What Is Short-Term Disability Insurance?
Short-term disability insurance provides financial protection to individuals who are unable to work for a temporary period due to illness, injury, or pregnancy complications. It replaces a portion of the individual's income during this period, ensuring financial stability.
Short-term disability insurance plays a crucial role in securing financial well-being during unforeseen circumstances. It enables individuals to focus on recovery without worrying about immediate financial obligations and helps maintain their quality of life.
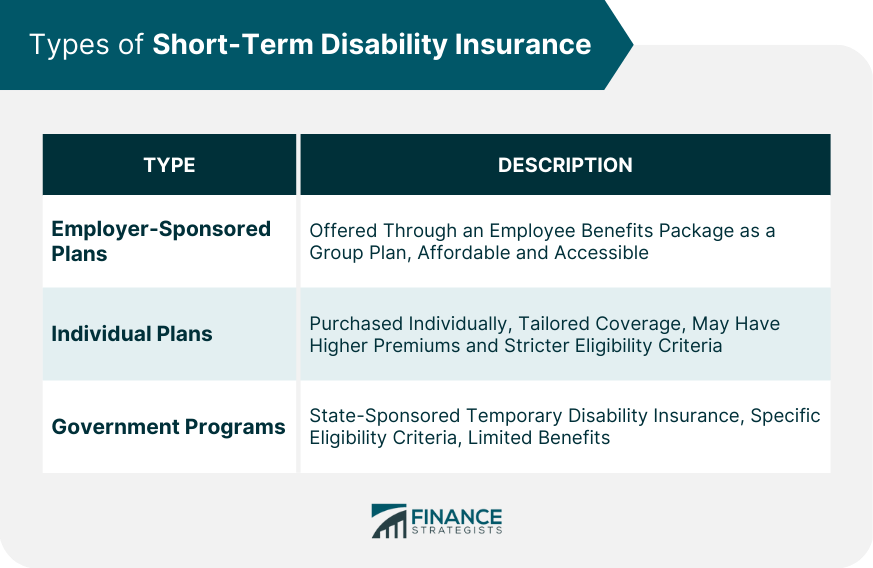
Types of Short-Term Disability Insurance
Employer-Sponsored Plans
Many employers offer short-term disability insurance as part of their employee benefits package. This type of coverage is typically more affordable and easier to obtain than individual policies, as it is often provided through a group plan.
Individual Plans
Individual short-term disability insurance policies are available for those who do not have access to an employer-sponsored plan or prefer additional coverage.
These policies can be tailored to meet individual needs but may have higher premiums and stricter eligibility criteria.
Government Programs
Some government programs, such as state-sponsored temporary disability insurance, provide short-term disability benefits to eligible residents.
These programs have specific eligibility criteria and may offer limited benefits compared to employer-sponsored or individual plans.
Coverage and Benefits of Short-Term Disability Insurance
Benefit Amounts
Short-term disability insurance policies typically pay a percentage of the insured's pre-disability income, often ranging from 50% to 70%. The exact amount depends on the policy terms and the individual's income level.
Benefit Periods
The duration of short-term disability benefits varies among policies, typically ranging from a few weeks to a few months.
Some policies offer extensions if the individual remains disabled, but this often requires additional premiums or approval from the insurance provider.
Waiting Periods
Short-term disability insurance policies usually have a waiting period, also known as an elimination period, before benefits begin. This period can range from a few days to several weeks and may differ depending on the cause of the disability.
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for short-term disability benefits, individuals must meet specific eligibility criteria outlined in their policy.
This may include being employed for a minimum period, experiencing a qualifying event, and providing necessary documentation to support the claim.
Costs and Considerations of Short-Term Disability Insurance
Premiums
The cost of short-term disability insurance depends on various factors, such as age, health, occupation, and coverage amount.
Employer-sponsored plans are generally more affordable, while individual policies may have higher premiums due to customization options and underwriting requirements.
Tax Implications
Short-term disability insurance benefits may be taxable or tax-free, depending on how the premiums are paid. Generally, if premiums are paid with pre-tax dollars, the benefits are taxable, while benefits from policies paid with after-tax dollars are tax-free.
Employer-Sponsored vs Individual Plans
Choosing between an employer-sponsored and individual short-term disability plan depends on individual circumstances, such as the quality of the offered coverage, affordability, and the need for additional benefits beyond what the employer-sponsored plan provides.
