Life insurance and annuities are two common retirement options that can provide financial security in retirement, though they serve different purposes. Life insurance is designed to provide coverage to protect yourself and your loved ones financially if you pass away prematurely. In exchange for regular payments, the beneficiary of your policy will receive a payout when you pass away. An annuity provides income for life after you retire, either as a lump sum or an ongoing stream of payments from an insurer or pension plan provider. Life insurance is purchased by paying a set amount each month, which goes towards the policyholder's death benefit upon passing away. This compensation can go to family members or other beneficiaries. On the other hand, an annuity pays out a fixed amount each month in exchange for an agreed-upon lump sum investment. Since these investments are invested in pre-tax dollars, annuities can come with tax advantages such as tax deferral. The return on these investments grows on a tax-deferred basis until it is withdrawn at retirement. Life insurance is a financial product that provides coverage in the event of a policyholder's death. It protects families and beneficiaries by providing a lump-sum cash payment upon the policyholder’s passing. The benefit amount is typically determined at the time of purchase, depending on the type of policy chosen by the policyholder. Term life insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for a specified period, or “term.” This type of policy is generally quite affordable and provides a death benefit if the holder passes away within the term. Generally, the premium payments are level over the term and are typically lower than those associated with permanent life policies, such as whole or universal life. The length of term policies can be one year, five years, or anywhere up to 30 years. Some policies also offer an option to renew at the end of each term. This allows policyholders to continue their coverage without interruption or to re-qualify for new insurance coverage due to changes in health or age. Permanent life insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for the policyholder's entire lifetime. This type of policy pays out upon the holder's death, regardless of when it occurs. It is more expensive than term life insurance and requires a higher premium payment in exchange for guaranteeing a death benefit at any time. Permanent life policies may also include additional cash accumulation benefits, such as dividends or interest, which can be added to the beneficiary’s death benefit over time. Whole life, universal life, and variable universal life insurance are all types of permanent life insurance that provide coverage for the insured's entire life as long as premiums are paid. Whole life insurance is a permanent life insurance offering a death benefit and a cash value component. The premiums for whole life insurance are typically higher than term life insurance, but they remain level for the life of the policy. Whole life insurance policies typically have a fixed rate of return on the cash value component, which grows tax-deferred over time. Universal life insurance is also a permanent life insurance offering a death benefit and a cash value component. Still, it provides more flexibility than whole-life insurance. With universal life insurance, policyholders can adjust the amount and frequency of their premium payments and the death benefit, which can increase or decrease depending on the policyholder's needs. The cash value component of universal life insurance grows at a variable interest rate, which can fluctuate based on market conditions. Variable universal life insurance is similar to universal life insurance, offering flexibility in premium payments and death benefit amounts. But it also provides the policyholder with investment options. The cash value component of variable universal life insurance can be invested in various sub-accounts, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, allowing for potential cash value growth. However, with this type of policy, the cash value and death benefit can also fluctuate based on the performance of the investments. Variable universal life insurance policies typically have higher fees and expenses than other types of life insurance. An annuity is an insurance product that provides a steady income stream over a specified period. It is essentially a contract between the policyholder and the insurance company in which the individual agrees to pay money into an account. The insurer agrees to pay a fixed amount for a certain duration at regular intervals. Immediate annuities begin paying out immediately, usually within one year after purchase. On the other hand, deferred annuities are designed to accumulate earnings over the contract length so that the policyholder can receive larger benefits later on. Immediate annuities typically have a lower upfront cost and offer stable income payments for a fixed duration. Deferred annuities, however, require a larger upfront investment and do not provide any income until the policy is triggered by either age or death. Deferred annuities allow for further growth through investments in stocks, bonds, and more, with the potential for higher earnings in exchange for greater risk. Fixed annuities offer a guaranteed rate of return, meaning that once you have purchased the policy, your annual returns will not change. Variable annuities, on the other hand, allow you to invest in stocks and bonds with the potential for greater earnings. While variable annuities offer more growth potential than fixed options, they also come with greater risk as their returns fluctuate depending on market conditions. Fixed annuities provide stability and are a good choice for those who want guaranteed income payments with little risk over the long term. Variable annuities can be suitable for investors looking to grow their funds in exchange for taking on more risk. Life insurance and annuities are financial products that provide different ways to help protect you and your loved