An Unbundled Life insurance policy, also known as flexible premium adjustable life insurance, is a policy where the different components - mortality, expense, and investment - are separated. This division allows for greater transparency and enables policyholders to adjust the policy in accordance with their changing needs and financial circumstances. The principle behind an unbundled life insurance policy lies in the ability to 'unbundle' or break down the elements of a traditional insurance policy. This allows policyholders to individually manage each aspect, offering a level of flexibility uncommon in traditional policies. The three key components of an unbundled life insurance policy are mortality, expense, and investment. The mortality component covers the cost of the insurance coverage, the expense component caters for the operational costs, and the investment component is where part of the premium is allocated towards building the policy's cash value which can be invested or borrowed against. In an unbundled life insurance policy, the three main components - mortality, expenses, and investment - are distinct. The mortality component covers the risk of death, the expense component covers administrative costs, and the investment component builds cash value that the policyholder can invest or borrow against. The principle behind unbundled life insurance policy hinges on flexibility and transparency. Instead of a single, indivisible package as in traditional policies, unbundled life insurance breaks down into three distinct components: mortality, expenses, and cash value. Policyholders have the freedom to manage each part individually, adjusting them to suit personal needs and circumstances. This unbundling facilitates a clear view of where and how premiums are allocated, offering a unique combination of protection, potential growth, and policyholder control. Unbundling refers to the process of breaking down a comprehensive life insurance policy into distinct components. It provides more control to policyholders who can adjust the premium, death benefit, or cash value independently of each other. In an unbundled policy, part of the premium pays for the mortality risk and expenses, while the remainder goes into an investment account that earns interest or investment income. Policyholders can adjust the amounts allocated to each component, offering a level of control and flexibility not found in traditional life insurance policies. Unbundled life insurance policies play an integral part in managing financial risks. They offer an investment component that can grow over time, providing a potential hedge against inflation. Also, the policyholder can adjust the death benefit according to changing financial obligations, such as the birth of a child or the payoff of a mortgage. Unbundled life insurance policies offer distinctive features that set them apart from traditional life insurance products. One of the primary features is flexibility. Policyholders can adjust the death benefit, premium payments, and investment allocations based on their financial needs and goals. They can increase or decrease the death benefit, skip premium payments under certain conditions, and choose how the cash value component is invested. Unbundled life insurance policies often come with a surrender value, representing the amount a policyholder receives if they choose to cancel the policy. It typically equals the cash value of the policy, minus any surrender charges. Another significant feature of unbundled life insurance is transparency. Policyholders can see exactly how their premiums are distributed among mortality, expenses, and investment components. Unbundled life insurance policies also offer tax advantages. The cash value grows on a tax-deferred basis, and death benefits are generally tax-free to beneficiaries. The unbundled life insurance policy comprises three main components: mortality, investment, and expense. The mortality component of an unbundled life insurance policy is essentially the cost of the insurance coverage itself. This portion of the premium goes towards providing the death benefit that will be paid out to beneficiaries upon the death of the policyholder. The investment component is the part of the premium that goes towards building the policy's cash value. This cash value can grow over time based on the performance of the investments chosen by the policyholder, offering a potentially significant source of tax-deferred savings or investment income. The expense component covers the various costs associated with maintaining the insurance policy, including administrative expenses, commissions to insurance agents, and other operational costs. There are several types of unbundled life insurance policies, each with its own unique features and benefits. Variable life insurance policies allow policyholders to invest their cash value in a variety of investment options, typically mutual funds. These policies offer significant growth potential but also come with more investment risk. Universal life insurance policies offer more flexibility in premium payments and death benefits while providing a fixed rate of return on the cash value. Indexed universal life insurance policies link the growth of the cash value to the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. These policies offer more growth potential than a traditional universal life policy but less risk than a variable life policy. As with any financial product, there are both advantages and disadvantages to unbundled life insurance policies. The advantages of unbundled life insurance policies include flexibility, investment growth potential, tax advantages, and transparency. These policies can be tailored to meet the policyholder's specific needs, and the investment component can provide a significant source of tax-deferred growth. The disadvantages include investment risk, potential for increased costs, and complexity. The cash value in an unbundled policy can decrease if the investments perform poorly, and there may be higher costs associated with maintaining the policy. Additionally, these policies can be more complicated to understand and manage than traditional life insurance policies. An unbundled life insurance policy may be the right choice for individuals who want more control over their policy, have a long-term investment horizon, and are comfortable with taking on some investment risk. Buying an unbundled life insurance policy involves several important steps, including determining your insurance needs, choosing the right insurance company, and understanding the policy terms and costs. The first step in buying an unbundled life insurance policy is to determine your insurance needs. This involves considering your financial obligations, dependents, income, assets, and financial goals. Choosing the right insurance company involves researching different companies, comparing their products, prices, financial strength, and customer service. It's also advisable to check the company's ratings with insurance rating agencies and reviews from other customers. Before purchasing an unbundled life insurance policy, it's crucial to understand the policy's terms, including the death benefit, premium payments, investment options, fees, and charges. A financial advisor or insurance agent can help explain these terms and ensure you're making an informed decision. An unbundled life insurance policy can play a significant role in various aspects of financial planning, including retirement planning, estate planning, and business succession. The cash value in an unbundled life insurance policy can provide a source of retirement income. Policyholders can make tax-free withdrawals or loans from the cash value, supplementing other sources of retirement income. For estate planning, the death