Cash value life insurance policies, also known as permanent life insurance, are insurance policies that provide both a death benefit and an investment component. These policies are designed to provide lifelong coverage, as long as the policy premiums are paid on time. Unlike term life insurance, which only provides coverage for a specified period, cash value policies have a savings component that builds up over time, known as the "cash value." This cash value is invested in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, and grows tax-deferred over time. Policyholders can access this cash value through policy loans or withdrawals, which can be used to supplement retirement income, pay for education expenses, or cover emergency expenses. However, accessing the cash value may reduce the death benefit or result in surrender charges. There are four main types of cash-value life insurance policies: Provides coverage for the entire lifetime of the insured, with a fixed premium and a guaranteed minimum cash value growth rate. Some whole life policies also pay dividends based on the performance of the insurance company. Offers greater flexibility than whole life insurance, allowing policyholders to adjust their premiums and death benefits within certain limits. The cash value grows based on a declared interest rate, which may fluctuate over time. Combines permanent life insurance with an investment component, allowing policyholders to invest the cash value in a variety of investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. The cash value and death benefit will vary depending on investment performance. A type of universal life insurance that links the cash value growth to the performance of a stock market index, such as the S&P 500. It offers a minimum guaranteed interest rate and a cap on returns, providing a balance between risk and reward. Before purchasing a cash-value life insurance policy, it is essential to assess one's financial goals and needs, such as providing for loved ones, leaving a legacy, or supplementing retirement income. Different cash-value life insurance policies offer varying levels of investment risk. Policyholders should consider their risk tolerance when selecting a policy type, especially when evaluating variable life insurance or indexed universal life insurance. Cash value life insurance policies are typically long-term commitments. Policyholders should consider their time horizon and whether they can afford to maintain the policy for an extended period. Policyholders should carefully evaluate their ability to afford the premiums of a cash value life insurance policy, taking into account the possibility of premium increases over time. It is essential to choose an insurance company with a strong financial rating and a good reputation for customer service claims to handle, and overall performance. Cash value life insurance policies provide lifelong coverage, ensuring that the policyholder's beneficiaries will receive the death benefit no matter when the insured passes away, as long as premiums are paid and the policy remains in force. Most cash value life insurance policies offer a guaranteed minimum rate of return on the cash value, which provides a level of financial security and predictability for policyholders. Cash value life insurance policies offer several tax advantages: Tax-Deferred Growth: The cash value grows tax-deferred, meaning policyholders do not have to pay taxes on the gains until they withdraw the funds. Tax-Free Loans and Withdrawals: Policyholders can take tax-free loans against the cash value or make tax-free withdrawals up to the policy's cost basis. The cash value accumulation feature in these policies acts as a forced savings vehicle, encouraging long-term savings and helping policyholders build wealth over time. Policyholders can use the cash value as collateral for loans, which can be useful for financing large purchases, such as a home or a child's education, or for providing liquidity during a financial crisis. Some whole life insurance policies, known as participating policies, pay dividends to policyholders based on the insurance company's performance. These dividends can be used to buy additional coverage, reduce premiums, or increase the cash value. Cash value life insurance can provide significant benefits to estate planning by providing a source of tax-free liquidity to pay estate taxes and other expenses, as well as potentially increasing the value of the estate. It can also offer flexibility in estate planning, allowing for the transfer of wealth outside of the probate process. Cash-value life insurance policies generally have higher premiums than term life insurance policies, which may make them less affordable for some individuals. The various features and options available in cash value life insurance policies can make them more complex and challenging to understand compared to simpler term life insurance policies. If a policyholder decides to surrender or cancel a cash-value life insurance policy during the early years, they may face surrender charges and fees, which can reduce the amount of cash value they receive. With the exception of variable life insurance, most cash-value life insurance policies have limited investment options, which may not align with a policyholder's investment preferences or risk