Life insurance policy conversions refer to the process of changing one type of life insurance policy to another to meet an individual's evolving financial and personal needs. Understanding the importance of policy conversions and the factors that influence the decision to convert a policy is crucial for securing the right coverage for you and your loved ones. Before discussing conversions, it's important to understand the various types of life insurance policies available in the market. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period or "term," usually ranging from 10 to 30 years. If the insured dies within the term, the death benefit is paid to the beneficiaries. If the insured outlives the term, the coverage ends without any payout. Whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage with guaranteed death benefits and cash value accumulation. Premiums are generally higher than term life insurance but remain level throughout the policyholder's lifetime. Universal life insurance offers flexible premiums, adjustable death benefits, and the potential for cash value accumulation. The policyholder can adjust the premium payments and death benefits to suit their financial needs. Variable life insurance combines permanent coverage with an investment component. The policy's cash value is invested in various investment options, such as stocks or bonds, which can result in higher potential returns but also increased risk. Indexed universal life insurance is a variation of universal life insurance that links cash value accumulation to the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. This provides the potential for higher returns while minimizing the risk associated with market fluctuations. There are several reasons why individuals might consider converting their life insurance policies, including: As people progress through different life stages, their financial needs and goals may change. For instance, a young family might need more coverage to protect against income loss, while someone nearing retirement might want to focus on wealth preservation and estate planning. Term life insurance policies expire at the end of the term without any payout. Converting to a permanent policy ensures that the policyholder maintains coverage and can accumulate cash value. Some policyholders may find the premiums of their current policy unaffordable and may opt to convert to a policy with lower or more flexible premiums. Individuals seeking to diversify their investment portfolio or improve their policy's performance may consider converting to a policy with an investment component, such as variable or indexed universal life insurance. Policyholders may be dissatisfied with the performance of their current policy and opt to convert to a policy that better aligns with their financial objectives. Converting a life insurance policy can offer tax advantages, such as tax-deferred cash value growth and potential tax-free death benefits. There are several conversion options available, including: This conversion entails changing a term life insurance policy to a whole life policy, providing lifelong coverage and cash value accumulation. Converting a term policy to a universal life policy offers flexible premiums, adjustable death benefits, and potential cash value accumulation. This conversion allows policyholders to maintain permanent coverage while benefiting from the flexible premium and death benefit options provided by universal life insurance. By converting a whole life policy to a variable life policy, policyholders can gain exposure to investment options and potentially enhance their policy's performance. Partial conversions involve converting a portion of the existing coverage to a new policy type, allowing policyholders to maintain some of the original policy's features while benefiting from the advantages of the new policy. Before converting a life insurance policy, consider the following factors: Converting a policy may involve additional costs, such as increased premiums, surrender charges, or administrative fees. It's essential to weigh these costs against the potential benefits of the new policy. Some conversions may require new medical underwriting, which could impact the policyholder's insurability or result in higher premiums. In some cases, guaranteed conversion options may be available without the need for additional underwriting. Consider the features and benefits of both the existing and new policies, such as death benefits, cash value accumulation, investment options, and policy riders, to ensure that the new policy aligns with your financial goals. Evaluate the financial strength and reputation of the insurance company offering the new policy, as this can impact the company's ability to fulfill its obligations to policyholders. Some permanent policies offer policy loans, allowing policyholders to borrow against the policy's cash value. Understand the terms and conditions of the policy loans before conversion. Follow these steps to convert a life insurance policy: 1. Review Current Policy and Financial Goals: Assess your current policy's performance and evaluate how it aligns with your financial objectives. 2. Consult With a Financial Advisor or Insurance Agent: Seek professional advice to determine whether a policy conversion is a right choice for your situation. 3. Compare Different Policy Options: Research and compare various policy types to find the best fit for your needs. 4. Submit Conversion Application: Complete and submit the required paperwork for the conversion, including any necessary medical underwriting. 5. Monitor the Performance of the New Policy: Regularly review the new policy's performance to ensure it continues to meet your financial goals. Converting a life insurance policy may come with potential risks and disadvantages, such as: Converting to a permanent policy often results in higher premiums compared to term life insurance. In some cases, converting a policy may result in the loss of any accumulated cash value in the existing policy. Depending on the specifics of the conversion, there may be tax consequences, such as capital gains or income tax liabilities. If a policyholder decides to surrender their current policy during the conversion process, they may face surrender charges. Some permanent policies, particularly those with investment components, can be more complex than term life policies. Policyholders should ensure they fully understand the intricacies of the new policy before conversion. Life insurance policy conversions involve changing one type of policy to another to meet changing financial and personal needs. There are several types of life insurance policies, including term, whole life, universal life, variable life, and indexed universal life insurance. Reasons for conversions include changing financial needs, expiring term policies, premium affordability, investment objectives, policy performance, and tax planning. Conversion options include term to whole life, term to universal life, whole life to universal life, whole life to variable life, and partial conversions. Factors to consider before conversion include costs and fees, health status and insurability, policy features and benefits, financial strength of the insurance company, and policy loan provisions. Converting a life insurance policy may come with potential risks and disadvantages, such as increased premiums, loss of accumulated cash value, possible tax implications, surrender charges, and complexity of the new policy.What Is Life Insurance Policy Conversions?