ones. While life insurance provides a death benefit to protect against financial hardship after the death of an insured, annuities offer a steady stream of income for retirement or other long-term goals. The primary purpose of life insurance is to provide beneficiaries with a lump sum payout in the event of the policyholder's death. Conversely, annuities are intended to provide income over time through fixed payments or variable returns, depending on how they are structured. The type of payout differs between life insurance and annuities. In the case of life insurance, the death benefit is typically paid out as a lump sum. On the other hand, annuities can be structured to payout over time with immediate or deferred options depending on the policyholder's needs. When it comes to the schedule of payout, life insurance typically pays out in one lump sum when the policyholder dies or at specific intervals if there is an ongoing benefit stream involved. With annuities, payments can be made either immediately, in fixed intervals (regularly scheduled payments), or deferred until certain conditions are met. The proceeds from a life insurance policy may be taxable if certain thresholds are exceeded. Annuity withdrawals are generally subject to tax as ordinary income for anything beyond what was paid into the contract. Additionally, any earnings generated by investments in an annuity account will be taxed at capital gains tax rates. Normally, people purchase life insurance between the ages of 30 to 60 and whole life insurance between the ages of 25 to 50 when they have dependents who will need financial support should they pass away suddenly. Annuity purchases usually occur when individuals enter retirement age and need additional sources of income during their golden years. Both products have become increasingly popular with people of all ages as investment vehicles for retirement savings and providing additional income sources once retired. Life insurance policies include a death benefit paying out money if the insured passes away. On the other hand, while some types of annuities offer death benefits, it is not their primary purpose. They often require additional riders or options added to the contract when purchased. Life insurance can be a valuable financial resource to help protect your family's future. Understanding life insurance's pros and cons is essential before purchasing a policy. Life insurance's main benefit is financial security for an unexpected death. They can be sold or borrowed against in times of need, providing additional liquidity sources for families with limited resources. Furthermore, some life insurance policies offer tax benefits, allowing policyholders to make pre-tax contributions and receive tax-free distributions upon passing. However, there are some drawbacks associated with life insurance as well. Premiums for life insurance can be expensive depending on the type and amount of coverage chosen. This may only sometimes make it financially feasible for those with limited budgets. Additionally, if you do not pass away during the coverage period specified on the policy, then no benefit is paid out, and any money spent on premiums is lost. Finally, if you opt for cash value policies such as universal life or variable universal life plans, they come with more significant risks than term life Insurance. A smaller portion of your premium may need to be contributed towards investments to guarantee full coverage upon passing. An annuity can be an effective way to save for retirement as it can provide a steady income stream that is often not subject to taxation. If you choose to cash out your annuity policy before you reach the age of 59 1/2, you may only be subject to taxes on the portion of the annuity that has already been earned in interest. However, there are some drawbacks associated with annuities too. Annuities can come with high fees, such as surrender or sales charges, which may make them difficult or expensive to get out of and reduce their liquidity. Additionally, depending on the type of annuity policy purchased, some payouts may be subject to taxation upon withdrawal and distribute income over a short time rather than giving a large lump sum at once. Deciding whether to purchase life insurance or an annuity is a personal decision and can depend on several factors, such as budget, goals, and current financial situation. Life insurance may be the more suitable option for those looking for short-term protection from unexpected death due to its low cost and flexibility. Life insurance also offers some liquidity benefits, allowing policyholders to borrow against their premiums in times of need. Annuities are better suited for long-term financial planning, providing a steady income stream for retirement that may not be subject to taxation. Annuities may also offer more security than other investments since the issuing company guarantees them. When considering both options, it is important to weigh the pros and cons of each before choosing one. It is also important to compare different policies and providers to find the best possible option that fits your needs and financial goals. Life insurance is a financial product that provides a lump sum payment to the policyholder's beneficiary in the event of their death or other unforeseen circumstances. Annuities are also a financial product, but instead of providing a large lump sum, they provide continuous payments over time and are primarily used for retirement planning. Generally speaking, life insurance is better suited for short-term protection. At the same time, annuities provide a steady income stream over a long period and are more suitable for retirement planning. Life insurance is usually lower cost and offers policyholders more flexibility with liquidity options. Annuities offer guarantees from the issuing company but may come with high fees and taxes on withdrawals. When deciding between the two, it is important to compare policies and providers to find the best option that fits your needs.Life Insurance vs Annuity: Overview
What Is Life Insurance?