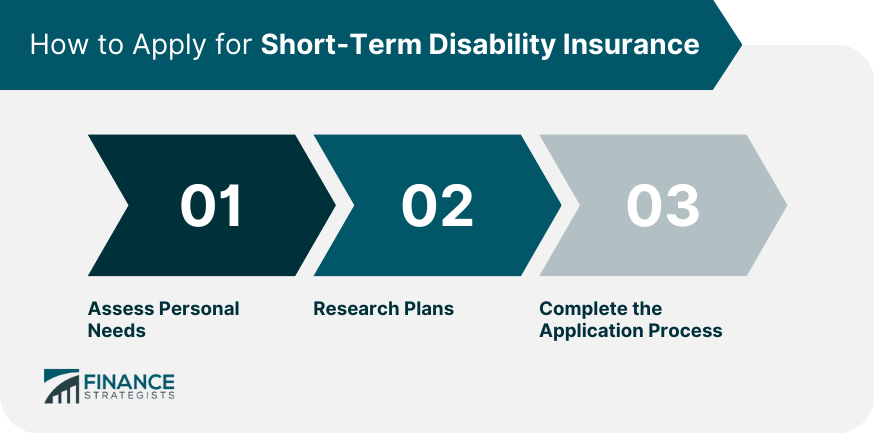
How to Apply for Short-Term Disability Insurance
Assess Personal Needs
Individuals should evaluate their financial needs and potential risks to determine the appropriate level of coverage. This may involve considering factors such as income, expenses, existing savings, and the likelihood of experiencing a short-term disability.
Research Plans
Before applying for short-term disability insurance, it is crucial to research and compare different plans. This includes reviewing coverage options, benefit amounts, and waiting periods to find the most suitable policy for individual needs.
Complete the Application Process
Applying for short-term disability insurance typically involves completing an application form, providing personal and medical information, and undergoing a medical exam.
The insurance provider may also request additional documentation to verify information and assess the applicant's risk level.
Once the application is submitted and approved, the individual will receive their policy details and premium information.
Filing a Claim for Short-Term Disability Insurance and Receiving Benefits
Understanding the Claim Process
To receive short-term disability benefits, individuals must file a claim with their insurance provider. This process typically involves notifying the insurer of the disability, submitting required documentation, and waiting for the claim to be reviewed and approved.
Necessary Documentation
Supporting documentation is crucial when filing a short-term disability claim. This may include medical records, proof of income, and a statement from the treating physician outlining the nature and expected duration of the disability.
Approval and Payment of Benefits
Once the insurer receives and reviews the claim documentation, they will determine whether the individual is eligible for benefits. If approved, benefits will be paid according to the policy terms, typically on a weekly or monthly basis.
Alternatives to Short-Term Disability Insurance
Emergency Savings
Having an emergency savings fund can help individuals cover expenses during a short-term disability. While this option requires disciplined saving and may not provide the same level of income replacement as insurance, it can be a useful financial safety net.
Long-Term Disability Insurance
Long-term disability insurance provides income replacement for an extended period, usually after a short-term disability policy's benefits have been exhausted.
Although it does not cover immediate expenses, it can protect against the financial impact of a long-lasting disability.
Workers' Compensation
Workers' compensation is a form of insurance that provides financial benefits to employees who sustain work-related injuries or illnesses. While it does not cover non-work-related disabilities, it can be a valuable source of income for those who qualify.
Conclusion
Planning for short-term disabilities is essential for maintaining financial stability during unforeseen circumstances. By securing appropriate coverage, individuals can focus on recovery without the added stress of financial strain.
Selecting the right short-term disability insurance policy requires careful consideration of personal needs, potential risks, and available options.
By thoroughly researching plans and evaluating individual circumstances, one can find the coverage that best suits their needs and ensures peace of mind during challenging times.
Short-Term Disability Insurance FAQs
Short-term disability insurance is a type of insurance policy that provides partial income replacement to an individual who is unable to work due to a covered disability.
Eligibility for short-term disability insurance varies depending on the insurance provider and policy. Typically, individuals who are employed and have a medical condition that prevents them from working may be eligible for short-term disability insurance.
Short-term disability insurance typically covers a portion of an individual's income while they are unable to work due to a covered disability. This may include illnesses, injuries, and other medical conditions that prevent an individual from working.
The duration of short-term disability insurance varies depending on the policy. Typically, short-term disability insurance lasts anywhere from a few weeks to several months, with some policies lasting up to a year.
To file a claim for short-term disability insurance, you will need to contact your insurance provider and provide documentation of your disability and the impact it has on your ability to work. Your insurance provider will then review your claim and determine your eligibility for benefits.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











