Voluntary life insurance is a type of life insurance policy that an individual can choose to purchase, either through their employer or independently. It is designed to provide financial protection for the policyholder's beneficiaries in the event of the insured's death. The main purpose of voluntary life insurance is to offer financial security and peace of mind to the policyholder and their loved ones. Having a voluntary life insurance policy is an essential aspect of a comprehensive financial plan. It ensures that the policyholder's family will have the financial resources to cover expenses, such as mortgage payments, college tuition, and funeral costs, in the event of the insured's death. Additionally, it can provide a tax-free lump sum payment to the beneficiaries, which can help them maintain their current lifestyle and financial stability. There are two main types of voluntary life insurance – term life insurance and permanent life insurance. Each type has its unique features and benefits, depending on an individual's needs and financial goals. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified term, usually between 10 and 30 years. If the insured dies during the term, the policy pays a death benefit to the beneficiaries. Term life insurance can be further categorized into the following subtypes: This type of term life insurance has a fixed premium and death benefit throughout the policy term. It provides stable coverage, and the insured knows exactly how much they will pay in premiums and what the beneficiaries will receive in case of their death. In decreasing term life insurance, the death benefit gradually decreases over the policy term while the premium remains the same. This type of policy is often used to cover a decreasing financial obligation, such as a mortgage or loan repayment. This policy provides coverage for one year at a time, with the option to renew each year without having to prove insurability. The premiums increase annually, reflecting the insured's increased age and risk. Permanent life insurance provides lifelong coverage as long as the premiums are paid. It also has a cash value component that can accumulate over time. There are several types of permanent life insurance: Whole life insurance offers guaranteed level premiums, a fixed death benefit, and a cash value component that grows at a guaranteed rate. The cash value can be accessed through loans or withdrawals, providing a source of funds for various purposes, such as retirement income or emergency expenses. Universal life insurance allows for greater flexibility in premium payments, death benefits, and cash value accumulation. The policyholder can adjust the premiums and death benefits based on their financial needs and goals, while the cash value accumulates based on prevailing interest rates. Indexed Universal Life Insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that ties the cash value accumulation to a market index, such as the S&P 500. It offers the potential for higher returns on the cash value, while still providing a guaranteed minimum interest rate. Variable universal life insurance allows the policyholder to allocate the cash value component among various investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. It offers the potential for higher returns but also involves greater risk due to market fluctuations. Voluntary life insurance offers several features and benefits that make it an attractive choice for many individuals seeking financial protection