Term Life Insurance
Permanent Life Insurance
Whole Life Insurance
Universal Life Insurance
Variable Universal Life Insurance
What Is an Annuity?
Immediate and Deferred Annuities
Fixed and Variable Annuities
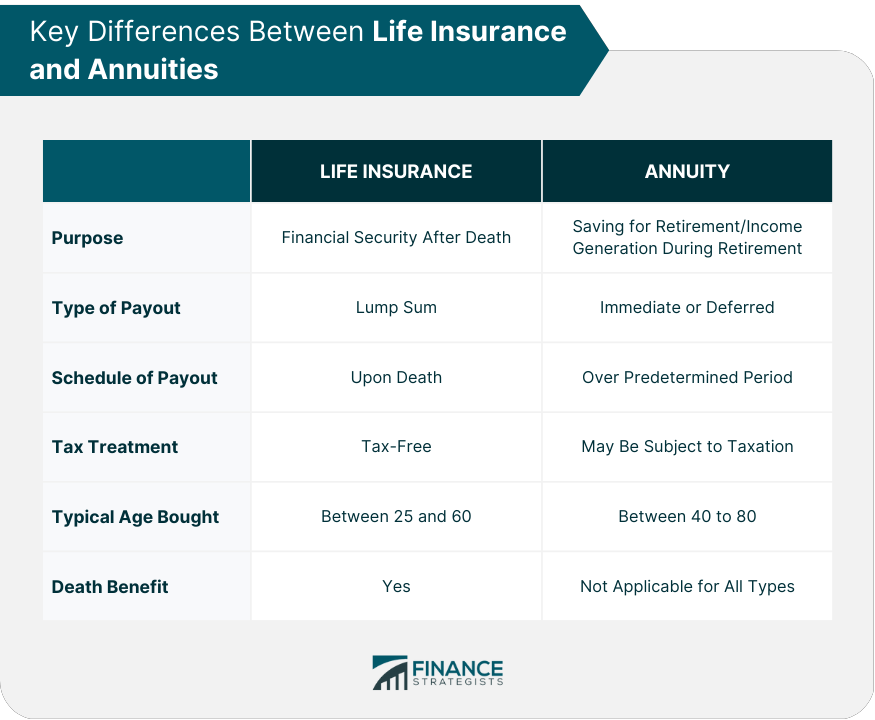
Life Insurance vs Annuity: Key Differences
Purpose of Product
Type of Payout
Schedule of Payout
Tax Treatment
Typical Age When Purchased
Death Benefit
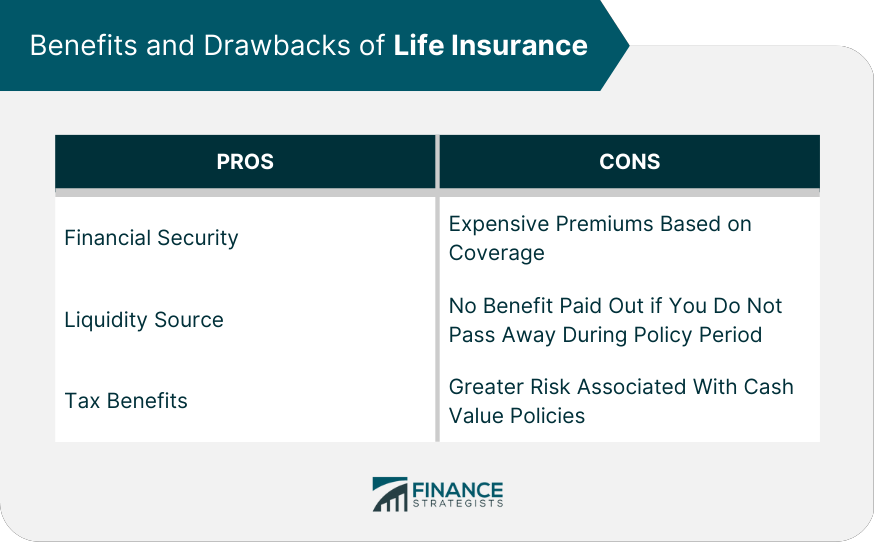
Benefits and Drawbacks of Life Insurance
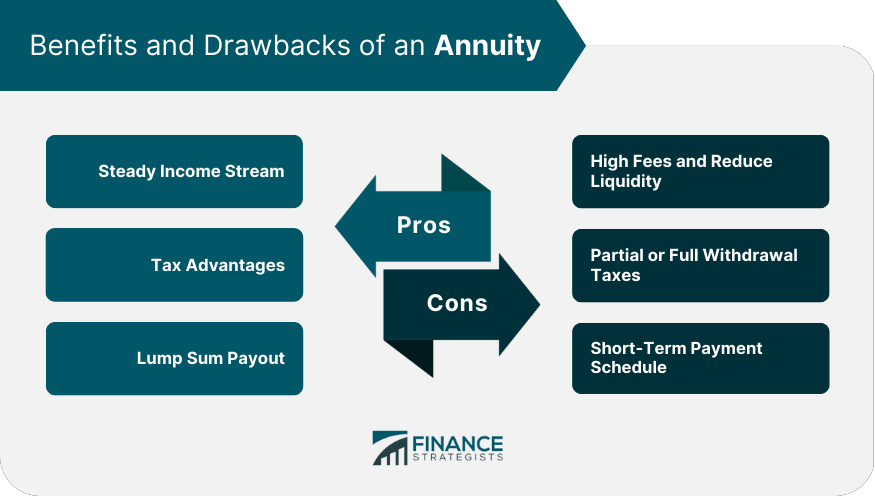
Benefits and Drawbacks of an Annuity
Life Insurance vs Annuity: Which Is Right for You?
The Bottom Line
Life Insurance vs Annuity FAQs
The primary purpose of life insurance is to provide financial protection for your family in the event of your passing. Life insurance policies can help cover expenses such as funeral costs, medical bills, and other debts that can arise due to a death. Additionally, life insurance policies can be used in estate planning, providing funds for potential beneficiaries to cover taxes or bills associated with settling the estate. Lastly, some life insurance policies offer additional riders to cover certain events such as critical illness or accidental death.
An annuity is a financial contract between an annuity provider and an investor. The investor pays money upfront for the provider to guarantee regular payments over a predetermined period. This can be provided as either a single lump sum that is paid out at the end of the term or as regular installments throughout the term. Annuities typically have higher interest rates than other investments, making them attractive for those looking to grow their money over time.
The primary benefits of life insurance are that it offers a death benefit to your family in the event of your passing. This death benefit can help provide financial stability for your family and alleviate some of the burden associated with losing a loved one. Additionally, life insurance policies could be used as part of an estate plan, providing funds for potential beneficiaries to cover taxes or bills associated with settling the estate. Lastly, some life insurance policies offer additional riders that can provide additional coverage for certain events, such as critical illness or accidental death.
The primary benefit of annuities is that they offer a guarantee from the issuing company. Annuities can be used to provide income in retirement, which is helpful for individuals who need a steady stream of payments. Additionally, annuities can protect your money as they offer more protection from market risks when compared to investments such as stocks and bonds. Lastly, annuities typically have higher interest rates than other savings options, making them attractive for those looking to grow their money over time.
When deciding between life insurance and annuities, several factors must be considered. These include cost, payment terms, the flexibility of use, and liquidity options. Additionally, it is important to compare provider offerings to understand potential hidden costs or restrictions. Lastly, it is important to consider the long-term implications of each product as they may have different tax implications depending on your individual needs.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











