Group disability insurance is a type of insurance that provides income replacement benefits to employees who become disabled and are unable to work. It is typically offered as part of an employer's benefits package, and covers a group of individuals rather than just one person. The purpose of group disability insurance is to provide financial protection to employees in the event of an unexpected illness or injury that results in the inability to work. The insurance policy typically specifies the circumstances under which a person is considered disabled and eligible for benefits, as well as the amount and duration of benefits that will be provided. One of the main advantages of group disability insurance is its cost-effectiveness. Insurers can provide coverage at lower rates due to the large number of participants in a group policy, making it more affordable for both employers and employees. In most cases, group disability insurance policies have a simplified underwriting process. This means that employees do not have to undergo medical examinations or provide detailed health histories, which can be time-consuming and invasive. Group disability insurance is often part of an employer-sponsored benefits package. Offering this type of coverage can help companies attract and retain top talent, as employees appreciate the financial protection and security provided by disability insurance. There are potential tax advantages associated with offering group disability insurance. Depending on the plan structure, premiums paid by employers may be tax-deductible, and employees may receive benefits tax-free. Offering group disability insurance can improve employee morale and retention, as it demonstrates that employers care about their employees' well-being and financial security. Short-term disability insurance provides financial support to employees who are temporarily unable to work due to illness, injury, or pregnancy. It typically covers a percentage of the employee's pre-disability income, with benefits lasting for a limited period. Short-term disability policies usually offer benefit periods ranging from a few weeks to several months, depending on the specific plan. Most short-term disability plans have a waiting period before benefits begin, typically ranging from a few days to a couple of weeks. Common triggers for short-term disability benefits include accidents, surgeries, and medical conditions that require extended recovery time. Long-term disability insurance provides financial support to employees who are unable to work for an extended period due to a serious illness or injury. Like short-term disability insurance, it typically covers a percentage of the employee's pre-disability income. Long-term disability policies offer benefit periods that can last several years or until the employee reaches retirement age, depending on the plan. Long-term disability plans usually have a waiting period of several months before benefits begin, which often coincides with the end of short-term disability benefits. Common triggers for long-term disability benefits include chronic illnesses, severe injuries, and debilitating mental health conditions. Group disability insurance policies typically provide a percentage of the employee's pre-disability income, often ranging from 50% to 70%. The definition of disability can vary between policies. Some plans define disability as the inability to perform the duties of one's own occupation, while others use a broader definition that includes the inability to work in any occupation. An "own occupation" policy pays benefits if the employee is unable to perform the duties of their own occupation, whereas an "any occupation" policy only pays benefits if the employee is unable to work in any occupation for which they are reasonably qualified. Own occupation policies generally offer more comprehensive coverage. Non-cancelable policies prevent the insurer from canceling the policy or raising premiums, as long as the employer continues to pay the premiums. Guaranteed renewable policies also ensure that coverage cannot be canceled, but the insurer may adjust premiums under certain conditions. Some group disability insurance policies include a cost of living adjustment (COLA) feature, which increases the benefit amount to account for inflation over time. This can help ensure that the employee's purchasing power is maintained during the benefit period. Partial or residual disability benefits provide financial support to employees who can return to work part-time or at reduced capacity due to their disability. This feature encourages employees to gradually transition back to work while still receiving some level of disability benefits. Many group disability insurance plans offer return-to-work incentives, such as assistance with job placement or vocational training, to support employees in their efforts to reenter the workforce. Before selecting a group disability insurance plan, it is important to assess the needs of your organization and its employees. Consider factors such as the nature of the work, the age and health of employees, and the desired level of coverage. Research and compare different insurance providers to ensure you select a reputable company with a track record of providing quality group disability insurance plans. Review the policy features and options available to find a plan that best meets the needs of your organization and its employees. Be sure to consider factors such as benefit amounts, waiting periods, and the definition of disability. Read the policy carefully and ensure you understand any exclusions or limitations that may apply. This can help prevent misunderstandings and ensure your employees receive the coverage they expect. Once a group disability insurance plan has been selected, enroll employees in the plan, providing them with the necessary documentation and instructions for participation. Communicate the details of the group disability insurance policy to employees, including coverage levels, waiting periods, and the claims process. Develop a process for handling disability claims and payments in a timely and efficient manner, ensuring that employees receive the support they need during their time of disability. Regularly review and update the group disability insurance plan to ensure it continues to meet the needs of your organization and its employees. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities in the workplace. Employers should be aware of their responsibilities under the ADA when administering group disability insurance plans. The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) provides eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave for specific family and medical reasons, including a serious health condition. Employers should be familiar with their obligations under the FMLA when offering group disability insurance. Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is a federal program that provides financial assistance to individuals with disabilities. Employers should understand the relationship between group disability insurance and SSDI benefits. Workers' compensation is a state-mandated insurance program that provides benefits to employees who sustain work-related injuries or illnesses. Employers should be aware of the interplay between group disability insurance and workers' compensation benefits, as well as their obligations under state-specific workers' compensation laws. Some states have additional regulations governing disability insurance, such as state disability insurance programs and mandated coverage requirements. Employers should familiarize themselves with the specific regulations in their state to ensure compliance. Group disability insurance is an important benefit that employers can offer to their employees to provide financial protection in the event of a disability. It can be cost-effective, simplify the underwriting process, improve employee morale and retention, and offer tax advantages. When selecting a plan, it is important to assess the needs of the group, compare providers, evaluate policy features, and understand the fine print and exclusions. Implementation and administration require enrolling employees, communicating policy details, handling claims and payments, monitoring and updating the plan, and complying with legal and regulatory aspects.What Is Group Disability Insurance?