for their families. One of the main advantages of voluntary life insurance is its flexibility. Policyholders can choose the type of coverage that best suits their needs, whether it's term or permanent life insurance. They can also adjust the death benefit and premium payments to fit their financial goals and budget. Voluntary life insurance policies often come with portability and conversion options. This means that if a policyholder leaves their job or changes employers, they can continue their coverage without interruption. Additionally, term life insurance policies may offer a conversion option that allows the policyholder to convert their policy to a permanent life insurance policy without undergoing medical underwriting. Some voluntary life insurance policies offer guaranteed issues or simplified underwriting, which means that the applicant is not required to undergo a medical exam or provide extensive health information. This can be beneficial for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those who want to avoid the inconvenience of a medical exam. Voluntary life insurance policies can be customized with various riders and endorsements, such as a waiver of premium rider or an accidental death benefit rider. These additional features can enhance the policy's value and provide extra protection for the policyholder and their beneficiaries. The death benefits from voluntary life insurance policies are generally paid tax-free to the beneficiaries. Additionally, the cash value accumulation in permanent life insurance policies is tax-deferred, meaning that the policyholder does not pay taxes on the growth until they access the funds. Permanent life insurance policies offer the potential for cash value accumulation, which can serve as a source of funds for various purposes, such as retirement income, emergency expenses, or funding a child's education. Before purchasing a voluntary life insurance policy, individuals should consider several factors to ensure they select the right coverage for their needs. It's essential to assess one's financial goals and needs before choosing a voluntary life insurance policy. This includes evaluating current and future expenses, such as mortgage payments, childcare costs, and college tuition, as well as determining the desired level of financial protection for the beneficiaries. The cost of voluntary life insurance should be considered in relation to the individual's budget. Term life insurance generally has lower premiums than permanent life insurance, making it more affordable for those with limited budgets. However, the long-term benefits of permanent life insurance, such as cash value accumulation, should also be taken into account. The desired length of coverage should be considered when selecting a voluntary life insurance policy. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, while permanent life insurance offers lifelong protection. Individuals should evaluate their needs and determine the most suitable option based on their age, health, and financial goals. The availability of different types of coverage and riders should also be considered when choosing a voluntary life insurance policy. Individuals should assess their unique needs and select a policy that offers the necessary coverage and additional features to provide comprehensive protection for their beneficiaries. Lastly, it's crucial to research the insurance company's reputation and financial strength before purchasing a voluntary life insurance