Buy-sell insurance is a risk management strategy used by businesses to ensure the continuity of operations in the event of an owner's death, disability, or departure from the company. This type of insurance is typically used in conjunction with a buy-sell agreement, which is a legally binding document outlining how a business's ownership will be transferred in the event of a specified triggering event. Buy-sell insurance helps protect the financial interests of business owners, their families, and other stakeholders by providing the necessary funds to facilitate the transfer of ownership. This ensures the business remains operational, prevents disputes among surviving owners, and provides financial security to the departing owner's family. In a cross-purchase agreement, each business owner purchases a life or disability insurance policy on the other owners. When a triggering event occurs, the surviving owners use the insurance proceeds to buy the departing owner's share of the business. Advantages of cross-purchase agreements include simplicity, equal distribution of ownership, and favorable tax treatment. Disadvantages include higher policy costs for older or less healthy owners, potential complications in businesses with numerous owners, and the need for regular policy updates to account for changes in business value. An entity-purchase agreement involves the business itself purchasing insurance policies on each owner. When a triggering event occurs, the business uses the insurance proceeds to buy the departing owner's share, which is then distributed among the remaining owners. Entity-purchase agreements offer simplicity for businesses with multiple owners and equalize policy costs among owners. However, they may result in less favorable tax treatment and concentrated ownership, potentially affecting the business's governance and decision-making. Wait-and-see agreements combine elements of cross-purchase and entity-purchase agreements. In this arrangement, the business and the remaining owners decide how to purchase the departing owner's share after a triggering event occurs, based on factors such as insurance proceeds, cash flow, and tax considerations. Wait-and-see agreements offer flexibility in responding to changes in business circumstances but may create uncertainty and delays in ownership transfers, as well as potential disputes among the remaining owners. Accurate valuation of the business is crucial to ensure that the departing owner receives a fair price for their share of the business, and to avoid disputes among the remaining owners. The valuation should be based on a thorough assessment of the business's assets, liabilities, and potential for future growth. Common methods for valuing a business include the income approach, market approach, and asset-based approach. The income approach determines the value of the business based on its potential to generate income in the future. The market approach compares the business to similar companies that have been sold recently. The asset-based approach determines the value of the business based on its tangible and intangible assets. In the event of the death of an owner, the buy-sell agreement will specify that the remaining owners will purchase the deceased owner's share of the business. If an owner becomes permanently disabled and is unable to work, the buy-sell agreement will provide for the purchase of the disabled owner's share of the business by the remaining owners. The buy-sell agreement may provide for the purchase of an owner's share of the business upon retirement, although this is not always the case. The buy-sell agreement may provide for the purchase of an owner's share of the business in the event of a divorce or separation. The buy-sell agreement may provide for the purchase of an owner's share of the business in the event of bankruptcy. One common way to fund a buy-sell agreement is through life insurance. Each owner takes out a life insurance policy on the other owners, and the proceeds of the policy are used to purchase the departing owner's share of the business. Disability insurance can also be used to fund a buy-sell agreement in the event of a permanent disability of one of the owners. Another way to fund a buy-sell agreement is through cash reserves. The business sets aside money each year to be used to purchase the departing owner's share of the business in the event of a triggering event. Installment payments can also be used to fund a buy-sell agreement. The remaining owners agree to make payments to the departing owner over time, rather than purchasing their share of the business all at once. Buy-sell agreements can have various income tax implications, depending on the structure of the agreement and the type of triggering event. Consult with a tax professional to understand and plan for potential tax consequences. Properly structured buy-sell agreements can help reduce estate tax liabilities by establishing the value of the business interest for estate tax purposes and providing liquidity for estate tax payments. Transfers of business interests through buy-sell agreements may be subject to gift tax rules. Proper planning and consultation with a tax professional can help minimize gift tax exposure. When implementing a buy-sell insurance agreement, it is essential to consult with the following professionals: Business valuation expert Financial advisor Tax professional Attorney Based on your business's unique circumstances and goals, choose the most suitable type of buy-sell insurance agreement: cross-purchase, entity-purchase, or wait-and-see. Consult with a business valuation expert to select the most appropriate valuation method for your business, taking into account factors such as industry norms, growth prospects, and the business's financial performance. Determine the best funding options for your buy-sell agreement, considering factors such as cost, flexibility, and tax implications. Common funding options include life insurance, disability insurance, cash reserves, and installment payments. Work with an attorney to draft a legally binding buy-sell agreement that clearly outlines the terms and conditions of the ownership transfer. Ensure all parties sign the agreement and keep it updated to reflect changes in the business's value or ownership structure. Regularly review and update your buy-sell insurance agreement to account for changes in the business's value, ownership structure, or tax laws. This helps ensure the agreement remains effective and equitable for all parties involved. Buy-sell insurance plays a critical role in ensuring business continuity and protecting the financial interests of business owners, their families, and other stakeholders. Implementing a buy-sell insurance agreement requires careful planning, consultation with professionals, and regular updates to ensure its effectiveness. By considering the various types of agreements, valuation methods, funding options, and tax implications, businesses can create a successful buy-sell insurance strategy that meets their unique needs and goals.What Is Buy-Sell Insurance?
