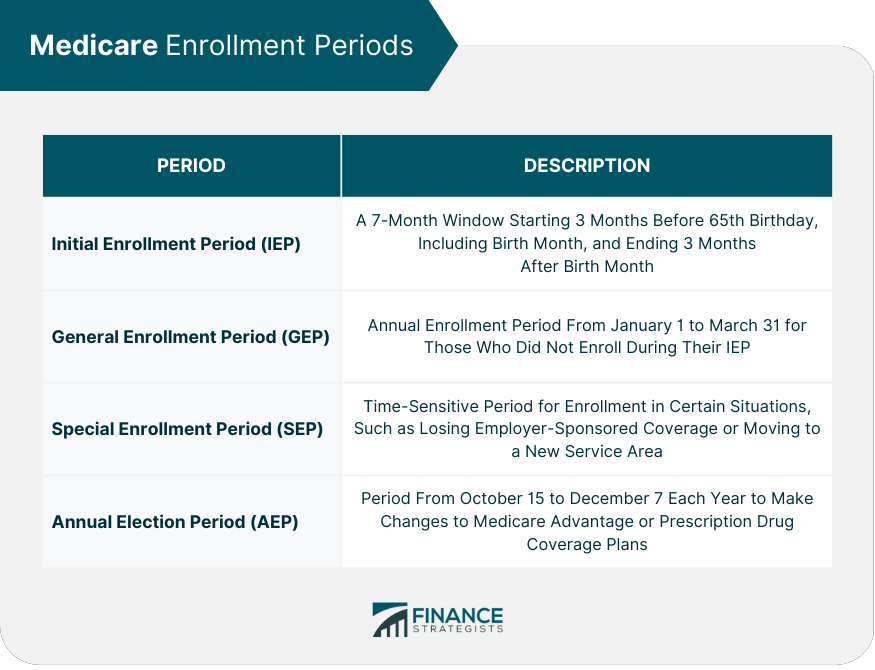
Medicare planning involves understanding the various aspects of the Medicare program and making informed decisions to select the best healthcare coverage for your needs. This process is essential to ensure you have access to affordable, high-quality healthcare services throughout your retirement years. Medicare is a federal health insurance program designed for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities or specific health conditions. The program is divided into four main parts: Original Medicare (Part A and Part B): Part A covers hospital services, while Part B covers medical services such as doctor visits and preventive care. Medicare Advantage (Part C): Private insurance plans that provide Part A and Part B benefits, and often include additional services, such as prescription drug coverage. Prescription Drug Coverage (Part D): Standalone plans that offer coverage for prescription medications. Medigap: Supplemental insurance policies that help cover out-of-pocket costs not covered by Original Medicare. To be eligible for Medicare, you must meet specific age, disability, or health condition criteria: Age requirements: You must be at least 65 years old or turning 65 within the next three months. Disability and other special circumstances: You may qualify for Medicare if you are under 65 and have been receiving Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) for at least 24 months, have end-stage renal disease (ESRD), or have amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). There are various enrollment periods during which you can sign up for Medicare: Initial Enrollment Period (IEP): A 7-month window that starts 3 months before your 65th birthday, includes your birth month, and ends 3 months after your birth month. General Enrollment Period (GEP): Held annually from January 1 to March 31, this period is for those who did not enroll during their IEP. Special Enrollment Period (SEP): A time-sensitive period that allows enrollment in certain situations, such as losing employer-sponsored coverage or moving to a new service area. Annual Election Period (AEP): From October 15 to December 7 each year, this period allows you to make changes to your Medicare Advantage or Prescription Drug Coverage plans. Understanding the various costs associated with Medicare, including premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance, is essential for effective planning. These costs can vary depending on the specific coverage you choose. Three primary factors influence the cost of your Medicare coverage: Income: Higher-income individuals may be required to pay higher premiums for Part B and Part D. Location: The cost of Medicare Advantage and Prescription Drug Coverage plans can vary based on your geographical location. Type of coverage: The coverage options you choose, such as Original Medicare, Medicare Advantage, or Medigap, will impact your overall costs. It's crucial to compare coverage options to find the best fit for your healthcare needs and budget: Original Medicare vs. Medicare Advantage: Original Medicare provides standard coverage for hospital and medical services, while Medicare Advantage plans often offer additional benefits and may have lower out-of-pocket costs. Prescription Drug Coverage: If you need prescription medication coverage, you can choose between a standalone Part D plan or a Medicare Advantage plan that includes drug coverage. Medigap Policies: If you have Original Medicare, you may want to consider a Medigap policy to help cover out-of-pocket costs, such as deductibles and coinsurance. It's crucial to estimate your healthcare costs in retirement to ensure you have adequate savings. Consider factors such as your expected healthcare needs, potential long-term care expenses, and the costs of various Medicare plans. There are several ways to save for healthcare expenses in retirement: Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): These tax-advantaged accounts can be used to save for qualified medical expenses, including Medicare premiums. Retirement Accounts: Contributing to retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, can help you build savings for healthcare costs. Long-term Care Insurance: Purchasing long-term care insurance can help cover costs associated with long-term care services not covered by Medicare. Understanding the tax implications of your healthcare expenses and Medicare premiums is essential to optimize your financial planning. Consult with a tax professional to ensure you're taking advantage of available deductions and credits. Selecting healthcare providers that accept Medicare is crucial for maximizing your coverage benefits. Use resources such as the Medicare.gov Physician Compare tool to find providers in your area. Be aware of the coverage rules and limitations