An insurance premium is the amount of money an individual or business pays to an insurance company for coverage against specific risks or losses. Premiums are typically paid on a regular basis, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, and are required to maintain the insurance policy's active status. Failure to pay the insurance premium may result in the cancellation of the policy, leaving the policyholder without coverage. The primary purpose of insurance premiums is to provide insurance companies with the necessary funds to pay out claims when policyholders experience covered losses or damages. Insurance companies pool the premiums from all policyholders and use these funds to cover claims, administrative expenses, and other operational costs. By charging premiums, insurers can effectively spread the risk among a large group of policyholders and maintain their financial stability in the face of uncertain events. Understanding insurance premiums is essential for policyholders, as it directly impacts the cost and affordability of insurance coverage. By recognizing the factors that influence premium costs and the various types of insurance premiums available, policyholders can make informed decisions when selecting coverage and ensure they are receiving the appropriate protection at a reasonable price. Age and gender are common factors that influence insurance premium rates, particularly for life and health insurance policies. Generally, younger individuals are considered lower risk and pay lower premiums, while older individuals face higher premiums due to increased likelihood of health issues or death. Similarly, gender can also play a role in determining premium rates, as statistically, women tend to live longer than men and may pay lower life insurance premiums. A policyholder's health and lifestyle can significantly impact their insurance premium, especially for life and health insurance policies. Insurers may charge higher premiums for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those who engage in high-risk behaviors, such as smoking or excessive alcohol consumption. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding risky behaviors can help policyholders secure lower premium rates. The location and environment in which a policyholder lives or operates can also influence insurance premium costs. Factors such as crime rates, natural disaster risks, and local regulations can impact premiums for home, auto, and business insurance policies. For example, a homeowner in a flood-prone area may pay higher premiums for flood insurance coverage, while an individual living in a low-crime area may pay lower auto insurance premiums. Generally, more comprehensive coverage or higher coverage limits will result in higher premiums, as the insurer takes on greater financial risk in the event of a claim. Policyholders should carefully consider their specific needs and risk tolerance when selecting coverage and balance their desired protection level with the associated premium costs. A policyholder's claims history can also affect their insurance premium rates. Individuals or businesses with a history of frequent or costly insurance claims may be considered higher risk by insurers and may face higher premiums as a result. Conversely, policyholders with a clean claims history may be eligible for discounts or reduced premium rates. Term insurance premium is the amount paid for term life insurance policies, which provide coverage for a specific period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. Term insurance premiums are typically lower than those for permanent life insurance policies, as they only provide coverage for a limited time and do not accumulate cash value. Whole life insurance