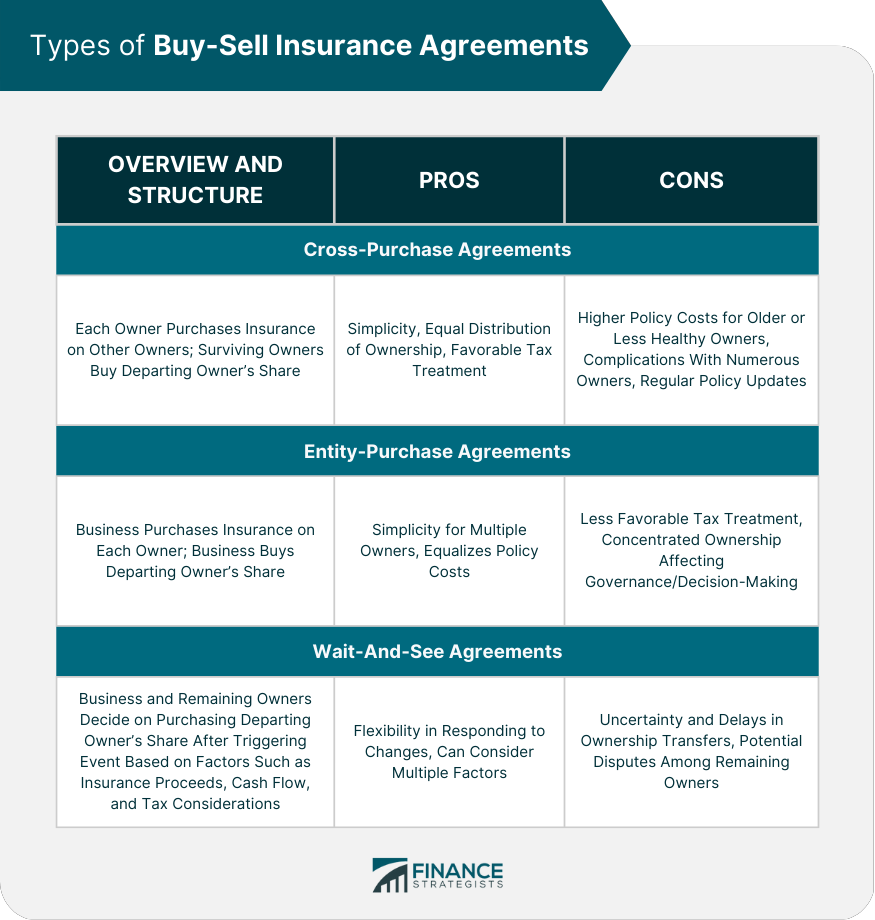
Types of Buy-Sell Insurance Agreements
Cross-Purchase Agreements
Overview and Structure
Advantages and Disadvantages
Entity-Purchase Agreements
Overview and Structure
Advantages and Disadvantages
Wait-And-See Agreements
Overview and Structure
Advantages and Disadvantages
Key Elements of a Buy-Sell Insurance Agreement
Valuation of the Business
Importance of Accurate Valuation
Common Valuation Methods
Triggering Events
Death
Disability
Retirement
Divorce
Bankruptcy
Funding Options
Life Insurance
Disability Insurance
Cash Reserves
Installment Payments
Tax Implications of Buy-Sell Insurance Agreements
Income Tax Considerations
Estate Tax Considerations
Gift Tax Considerations
Steps to Implement a Buy-Sell Insurance Agreement
Consult With Professionals
Choose the Appropriate Type of Agreement
Determine the Valuation Method
Establish Funding Mechanisms
Draft and Execute the Agreement
Review and Update the Agreement Periodically

Conclusion
Buy-Sell Insurance FAQs
Buy-sell insurance is a type of life insurance policy that is used to facilitate the purchase of a deceased owner's share of a business by the surviving co-owners. This insurance can help ensure that the remaining owners have the funds necessary to buy out the deceased owner's interest, which can help prevent disputes and ensure a smooth transition of ownership.
Buy-sell insurance is typically used by businesses that have multiple owners, especially those that are closely held or family-owned. This insurance can help provide liquidity to the business and ensure that the ownership structure remains stable in the event of the death of one of the owners.
With buy-sell insurance, the owners of the business enter into a legal agreement that outlines how the business will be valued and how the surviving owners will purchase the deceased owner's share of the business. The owners then purchase life insurance policies on each other, with the proceeds of the policies being used to buy out the deceased owner's share of the business.
Buy-sell insurance can provide several benefits for businesses with multiple owners, including ensuring the stability of the ownership structure, providing liquidity to the business in the event of an owner's death, and helping prevent disputes among co-owners. This insurance can also help ensure that the deceased owner's family receives fair compensation for their share of the business.
The amount of buy-sell insurance needed will depend on several factors, including the value of the business, the ownership structure, and the number of owners. A professional financial advisor can help determine the appropriate amount of coverage needed for your specific situation.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











