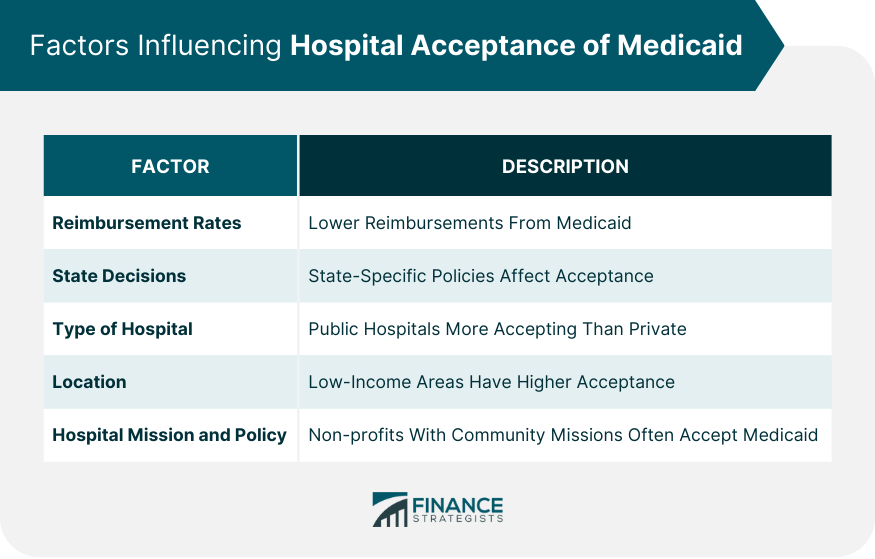
Medicaid is a health insurance program jointly funded by the federal government and individual states. It's designed to aid those with limited financial resources, such as children, elderly adults, pregnant women, and individuals with disabilities. Medicaid acts as a safety net, ensuring health coverage for those who might otherwise go uninsured. While emergency care is universally mandated, hospitals often have the discretion to choose whether to offer non-emergency services based on a patient's insurance coverage. Not all hospitals accept Medicaid. Medicaid is a joint federal and state program in the United States that helps cover medical costs for individuals with limited income and resources. While many hospitals do accept Medicaid because of the substantial number of patients who use it, it's not a requirement for hospitals to do so. Several factors influence whether a hospital accepts Medicaid: Reimbursement Rates: Medicaid often reimburses providers at lower rates compared to private insurance or Medicare. Some hospitals might find these rates unsustainable or feel they do not cover the costs of the services provided. State Decisions: Since Medicaid is a joint federal-state program, individual states have leeway in setting their own Medicaid policies, reimbursement rates, and provider requirements. As a result, acceptance of Medicaid can vary significantly from state to state.6 Type of Hospital: Public or community hospitals are more likely to accept Medicaid compared to some private or specialty hospitals. Location: Hospitals in areas with a higher concentration of low-income patients are more likely to accept Medicaid. Hospital Mission and Policy: Some hospitals, especially non-profit ones, may have a mission to serve all members of the community, regardless of their ability to pay. These hospitals are more likely to accept Medicaid. If you or someone you know is a Medicaid beneficiary and requires hospital services, it's crucial to check in advance if the specific hospital accepts Medicaid to avoid unexpected bills. You can typically do this by calling the hospital's billing or patient services department or checking their website. The state's Medicaid office or website often provides a list of participating providers. Medicaid compensates hospitals through a system that's often less generous than other insurance providers. State-dictated Medicaid fee schedules establish how much each service garners in terms of reimbursement. These fees are essential in shaping a hospital's decision-making process regarding which insurance types to accept. The reimbursement rates from Medicaid often fall below what Medicare or private insurers offer. This difference can pose a financial challenge for hospitals, especially when treating patients requiring resource-intensive care. Economics plays a pivotal role in hospital decisions. In areas with significant low-income populations, Medicaid patients might constitute a large part of a hospital's patient flow. While this ensures consistent patient traffic, it also comes with the challenge of balancing budgets due to lower reimbursement rates. State policies can serve as either incentives or deterrents for hospitals considering Medicaid acceptance. Some states might enhance reimbursement rates or offer additional financial incentives, altering the cost-benefit analysis for hospitals. Public hospitals, sustained by public funds, often serve broader community needs, leading them to accept a wide range of insurance, including Medicaid. On the other hand, private institutions might make decisions leaning more toward profitability, which can sometimes mean limiting Medicaid acceptance. By accepting Medicaid, hospitals can drastically reduce healthcare access barriers for vulnerable communities. This ensures these communities receive vital healthcare services and contributes positively to overall public health. Despite the lower imbursement rates, Medicaid acceptance can guarantee a consistent stream of patients. Over time, this can provide financial stability, especially when supplemented by other federal and state financial programs. While Medicaid serves a noble cause, the associated reimbursement rates can strain hospital finances. In situations where costs of services surpass reimbursement amounts, hospitals