tolerance. If premiums are not paid on time, there is a risk of policy lapse for cash value life insurance. This means the policy may terminate, and the insured may lose all accumulated benefits. To avoid this risk, it is important to stay current with premium payments and understand the grace period allowed by the policy. Customizing the Policy With Riders Accelerated Death Benefit Rider: This rider allows policyholders to access a portion of the death benefit before death if diagnosed with a terminal illness. Waiver of Premium Rider: This rider waives premium payments if the policyholder becomes disabled and cannot work. Guaranteed Insurability Rider: This rider enables policyholders to purchase additional insurance coverage without undergoing medical underwriting. Long-Term Care Rider: This rider provides benefits to cover long-term care expenses, such as nursing home or home health care costs. To optimize the performance of a cash-value life insurance policy, policyholders should regularly monitor investment performance, adjust premiums and death benefits as needed, and rebalance investments in variable life insurance policies. Cash-value life insurance policies can be an essential part of a retirement income strategy. Policyholders can access the cash value through tax-free policy loans, withdrawals up to the policy's cost basis, or annuitizing the cash value for a guaranteed income stream. Cash value life insurance offers lifelong coverage, a savings component, and various tax advantages. With multiple policy types available, including whole life, universal life, variable life, and indexed universal life, policyholders can find a policy that meets their unique financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Cash value life insurance also provides estate planning benefits, such as tax-free death benefits, equalizing inheritances, and charitable giving opportunities. By carefully considering their individual financial circumstances, understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks, and being prepared to monitor and adjust policy features over time, policyholders can choose the right cash value life insurance policy to achieve their financial goals. Consulting with a financial professional or insurance agent can provide additional guidance in making an informed decision.Cash Value Life Insurance Policies Overview
Types of Cash Value Life Insurance Policies
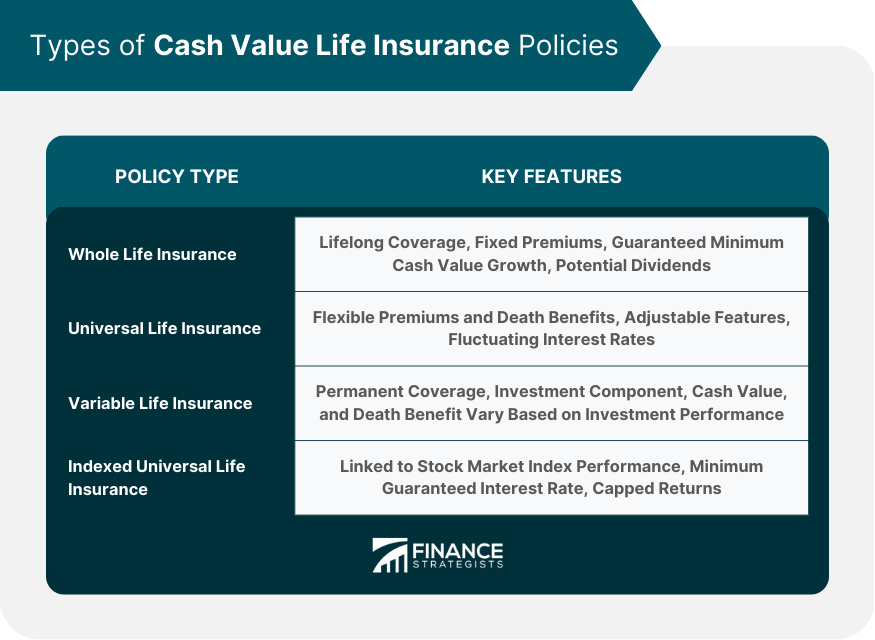
Whole Life Insurance
Universal Life Insurance
Variable Life Insurance
Indexed Universal Life Insurance
Factors to Consider When Choosing Cash Value Life Insurance
Financial Goals and Needs
Risk Tolerance
Time Horizon
Affordability of Premiums
Strength and Reputation of the Insurance Company
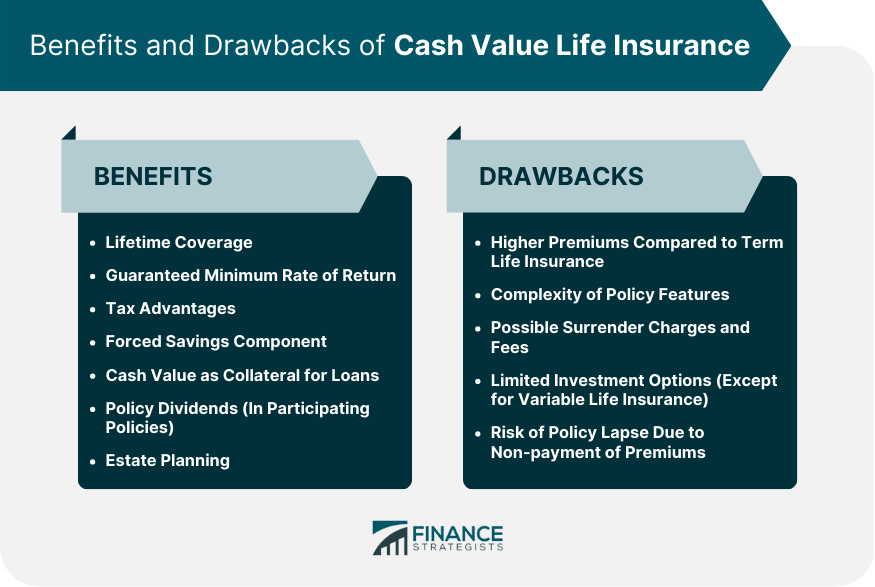
Benefits of Cash Value Life Insurance
Lifetime Coverage
Guaranteed Minimum Rate of Return
Tax Advantages
Forced Savings Component
Cash Value as Collateral for Loans
Policy Dividends
Estate Planning
Drawbacks of Cash Value Life Insurance
Higher Premiums Compared to Term Life Insurance
Complexity of Policy Features
Possible Surrender Charges and Fees
Limited Investment Options
Risk of Policy Lapse Due to Non-payment of Premiums
Strategies for Optimizing Cash Value Life Insurance
Policyholders can enhance their coverage and tailor the policy to their needs by adding riders. Some common riders include:Maintaining Policy Performance
Using Cash Value in Retirement
Conclusion
Cash Value Life Insurance FAQs
Cash value life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that provides lifelong coverage and a savings component that accumulates cash value over time. Unlike term life insurance, which only provides coverage for a specified term, cash value life insurance policies remain in force for the policyholder's entire life, as long as premiums are paid.
The main types of cash value life insurance policies are whole life insurance, universal life insurance, variable life insurance, and indexed universal life insurance. Each policy type offers varying degrees of flexibility, guaranteed returns, and investment options to suit different policyholders' needs and risk tolerances.
Cash value life insurance offers several tax advantages, including tax-deferred growth on the cash value, which means policyholders do not pay taxes on the gains until they withdraw the funds. Additionally, policyholders can take tax-free loans against the cash value or make tax-free withdrawals up to the policy's cost basis.
When choosing a cash value life insurance policy, factors to consider include financial goals and needs, risk tolerance, time horizon, affordability of premiums, and the strength and reputation of the insurance company. These factors can help determine the most suitable policy type and features for the policyholder's unique circumstances.
Cash value life insurance can be an effective estate planning tool by providing tax-free death benefits to beneficiaries, helping to offset potential estate taxes, and offering liquidity for the estate. Policyholders can also use strategies such as setting up an Irrevocable Life Insurance Trust (ILIT), equalizing inheritances, or designating a charity as a beneficiary to further enhance the estate planning benefits of cash value life insurance.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











