Coinsurance is a term used in insurance policies that refers to the percentage of covered costs that the insured individual is responsible for after the deductible has been met. It's a form of cost-sharing between the insurance company and the policyholder. For example, if your health insurance plan has a coinsurance rate of 20%, once you've met your deductible, you would pay 20% of the cost of any additional covered healthcare services, and your insurance company would pay the remaining 80%. If your healthcare costs exceed the out-of-pocket maximum specified in your policy, your insurance will typically cover 100% of the additional costs. Coinsurance is common in health insurance policies but can also be found in other types of insurance, such as property insurance. It's important to understand the terms of your insurance policy, including the deductible, coinsurance rate, and out-of-pocket maximum, as these determine how much you could end up paying out-of-pocket for your healthcare or other insured services. Health insurance policies often include coinsurance provisions. These provisions require the policyholder to share a percentage of the cost of healthcare services, such as hospitalizations, surgeries, and prescription medications. Property insurance, such as homeowners and commercial property insurance, may also have coinsurance clauses. These clauses determine the cost-sharing between the policyholder and the insurance company in case of a covered loss. Professional liability insurance, which protects individuals and businesses from claims related to professional errors, may also include coinsurance provisions. These provisions specify the percentage of a claim that the policyholder is responsible for paying. Coinsurance can also be found in various other insurance policies, such as auto, marine, and disability insurance. It serves as a mechanism for cost-sharing and responsible behavior, promoting effective cost management. The coinsurance percentage is the portion of the cost that the policyholder is responsible for paying. This percentage varies depending on the specific insurance policy and can range from 10% to 50% or more. Most insurance policies have a cap on the total amount that the policyholder must pay in a given period, known as the maximum out-of-pocket expenses. Once this cap is reached, the insurance company covers 100% of the remaining costs. The deductible is the amount the policyholder must pay before the insurance company begins covering expenses. Coinsurance comes into play after the deductible has been met and affects the amount that the policyholder is responsible for paying. To illustrate how coinsurance works, consider the following: A policyholder has a health insurance policy with a $1,000 deductible and a 20% coinsurance rate. They incur $5,000 in medical expenses. After meeting the $1,000 deductible, there is a remaining balance of $4,000. With a 20% coinsurance rate, the policyholder pays an additional $800 (20% of $4,000), and the insurance company covers the remaining $3,200. As mentioned, the deductible is the initial amount the policyholder must pay before the insurance company starts covering expenses. Deductibles can vary widely, depending on the policy and the policyholder's preferences. While both coinsurance and deductibles are forms of cost-sharing, they function differently. The deductible is a fixed amount, whereas coinsurance is a percentage of the remaining costs after the deductible has been met. Coinsurance and deductibles work in tandem to manage the costs of insurance claims. After the policyholder pays the deductible, the coinsurance rate determines the percentage of the remaining expenses that the policyholder and insurance company share. Coinsurance offers several advantages for both policyholders and insurance companies. These benefits include: Encouraging Cost-Sharing and Consumer Responsibility: Coinsurance helps policyholders become more aware of the cost of services. It encourages them to make more informed care or insurance coverage decisions. Lower Premiums for Policyholders: By sharing the cost of claims, coinsurance can help reduce the overall cost of insurance premiums for policyholders. Reducing Overutilization of Insurance Services: Since policyholders are responsible for some of their expenses, they are less likely to overuse services or seek unnecessary treatments. Providing Insurance Companies With Financial Stability: Coinsurance helps insurance companies manage financial risks by distributing costs between policyholders and insurers, which can lead to greater financial stability in the industry. Despite its benefits, coinsurance also has some drawbacks: Out-Of-Pocket Expenses for Policyholders: coinsurance can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses, which may be burdensome for some individuals, especially those with low incomes or chronic health conditions. Confusion Surrounding Coinsurance Calculations: Understanding and calculating coinsurance can be complex and confusing, leading to potential misunderstandings and financial surprises. Potential Financial Barriers to Accessing Care or Services: High coinsurance rates may discourage some policyholders from seeking necessary care or services due to the financial burden. Burden on Low-Income Policyholders: Coinsurance can disproportionately affect low-income individuals who may struggle to cover their share of costs. There are several strategies that policyholders can employ to manage coinsurance costs: Understand Your Insurance Policy: Thoroughly reviewing and understanding the details of an insurance policy can help policyholders make informed decisions about their coverage and potential costs. Choose the Right Coinsurance Plan: When selecting an insurance plan, it is essential to consider the coinsurance rate and how it may impact out-of-pocket expenses. Shop for Healthcare Providers and Services: Policyholders can research and compare various healthcare providers and services costs to ensure they receive the best value for their coinsurance payments. Utilize Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs): These accounts allow individuals to set aside pre-tax funds to cover out-of-pocket medical expenses, including coinsurance costs. Coinsurance is a critical financial concept that plays a significant role in various insurance policies, such as health, property, and professional liability insurance. A thorough understanding of coinsurance, its implications, and its relationship with deductibles is essential for policyholders to make well-informed decisions about their insurance coverage. Policyholders can better anticipate their financial responsibilities by examining the coinsurance formula, its percentage, maximum out-of-pocket expenses, and the impact of the deductible. Weighing the benefits of coinsurance, such as lower premiums and reduced overutilization of services, against the potential drawbacks, like increased out-of-pocket expenses and financial barriers, is crucial for informed decision-making. To effectively manage coinsurance costs, policyholders should understand their insurance policies, choose the right coinsurance plan, shop for cost-effective healthcare providers and services, and consider utilizing Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs). By keeping an eye on emerging trends and future developments in the insurance industry, individuals can better navigate the complexities of coinsurance, leading to greater financial security and overall peace of mind.What Is Coinsurance?
