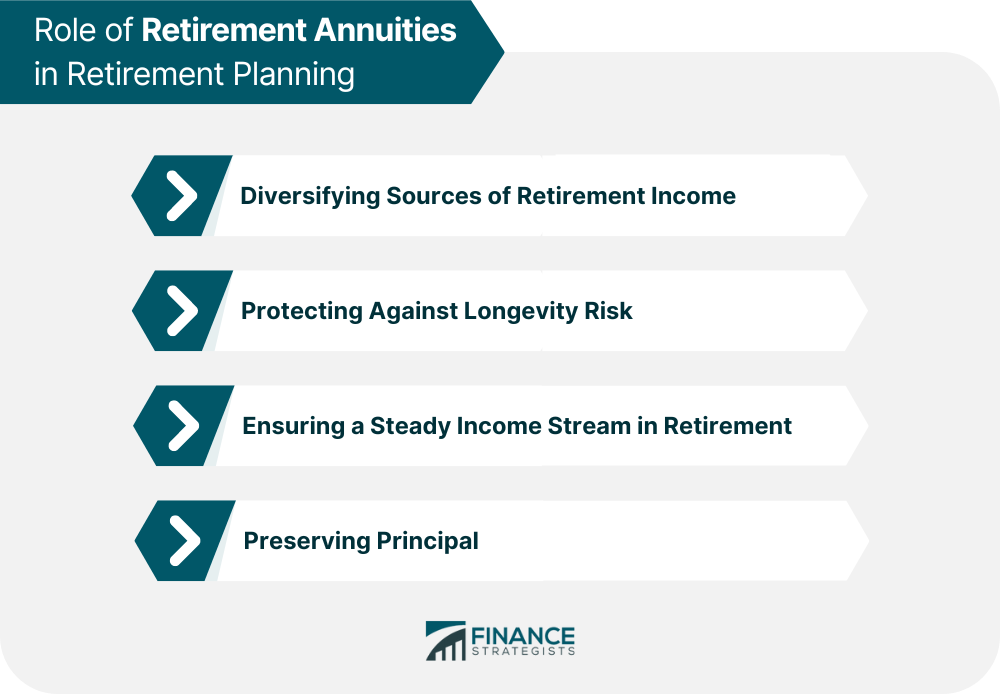
Role of Retirement Annuities in Retirement Planning
Diversifying Sources of Retirement Income
Protecting Against Longevity Risk
Ensuring a Steady Income Stream in Retirement
Preserving Principal
Possible Alternatives to Retirement Annuities
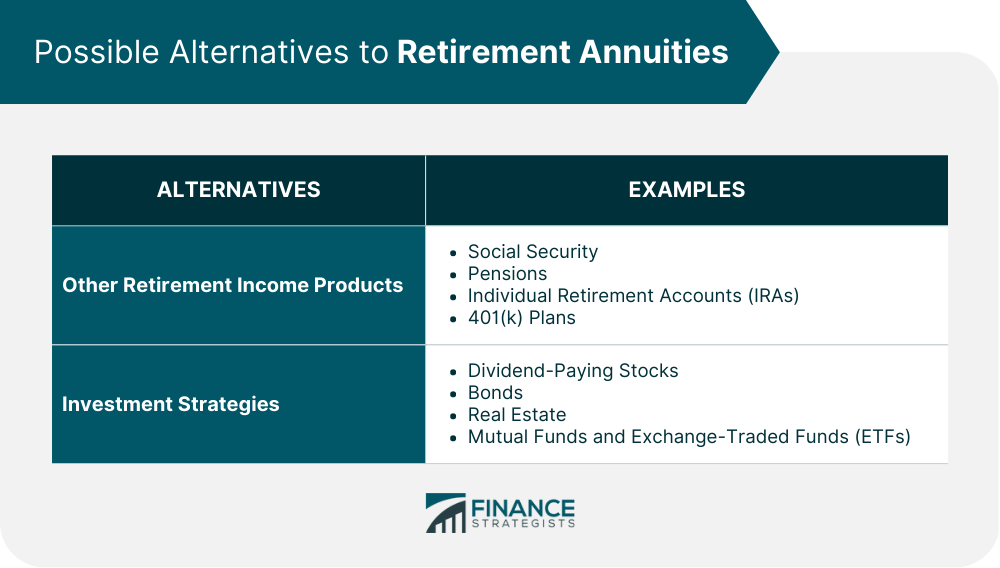
Other Retirement Income Products
Social Security
Pensions
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
401(k) Plans
Investment Strategies
Dividend-Paying Stocks
Bonds
Real Estate
Mutual Funds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Bottom Line
Retirement Annuities FAQs
The main types of retirement annuities include immediate annuities, deferred annuities, fixed annuities, variable annuities, and indexed annuities. Each type offers unique features and benefits, catering to different financial goals and risk tolerances.
Retirement annuities can serve as a stable and secure source of income during retirement, alongside other income sources such as Social Security, pensions, and investments. They help diversify your retirement income, reducing reliance on any single source and providing financial stability.
When choosing a retirement annuity, consider your financial goals and risk tolerance, payout options, fees and charges, tax implications, inflation protection, and the financial strength of the annuity provider.
Yes, retirement annuities can provide a guaranteed lifetime income, ensuring financial security and mitigating the risk of outliving your savings during retirement.
Alternatives to retirement annuities include other retirement income products such as Social Security, pensions, Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), and 401(k) plans, as well as investment strategies like dividend-paying stocks, bonds, real estate, mutual funds, and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs).
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