policy. Policyholders should ensure that the company has a solid history of claims payment and financial stability to guarantee the long-term security of their policy. There are two primary ways to obtain voluntary life insurance: through employer-sponsored programs or by purchasing an individual policy. Many employers offer voluntary life insurance as part of their employee benefits package. These group policies often provide more affordable rates and simplified underwriting compared to individual policies. To obtain employer-sponsored voluntary life insurance, employees should consider the following steps: Typically, employees can enroll in voluntary life insurance during their initial benefits enrollment period or during the annual open enrollment period. They should check with their human resources department for specific enrollment dates and eligibility requirements. Group rates for voluntary life insurance are often lower than individual rates due to the pooled risk among employees. Employees should review the coverage options available through their employer, such as the types of policies offered, coverage amounts, and optional riders. Individuals can also purchase voluntary life insurance independently of their employer. To obtain an individual policy, they should consider the following steps: To find the best policy, individuals should compare quotes from multiple insurance companies. They can use online comparison tools, consult with an insurance agent or broker, or contact insurance companies directly for quotes. Once an individual has selected a policy, they will need to complete an application and undergo the underwriting process. This may involve providing personal and health information, as well as undergoing a medical exam, depending on the policy's underwriting requirements. Working with an insurance agent or broker can be beneficial when purchasing individual voluntary life insurance. These professionals can provide guidance on the types of policies and coverage amounts that best suit an individual's needs and can help navigate the application and underwriting process. Understanding the costs associated with voluntary life insurance is essential for making an informed decision. Premiums for voluntary life insurance vary based on factors such as the type of policy, coverage amount, and the insured's age, health, and lifestyle. Payment options typically include monthly, quarterly, semi-annual, or annual payments, depending on the policy and the policyholder's preference. In addition to premiums, voluntary life insurance policies may have fees and charges, such as policy administration fees, surrender charges (for early termination of a permanent life insurance policy), and investment management fees (for variable universal life insurance). Several factors can impact the premium rates for voluntary life insurance, including the insured's age, health, occupation, and lifestyle choices (such as smoking or high-risk hobbies). Policyholders should be aware of these factors and take steps to improve their risk profile, if possible, to obtain more favorable premium rates. Voluntary life insurance plays a crucial role in providing financial security and peace of mind for policyholders and their beneficiaries. With its flexible coverage options, portability, and potential tax benefits, it is an essential component of a well-rounded financial plan. Understanding the differences between term and permanent life insurance, as well as the unique features and benefits of