Advantages of Group Disability Insurance
Cost-Effective Coverage
Simplified Underwriting Process
Employer-Sponsored Benefits
Tax Advantages
Employee Morale and Retention
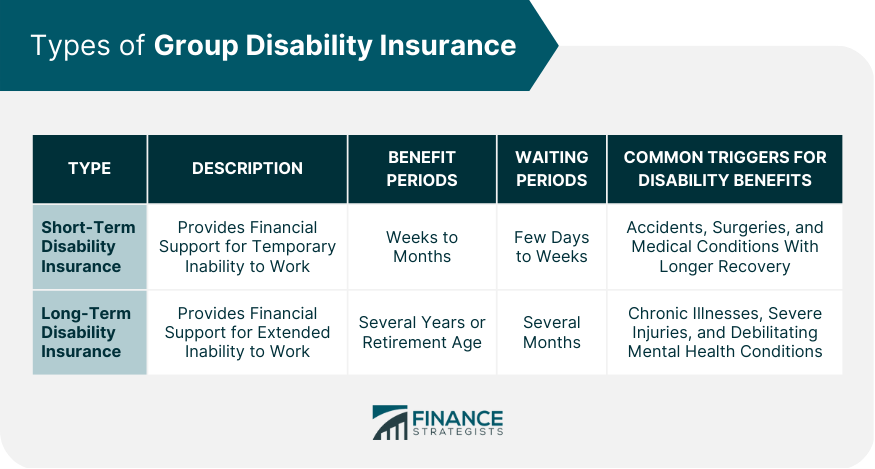
Types of Group Disability Insurance
Short-Term Disability Insurance
Definition and Coverage
Benefit Periods
Waiting Periods
Common Short-Term Disability Triggers
Long-Term Disability Insurance
Definition and Coverage
Benefit Periods
Waiting Periods
Common Long-Term Disability Triggers
Key Features of Group Disability Insurance
Benefit Amount
Definition of Disability
Own Occupation vs Any Occupation
Non-cancelable and Guaranteed Renewable Policies
Cost-Of-Living Adjustments (COLA)
Partial or Residual Disability Benefits
Return-To-Work Incentives
Selecting the Right Group Disability Insurance Plan
Assessing the Needs of the Group
Comparing Different Insurance Providers
Evaluating Policy Features and Options
Understanding the Fine Print and Exclusions

Implementation and Administration
Enrolling Employees
Communicating Policy Details
Handling Claims and Payments
Monitoring and Updating the Plan
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA)
Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)
Workers' Compensation
State-Specific Regulations
Conclusion
Group Disability Insurance FAQs
Group Disability Insurance is a type of insurance policy provided by an employer that pays a portion of an employee's income if they become disabled and unable to work. It is designed to provide income replacement for employees who are unable to work due to an injury or illness.
Group Disability Insurance is typically provided by an employer as part of an employee benefits package. The policy pays a percentage of the employee's income, usually 50-60%, if they become disabled and unable to work. The policy may also include additional benefits, such as rehabilitation services or survivor benefits.
Eligibility for Group Disability Insurance varies depending on the employer's policy. In most cases, employees who work full-time and are not in a probationary period are eligible. Some policies may also cover part-time employees, but this varies by employer.
The types of disabilities covered by Group Disability Insurance depend on the policy. Some policies cover both short-term and long-term disabilities, while others may only cover long-term disabilities. Disabilities that are covered may include illnesses, injuries, and mental health conditions.
Enrollment periods for Group Disability Insurance vary depending on the employer's policy. In most cases, employees can enroll during an open enrollment period or when they are first hired. Some policies may allow for enrollment outside of these periods if an employee experiences a life-changing event, such as the birth of a child or a divorce.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