premium is the amount paid for whole life insurance policies, which provide coverage for the policyholder's entire life and accumulate cash value over time. These premiums are generally higher than term insurance premiums, as they offer lifelong coverage and include a cash value component that can be accessed or borrowed against during the policyholder's lifetime. Universal life insurance premium is the amount paid for universal life insurance policies, which are a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexible premium payments and an adjustable death benefit. Universal life insurance premiums can be adjusted by the policyholder within certain limits, allowing for greater control over the cost and coverage provided by the policy. Variable life insurance premium is the amount paid for variable life insurance policies, which are a type of permanent life insurance that includes an investment component. With variable life insurance, a portion of the premium is invested in a separate account, which can fluctuate in value based on the performance of the underlying investments. These premiums may be higher than other types of life insurance premiums, as they provide the potential for investment growth in addition to the death benefit. Group insurance premium is the amount paid for group insurance policies, which are typically offered by employers or other organizations to their employees or members. Group insurance premiums are often lower than individual policy premiums, as the risk is spread across a large group of individuals, allowing the insurer to offer more favorable rates. Insurance premiums are calculated using actuarial methods, which involve the use of complex mathematical formulas and statistical analysis to determine the likelihood of specific events or risks occurring. Actuaries use historical data and other factors to estimate the probability of claims being filed and the potential costs associated with those claims. These calculations help insurers determine the appropriate premium rates to charge policyholders based on their unique risk profiles. Risk assessment is a crucial part of the premium calculation process, as it helps insurers evaluate the potential for claims and losses associated with each policyholder. Insurers consider various factors, such as age, gender, health, location, and claims history, to assess the risk associated with a specific policy and determine the appropriate premium rate. The underwriting process is the method by which insurers evaluate the risks associated with policyholders and determine the appropriate insurance coverage and premium rates. Underwriters review an applicant's risk factors, such as their health, lifestyle, location, and claims history, and use this information to decide whether to issue a policy and at what premium rate. The underwriting process helps insurers manage their overall risk exposure and ensure they charge adequate premiums to cover potential claims and losses. Insurance premiums can typically be paid using various payment options, such as monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. Policyholders may be eligible for discounts or reduced rates by choosing certain payment options or paying their premiums in advance. Additionally, some insurers offer flexible payment options, such as grace periods or payment plans, to help policyholders manage their premium costs more effectively. Many auto insurance companies offer safe driver discounts to policyholders who have a clean driving record and demonstrate responsible driving habits. By maintaining a good driving record and avoiding accidents or traffic violations, policyholders can potentially reduce their auto insurance premium costs. Insurers often provide discounts