can face significant financial stress. Medicaid, with its intricate set of regulations and requirements, can be a daunting program to navigate. The administrative burden, from ensuring compliance to processing claims, might deter certain hospitals from participating. Critical Access Hospitals are typically located in rural areas where the population is sparse, and healthcare resources are limited. Due to their remote settings, these hospitals often serve as the primary or only healthcare facility available to the local community. They encounter unique challenges such as a small patient base, limited financial resources, and difficulty attracting healthcare professionals. In these situations, Critical Access Hospitals might rely heavily on Medicaid because many of their patients are Medicaid beneficiaries. For these hospitals, accepting Medicaid isn't just an option; it's often a necessity for their survival and for ensuring that people in rural areas have access to essential healthcare services. Pediatric hospitals specialize in providing healthcare exclusively to children. Children make up a significant portion of Medicaid beneficiaries, as the program is designed to help vulnerable populations, including low-income families with children. Pediatric hospitals often have no choice but to accept Medicaid because a substantial portion of their patient population relies on this insurance program. They provide specialized care tailored to the unique healthcare needs of children, which makes Medicaid acceptance essential for their effective operation. Teaching and tertiary hospitals are academic medical centers that focus on advanced medical care, research, and medical education. They often play a crucial role in healthcare innovation and training the next generation of healthcare professionals. These hospitals offer a wide spectrum of specialized services, and they serve a diverse patient base, including patients with complex medical conditions. The decision to accept Medicaid can be more complex for these institutions due to their multifaceted mission. While they may be more likely to accept Medicaid to ensure access to care for a diverse patient population, they also have to consider the financial implications and how Medicaid reimbursement rates may affect their ability to fund research and education initiatives. Medicaid isn't uniform across states. While one state might see broad hospital participation in Medicaid, another might struggle with limited acceptance due to the nuances of its Medicaid program. Certain regions have adopted strong stances on Medicaid, either pushing hospitals towards acceptance through incentives or making it mandatory, ensuring more widespread healthcare access. Identify Medicaid-Accepting Hospitals: Tools and databases, often hosted on state-specific Medicaid websites, can guide beneficiaries in locating hospitals that cater to their insurance. Explore Alternatives When a Hospital Doesn't Accept Medicaid: Beneficiaries can explore other avenues for non-emergency care, like community health clinics, which often accept Medicaid. Understand Rights and Protections for Medicaid Beneficiaries: Access to emergency care is a right. Outside of that, it's paramount for beneficiaries to be informed about their entitlements when seeking healthcare services, ensuring they are never unfairly turned away. Medicaid is a government-sponsored health insurance program that helps low-income individuals and families access essential medical care. However, not all hospitals accept Medicaid due to various factors, such as reimbursement rates, state policies, hospital type, location, and mission. Hospitals that accept Medicaid can benefit from increased access to care for vulnerable communities and financial stability, but they also face challenges such as lower reimbursement rates and administrative burdens. Medicaid beneficiaries need to be aware of their rights and options when seeking hospital services and use available tools and resources to find hospitals that accept their insurance. Understanding the intricate relationship between Medicaid and hospitals offers a lens into the broader challenges and considerations of healthcare accessibility. Medicaid acceptance is a complex issue with varying reimbursement rates, state policies, and hospital types.What Is Medicaid?