Types of Life Insurance Policies
Term Life Insurance
Whole Life Insurance
Universal Life Insurance
Variable Life Insurance
Indexed Universal Life Insurance
Reasons for Life Insurance Policy Conversions
Changing Financial Needs
Expiring Term Policies
Premium Affordability
Investment Objectives
Policy Performance
Tax Planning
Conversion Options
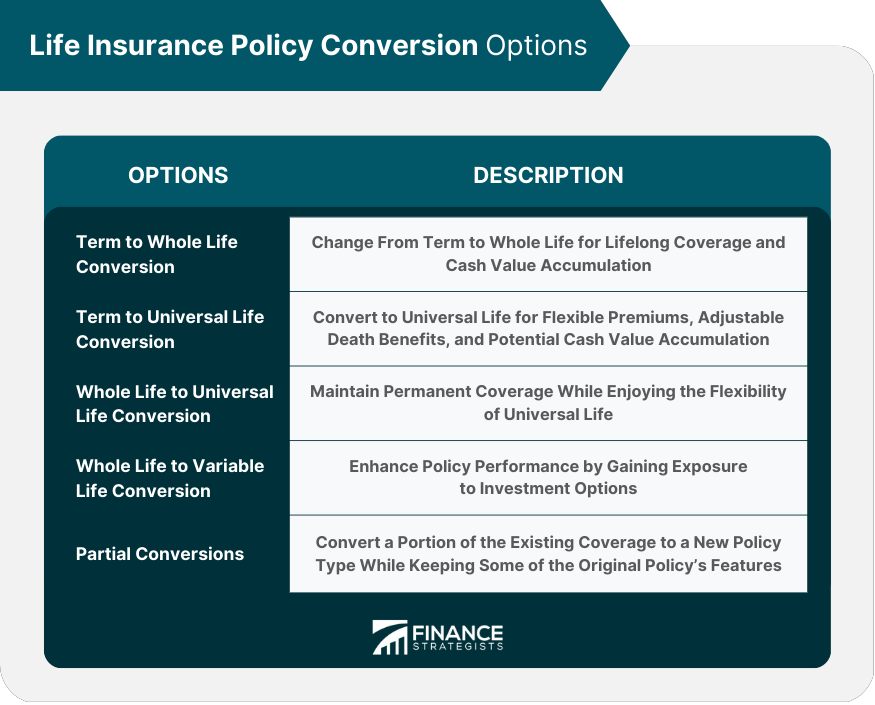
Term to Whole Life Conversion
Term to Universal Life Conversion
Whole Life to Universal Life Conversion
Whole Life to Variable Life Conversion
Partial Conversions
Factors to Consider Before Conversion
Costs and Fees
Health Status and Insurability
Policy Features and Benefits
Financial Strength of the Insurance Company
Policy Loan Provisions
Steps for Converting a Life Insurance Policy
Potential Risks and Disadvantages of Conversion
Increased Premiums
Loss of Accumulated Cash Value
Possible Tax Implications
Surrender Charges
Complexity of New Policy
Conclusion
Life Insurance Policy Conversions FAQs
Individuals consider life insurance policy conversions to adapt to changing financial needs, address expiring term policies, manage premium affordability, align with investment objectives, improve policy performance, and for tax planning purposes.
Before converting a life insurance policy, consider costs and fees, health status and insurability, policy features, and benefits, the financial strength of the insurance company, and policy loan provisions.
Conversions involving variable life insurance or indexed universal life insurance policies offer investment opportunities, as these policy types have an investment component linked to various investment options or market indices.
Yes, partial conversions are possible, allowing policyholders to maintain some features of their existing policy while benefiting from the advantages of the new policy type.
Life insurance policy conversions may come with risks and disadvantages, such as increased premiums, loss of accumulated cash value, possible tax implications, surrender charges, and increased complexity of the new policy.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