of your chosen Medicare plan. For example, Original Medicare typically does not cover dental, vision, or hearing services, while Medicare Advantage plans may have provider network restrictions. If you disagree with a coverage or payment decision made by Medicare, you have the right to appeal. Familiarize yourself with the appeals process to ensure your healthcare needs are met. Take advantage of preventive services and wellness programs covered by Medicare, such as annual wellness visits and screenings, to maintain your health and reduce potential healthcare costs. Utilize government resources to assist with your Medicare planning: Medicare.gov: The official government site for Medicare provides comprehensive information and resources, including plan comparison tools and enrollment support. Social Security Administration: This agency handles Medicare enrollment and can provide assistance with eligibility and premium questions. Non-profit organizations can offer valuable support and guidance for Medicare planning: State Health Insurance Assistance Programs (SHIPs): These programs provide free, unbiased counseling and assistance for Medicare beneficiaries. AARP: A trusted source of information, resources, and advocacy for older adults, AARP offers various tools and guidance on Medicare planning. Consulting with professional advisors can help ensure you make informed decisions about your Medicare coverage: Financial Planners: These professionals can help you incorporate Medicare planning into your overall retirement strategy. Insurance Agents: Licensed insurance agents can help you navigate the various Medicare plans and find the best coverage for your needs. Proactive Medicare planning plays a crucial role in securing access to the healthcare services you need during your retirement years. By understanding the various aspects of the Medicare program, evaluating your options, and making informed decisions, you can select the best coverage for your needs. Continuously monitoring and adjusting your Medicare plan as your healthcare needs evolve is essential to ensuring you receive the maximum benefits from your coverage. Staying informed about updates and changes to the Medicare program is equally important in maintaining an effective healthcare strategy. Utilize resources from the government, non-profit organizations, and professional advisors to support your planning efforts and stay abreast of any developments in the Medicare system. By taking a proactive approach to Medicare planning, you can optimize your healthcare coverage and enjoy a healthier, more financially secure retirement.What Is Medicare Planning?
Overview of the Medicare Program
Medicare Eligibility and Enrollment
Determining Eligibility
Medicare Enrollment Periods
Medicare Costs and Coverage
Premiums, Deductibles, and Coinsurance
Factors Influencing Costs
Comparison of Coverage Options
Retirement and Financial Planning
Estimating Healthcare Costs in Retirement
Saving for Healthcare Expenses
Tax Implications
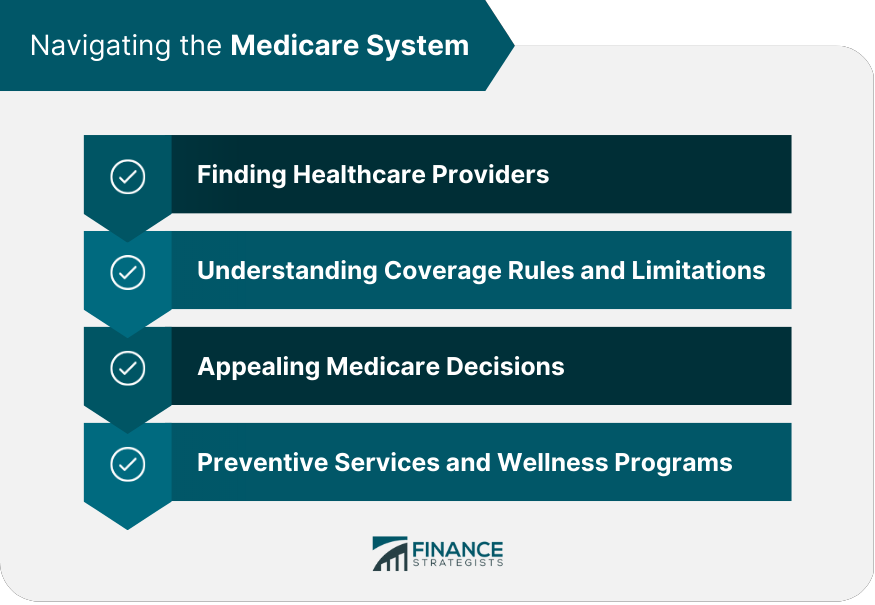
Navigating the Medicare System
Finding Healthcare Providers
Understanding Coverage Rules and Limitations
Appealing Medicare Decisions
Preventive Services and Wellness Programs
Resources for Medicare Planning
Government Resources
Non-profit Organizations
Professional Advisors
Conclusion
Medicare Planning FAQs
Medicare planning involves assessing and optimizing an individual's Medicare coverage and benefits to ensure they have the most comprehensive and cost-effective coverage for their healthcare needs.
It's recommended to start Medicare planning three months before you turn 65 or become eligible for Medicare, to ensure you have the coverage you need when you become eligible. However, if you missed the initial enrollment period, you may still be able to enroll during the annual enrollment period or a special enrollment period.
Medicare covers a range of healthcare services, including hospital stays, doctor visits, preventive care, and prescription drugs. However, there may be gaps in coverage or out-of-pocket costs that beneficiaries should be aware of.
There are several ways to optimize Medicare coverage, such as enrolling in a Medicare Advantage plan, choosing a plan with a lower premium or deductible, reviewing the formulary for prescription drug coverage, and exploring supplemental coverage options like Medigap plans.
Yes, beneficiaries can make changes to their Medicare coverage during the annual enrollment period (October 15 to December 7) or a special enrollment period if they experience a qualifying life event, such as moving to a new state or losing their current coverage. It's important to review coverage options annually and make changes as needed to ensure you have the best coverage for your healthcare needs.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