to policyholders who bundle multiple insurance policies, such as home, auto, and life insurance, with the same company. By consolidating their insurance coverage with a single provider, policyholders can often secure lower premium rates and simplify their insurance management. Certain age groups, such as seniors or young drivers, may be eligible for discounts on their insurance premiums based on their age. Insurers may offer these discounts to reward experienced drivers or encourage safe driving habits among younger drivers. Policyholders who maintain a claims-free record over a specified period may be eligible for a claims-free discount on their insurance premiums. Insurers offer this discount to reward policyholders for their low-risk behavior and to incentivize continued responsible behavior. Conversely, policyholders with high-risk factors, such as a poor driving record, a history of claims, or hazardous occupations, may face surcharges on their insurance premiums. These surcharges help insurers offset the increased risk associated with covering these individuals and encourage policyholders to take steps to reduce their risk exposure. Insurance premiums are an integral part of the insurance process, and understanding their purpose and the factors that influence their costs is crucial for policyholders. By considering the various factors that affect premium rates and exploring available discounts and surcharges, policyholders can make informed decisions about their insurance coverage and ensure they are receiving the appropriate protection at a reasonable price. When purchasing insurance coverage, it's essential to carefully consider your unique needs and risk factors and to compare multiple quotes from different insurers to find the best value. Be sure to explore available discounts and payment options to help manage your premium costs more effectively. Lastly, maintain open communication with your insurer to promptly address any changes in your circumstances or risk profile that may impact your premium rates. By taking these steps, you can ensure that you have the appropriate insurance coverage in place to protect yourself and your assets in the face of life's uncertainties.What Is an Insurance Premium?
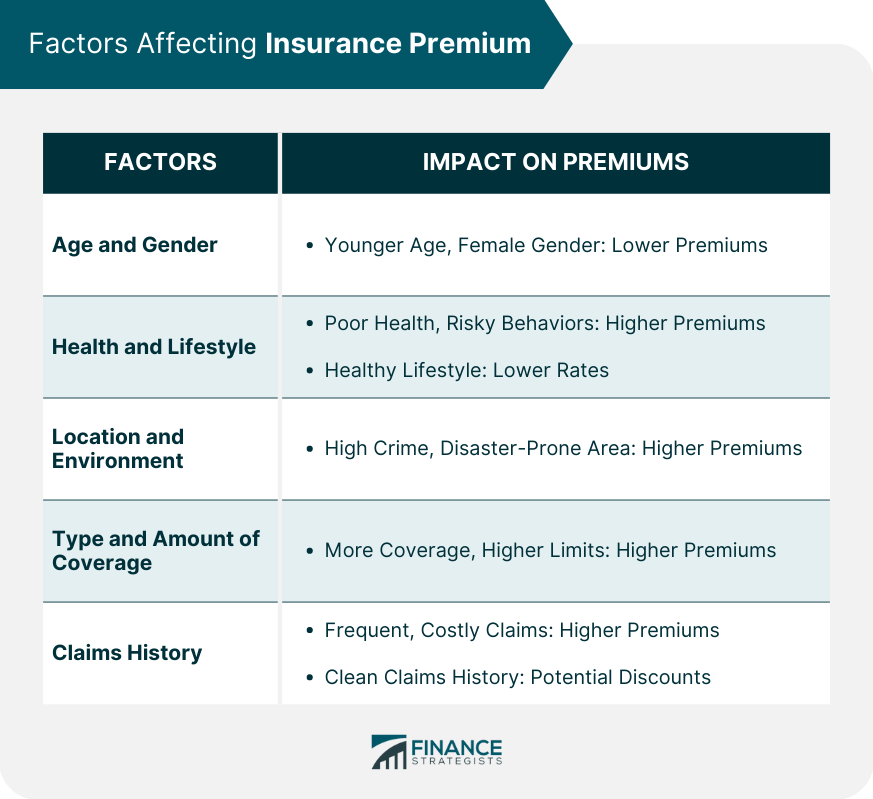
Factors Affecting Insurance Premium
Age and Gender
Health and Lifestyle
Location and Environment
Type and Amount of Coverage
Claims History
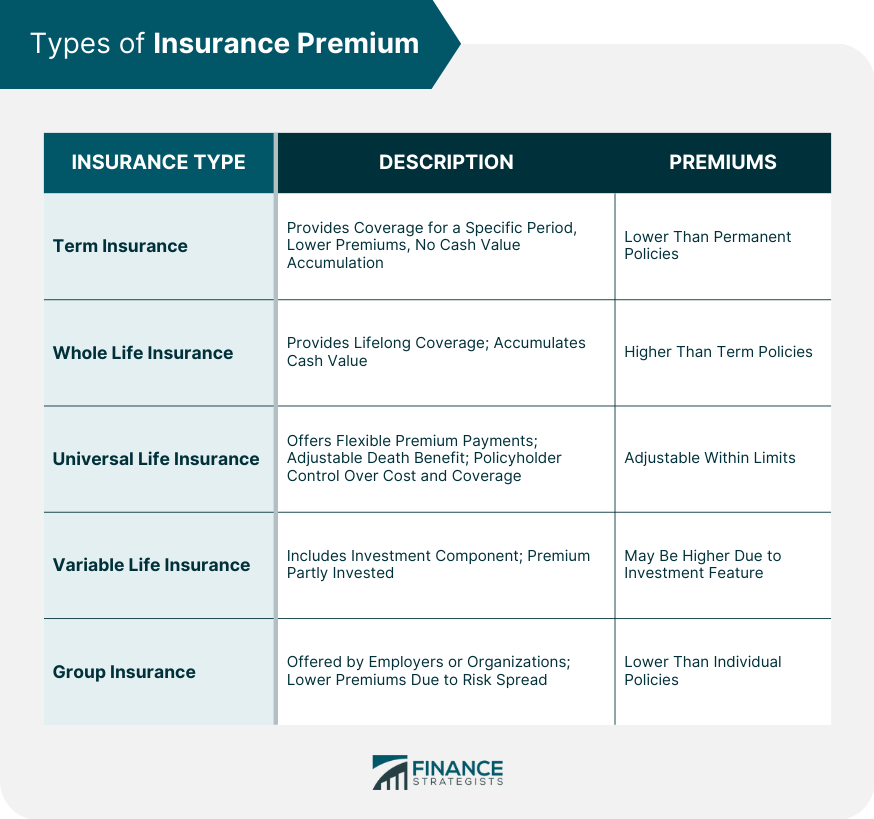
Types of Insurance Premium
Term Insurance Premium
Whole Life Insurance Premium
Universal Life Insurance Premium
Variable Life Insurance Premium
Group Insurance Premium
Calculation of Insurance Premium
Actuarial Methods
Risk Assessment
Underwriting Process
Premium Payment Options
Discounts and Surcharge
Safe Driver Discount
Multiple Policy Discount
Age Discount
Claims-Free Discount
Surcharge for High-Risk Factors
Final Thoughts
Insurance Premium FAQs
An insurance premium is the amount of money paid by the policyholder to the insurance company to maintain their coverage.
Several factors can impact the cost of insurance premiums, including age, gender, health, location, and claims history.
Insurance premiums are calculated based on actuarial methods, risk assessment, and the underwriting process, taking into account factors such as age, coverage type, and claims history.
Yes, insurance premiums can be reduced through various discounts, such as safe driver discounts, multiple policy discounts, and age discounts.
There are several types of insurance premiums, including term insurance premiums, whole life insurance premiums, universal life insurance premiums, variable life insurance premiums, and group insurance premiums.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