Do All Hospitals Accept Medicaid?
How Medicaid Hospital Acceptance Works
Funding and Reimbursement Mechanisms
How Medicaid Compensates Hospitals
Differences Between Medicaid and Other Insurance Reimbursement Rates
Hospital Medicaid Acceptance Factors
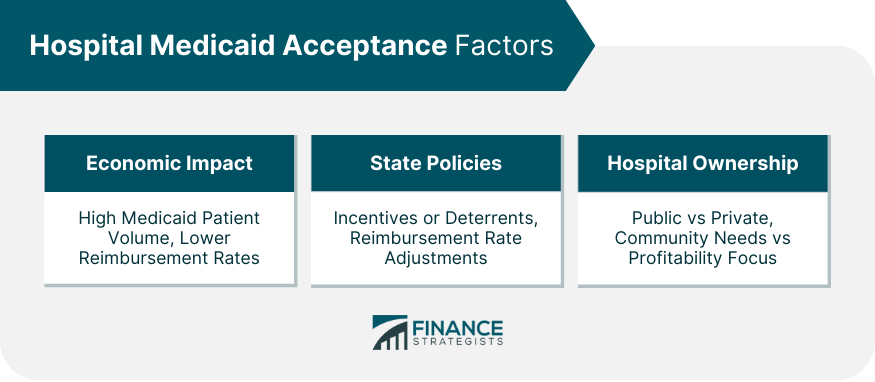
Economic Considerations
Role of State Policies
Influence of Hospital Ownership
Benefits of Medicaid Acceptance for Hospitals
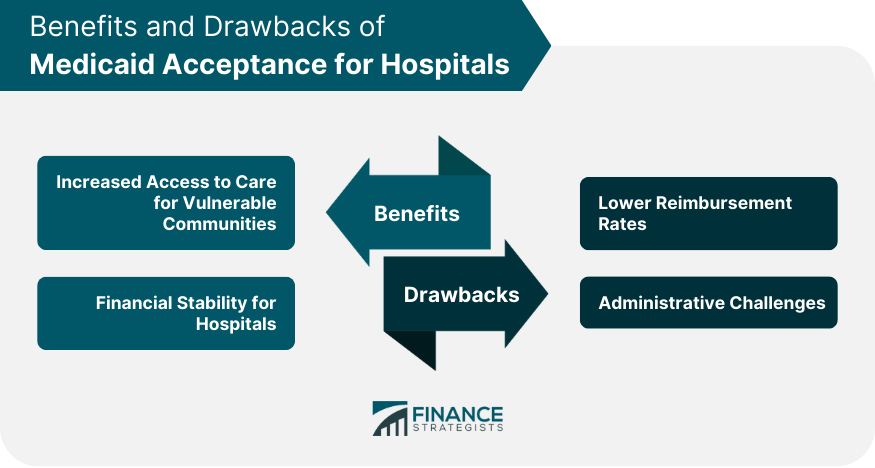
Increased Access to Care
Financial Stability for Hospitals
Drawbacks of Medicaid Acceptance for Hospitals
Lower Reimbursement Rates
Administrative Challenges
Notable Exceptions and Special Cases
Critical Access Hospitals
Pediatric Hospitals
Teaching and Tertiary Hospitals

Impact of Local Legislation and Policies on Medicaid
State-Specific Medicaid Programs
Local Mandates and Incentives
Strategies for Beneficiaries Navigating Hospital Choices

Conclusion
Do All Hospitals Accept Medicaid? FAQs
Medicaid acceptance at hospitals refers to whether a hospital provides services to patients insured under Medicaid, a government-funded health insurance program.
Hospitals accepting Medicaid ensure increased access to care for vulnerable communities and maintain financial stability despite lower reimbursement rates.
Hospitals accepting Medicaid encounter lower reimbursement rates and administrative challenges related to Medicaid's regulations and requirements.
State policies can either incentivize or deter hospitals from accepting Medicaid, impacting the decision-making process.
Yes, beneficiaries can explore alternatives like community health clinics for non-emergency care if a hospital doesn't accept Medicaid.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