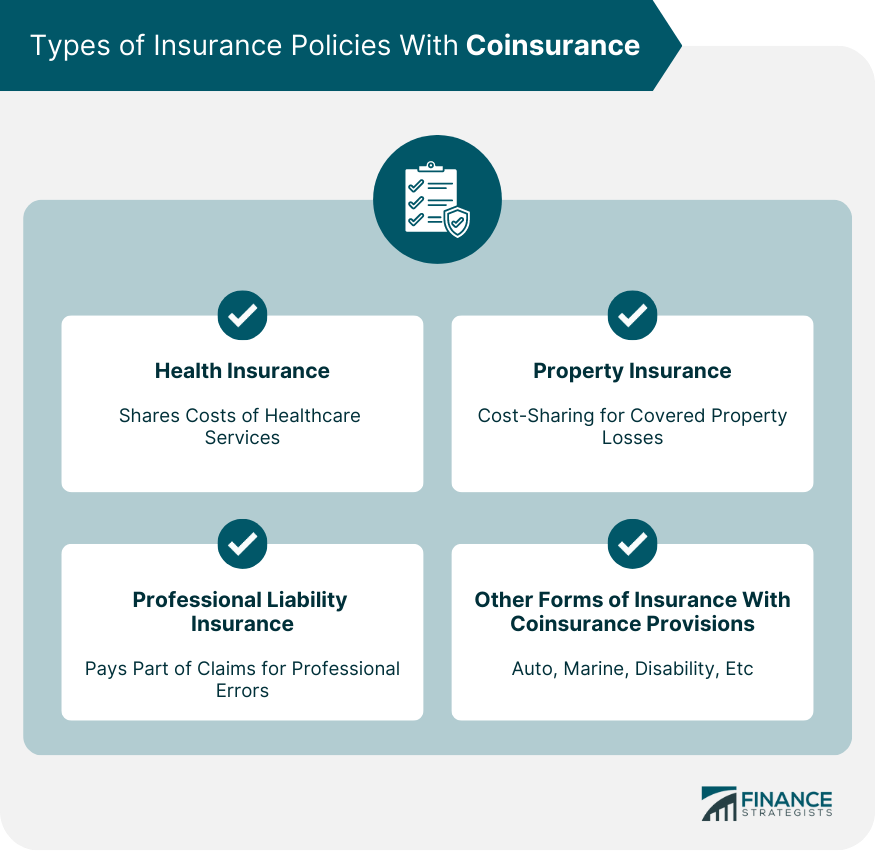
Types of Insurance Policies With Coinsurance
Health Insurance
Property Insurance
Professional Liability Insurance
Other Forms of Insurance With Coinsurance Provisions
Coinsurance Formula and Calculation
Coinsurance Percentage
Maximum Out-Of-Pocket Expenses
Impact of the Deductible on Coinsurance
Coinsurance Calculation Example
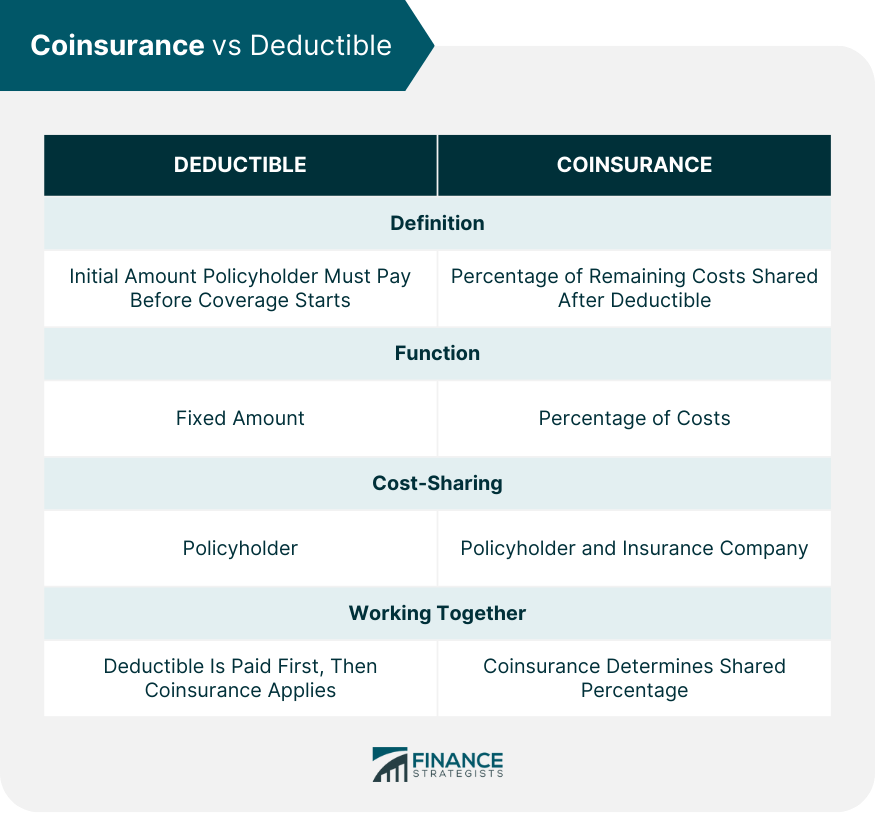
Coinsurance vs Deductible
Definition of Deductible
Comparison Between Coinsurance and Deductible
How Coinsurance and Deductible Work Together
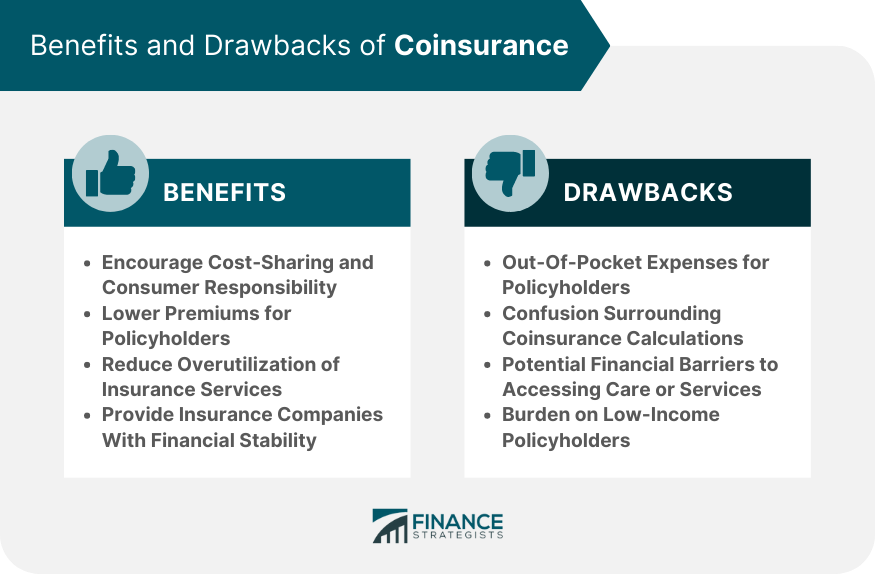
Benefits of Coinsurance
Drawbacks of Coinsurance
Tips for Managing Coinsurance Costs

Conclusion
Coinsurance FAQs
Coinsurance is a type of cost-sharing arrangement in health insurance where the insured pays a certain percentage of the covered healthcare costs after meeting their deductible. For example, if your coinsurance is 20%, you would pay 20% of the cost of covered healthcare services, and your insurance would pay the remaining 80%.
Coinsurance and copay are both forms of cost-sharing, but they work differently. A copay is a fixed amount you pay for a specific service or prescription, regardless of the actual cost of the service. Coinsurance, conversely, is a percentage of the cost of a service you pay after your deductible has been met.
An 80/20 coinsurance means that once you've met your deductible, your insurance company will pay 80% of your covered healthcare costs, and you will be responsible for the remaining 20%. If your healthcare costs exceed the out-of-pocket maximum, your insurance typically covers 100% of the additional costs.
Coinsurance applies after the deductible is met. For example, if you have a $1,000 deductible and 20% coinsurance, you would first pay 100% of your healthcare costs until you've spent $1,000. After that, you would pay 20% of additional healthcare costs, with your insurance covering the remaining 80%.
If you can't afford to pay your coinsurance, you can set up a payment plan with your healthcare provider. However, it's important to understand that not paying your coinsurance can lead to medical debt and potentially damage your credit. If you're having trouble affording your healthcare costs, consider looking into financial assistance programs or choosing a health insurance plan with lower coinsurance.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