benefit from an unbundled life insurance policy can provide liquidity to pay estate taxes and other expenses, ensuring the policyholder's heirs receive the intended inheritance. In business succession planning, an unbundled life insurance policy can provide funds to buy out a deceased owner's interest in a business, ensuring a smooth transition of ownership. An unbundled life insurance policy presents a nuanced way to manage insurance and investment separately under one product. It operates on the principle of separating the mortality, investment, and expense components, offering a unique blend of flexibility and transparency. The policyholder has the liberty to manage these elements according to their financial goals and life situations. The mortality component covers life risk, the investment segment builds a cash-value over time, and the expense component handles the policy's administrative costs. Ultimately, an unbundled life insurance policy provides an efficient and flexible approach for individuals who desire a higher degree of control over their life insurance and investment strategy, adapting to their changing financial needs over time.Definition of Unbundled Life Insurance Policy
Basic Components
Principle Behind Unbundled Life Insurance Policies
Understanding Unbundling in Insurance
Mechanism
Role in Risk Management
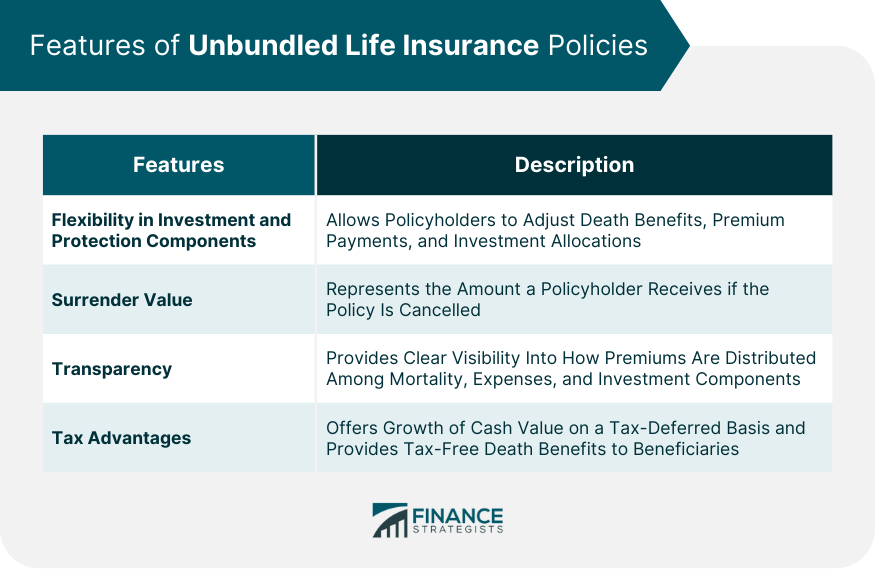
Features of Unbundled Life Insurance Policies
Flexibility in Investment and Protection Components
Surrender Value
Transparency
Tax Advantages
Components of Unbundled Life Insurance Policies
Mortality Component
Investment Component
Expense Component
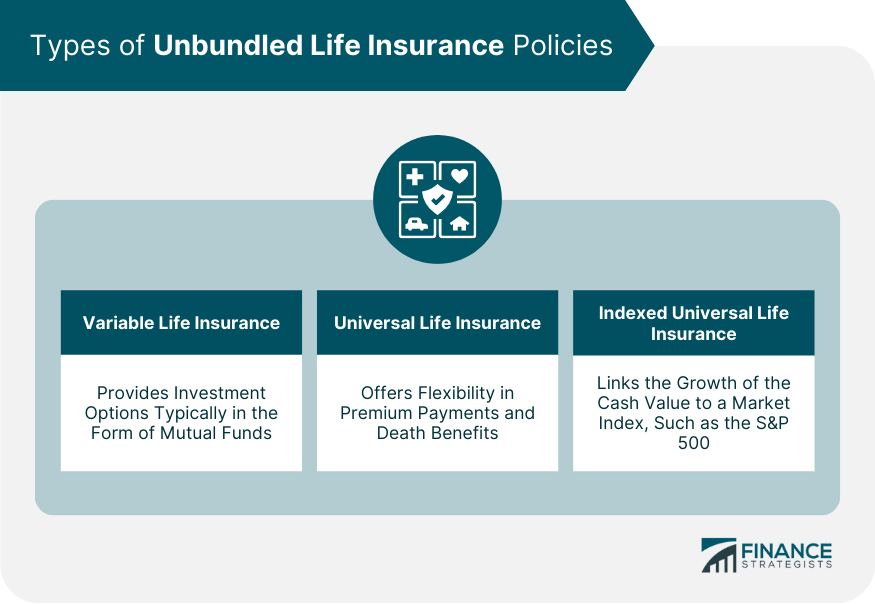
Types of Unbundled Life Insurance Policies
Variable Life Insurance
Universal Life Insurance
Indexed Universal Life Insurance
Pros and Cons of Unbundled Life Insurance Policies
Pros
Cons
When an Unbundled Life Insurance Policy is the Right Choice
How to Buy an Unbundled Life Insurance Policy
Determining Your Insurance Needs
Choosing the Right Insurance Company
Understanding Policy Terms and Costs
Role of Unbundled Life Insurance Policies in Financial Planning
Incorporating Into Retirement Planning
Estate Planning
Unbundled Life Insurance Policy as a Business Succession Tool
Conclusion
Unbundled Life Insurance Policy FAQs
An unbundled life insurance policy, also known as a flexible premium adjustable life insurance, separates the main components of traditional life insurance into mortality, expenses, and cash value. This separation provides policyholders greater transparency and the flexibility to adjust the policy as per their changing needs and financial situations.
An unbundled life insurance policy is composed of three main elements: the mortality component, which covers the risk of death; the expense component, which covers administrative costs; and the investment component, which is used to build cash value that can be invested or borrowed against.
There are several types of unbundled life insurance policies, including variable life insurance, universal life insurance, and indexed universal life insurance. Each type offers different features, with varying levels of risk and return.
Unbundled life insurance policies offer flexibility, transparency, potential for investment growth, and tax advantages. However, they also present certain disadvantages such as investment risk, potential for increased costs, and complexity compared to traditional life insurance policies.
An unbundled life insurance policy can play a crucial role in financial planning, including retirement planning, estate planning, and business succession. For instance, the cash value component can serve as a source of retirement income, the death benefit can provide liquidity in estate planning, and in the case of business succession, it can offer funds for smooth ownership transition.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