each, can help individuals make informed decisions about the coverage that best suits their needs and financial goals. Additionally, considering factors such as personal financial goals, affordability, length of coverage, and the reputation and financial strength of the insurance company can ensure that the chosen policy provides comprehensive protection for loved ones. As life circumstances change, it is essential to review and update voluntary life insurance coverage regularly. To navigate the complexities of voluntary life insurance and select the best policy for your unique needs, it's advisable to seek the guidance of a professional insurance agent or broker.Definition and Purpose of Voluntary Life Insurance
Types of Voluntary Life Insurance
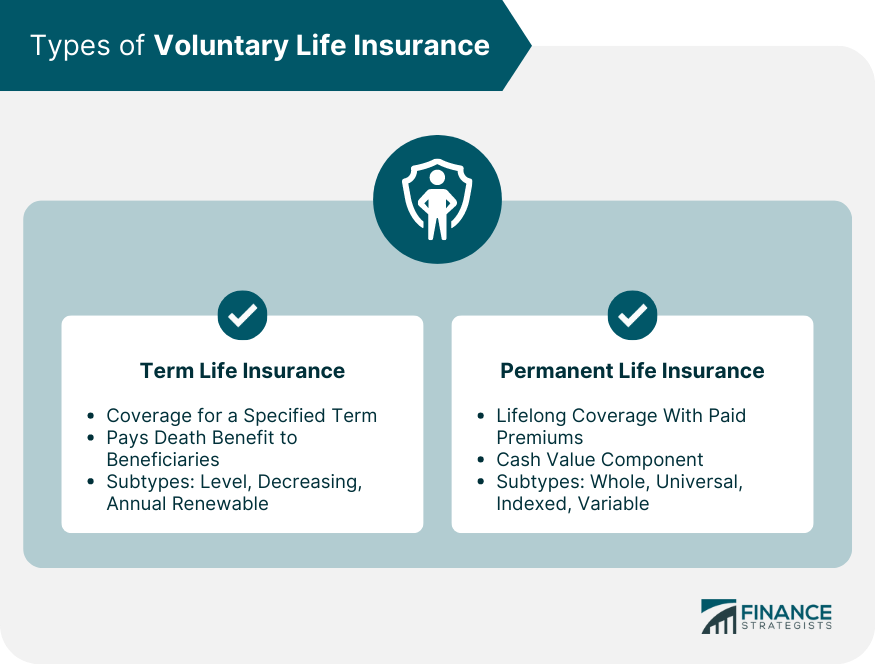
Term Life Insurance
Level Term Life Insurance
Decreasing Term Life Insurance
Annual Renewable Term Life Insurance
Permanent Life Insurance
Whole Life Insurance
Universal Life Insurance
Indexed Universal Life Insurance
Variable Universal Life Insurance
Features and Benefits of Voluntary Life Insurance
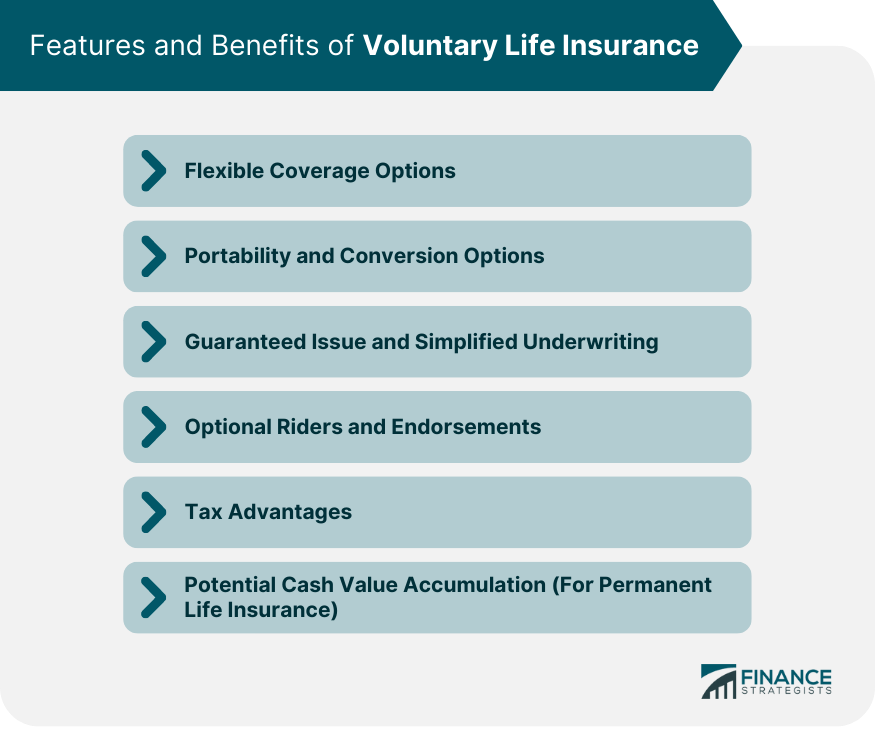
Flexible Coverage Options
Portability and Conversion Options
Guaranteed Issue and Simplified Underwriting
Optional Riders and Endorsements
Tax Advantages
Potential Cash Value Accumulation (for Permanent Life Insurance)
Factors to Consider When Choosing Voluntary Life Insurance
Personal Financial Goals and Needs
Affordability and Budget
Length of Coverage
Types of Coverage and Riders Available
Insurance Company Reputation and Financial Strength
How to Obtain Voluntary Life Insurance
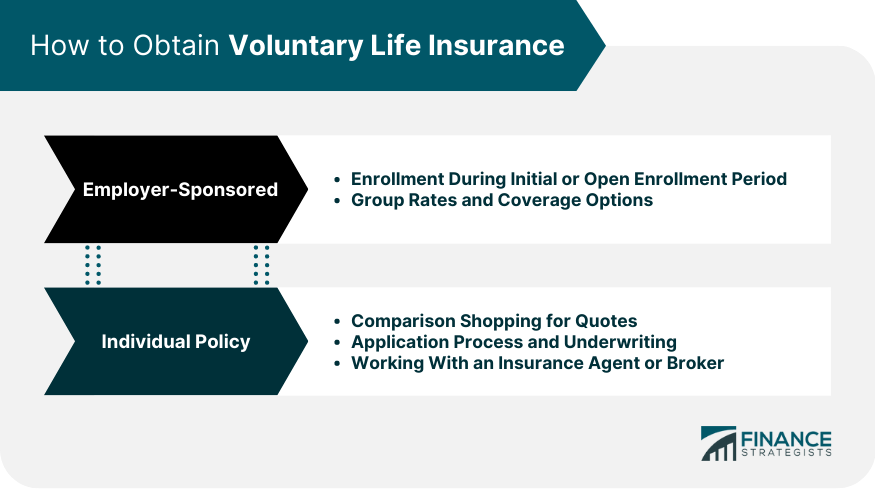
Employer-Sponsored Voluntary Life Insurance
Enrollment Process and Eligibility
Group Rates and Coverage Options
Individual Voluntary Life Insurance
Comparison Shopping
Application Process and Underwriting
Working With an Insurance Agent or Broker
Costs Associated With Voluntary Life Insurance
Premiums and Payment Options
Policy Fees and Charges
Factors That Impact Premium Rates
Conclusion
Voluntary Life Insurance FAQs
Term voluntary life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, typically 10 to 30 years, whereas permanent voluntary life insurance offers lifelong coverage and includes a cash value component that can accumulate over time.
Many term voluntary life insurance policies offer a conversion option, allowing policyholders to convert their term policy to a permanent life insurance policy without undergoing additional medical underwriting.
When choosing a voluntary life insurance policy, consider factors such as your financial goals, budget, desired length of coverage, and the types of coverage and riders available. Assess your unique needs and select a policy that offers the necessary coverage and features for your situation.
Yes, there are tax benefits associated with voluntary life insurance policies. Generally, the death benefits paid to beneficiaries are tax-free. In addition, the cash value accumulation in permanent life insurance policies is tax-deferred, meaning taxes are not paid on the growth until funds are accessed.
In many cases, employer-sponsored voluntary life insurance policies offer portability and conversion options, allowing policyholders to continue their coverage without interruption when changing jobs or retiring. However, it's essential to review the specific terms and conditions of your policy to determine the available options.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











