Earthquake insurance is a type of insurance policy that provides coverage for property damage or loss resulting from an earthquake. Earthquake insurance is designed to protect property owners from the financial burden of repairing or rebuilding their homes or businesses in the aftermath of an earthquake. Unlike standard homeowner's insurance policies, earthquake insurance is specifically designed to cover the unique risks associated with seismic activity, including structural damage, foundation damage, and damage to personal property. Earthquake insurance policies may vary in terms of the types of damage they cover, the coverage limits, and the deductibles required. Individuals who live in areas with a high risk of earthquakes are often advised to consider purchasing earthquake insurance to protect their property and finances in the event of an earthquake. There are two primary types of earthquake insurance: comprehensive policies and stand-alone policies. Homeowners Insurance: Some homeowners insurance policies may include earthquake coverage as part of their standard offering or as an optional endorsement. It is essential to review your policy to determine if earthquake coverage is included or available as an add-on. Renters Insurance: Similar to homeowners insurance, some renters insurance policies may offer earthquake coverage as part of their basic coverage or as an optional endorsement. Renters should review their policy and discuss their options with their insurance provider. Dwelling Coverage: This type of policy specifically covers the dwelling structure in the event of an earthquake, including damage to the foundation, walls, and roof. Personal Property Coverage: This coverage protects your personal belongings inside the home, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing, from earthquake damage. Loss of Use Coverage: This policy covers additional living expenses incurred if you are temporarily displaced from your home due to earthquake damage. Understanding the essential components of an earthquake insurance policy is crucial when evaluating and comparing policies. These are the maximum amounts the insurance company will pay for specific categories of losses, such as dwelling, personal property, and loss of use. It's essential to ensure your coverage limits are adequate to cover the potential cost of rebuilding or repairing your home and replacing your belongings. A deductible is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Earthquake insurance policies often have separate, higher deductibles than standard homeowners or renters policies. Some policies may exclude specific types of damage, such as damage due to landslides or tsunamis triggered by an earthquake. It's essential to understand these exclusions and consider additional coverage if necessary. These are optional add-ons that can provide additional coverage or modify the terms of your policy. For example, you may be able to purchase coverage for building code upgrades required after an earthquake. Several factors can influence the cost of earthquake insurance premiums, including: The geographic location of your property plays a significant role in determining your premiums, as some areas are more prone to earthquakes than others. Homes built with materials and methods that are more resistant to earthquake damage, such as wood framing and shear walls, may have lower premiums. Additionally, newer homes built to modern building codes may be less expensive to insure than older homes. Homes with a slab foundation may be less vulnerable to earthquake damage than those with a raised foundation, which could result in lower premiums. Taking steps to strengthen your home against earthquake damage, such as retrofitting or installing seismic bracing, can lead to reduced insurance premiums. To determine if earthquake insurance is necessary for your situation, consider the following factors: Seismic Hazard Maps: Review local seismic hazard maps to understand the potential for earthquake activity in your area. Fault Proximity: Evaluate your property's proximity to known fault lines, as this can impact your risk of earthquake damage. Soil and Building Conditions: Consider local soil conditions and the construction quality of your home, as these factors can influence the severity of earthquake damage. Replacement Cost of the Property: Determine the cost to rebuild or repair your home and replace your personal belongings in the event of a significant earthquake. Personal Financial Situation: Assess your ability to cover the costs of earthquake damage out-of-pocket or through a loan, and weigh that against the cost of earthquake insurance premiums. Comparing Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers to find the best coverage and price for your needs. Researching Providers: Investigate the financial stability and customer service reputation of each insurance provider you're considering. Understanding Policy Details: Carefully read the policy terms and conditions, including coverage limits, deductibles, exclusions, and endorsements. Working with an Insurance Agent or Broker: An experienced insurance professional can help you navigate the process of selecting and purchasing the appropriate earthquake insurance policy. After an earthquake, ensure the safety of your family, assess the damage to your property, and take steps to prevent further damage. Document the damage to your property by taking photos or videos, creating an inventory of damaged items, and collecting any relevant receipts or records. Contact your insurance provider as soon as possible to report the damage and initiate the claims process. Be prepared to provide documentation and cooperate with any investigations or inspections conducted by the insurance company. Earthquake insurance serves as a crucial financial safety net for homeowners and renters residing in earthquake-prone areas. It is essential to carefully evaluate personal risk factors, including geographic location, property construction, and financial circumstances, in order to make an informed decision about purchasing the right policy. By understanding policy details, coverage limits, deductibles, exclusions, and endorsements, you can choose a policy that provides the necessary protection without overburdening your finances. In addition to evaluating your own needs, it is helpful to work with an experienced insurance professional who can guide you through the process of selecting and purchasing the appropriate earthquake insurance policy. Having the right coverage in place can provide peace of mind and ensure that you are prepared to face the financial consequences of earthquake damage. Investing time and effort into understanding and acquiring earthquake insurance can ultimately save you from significant financial loss and provide security for your home and belongings.What Is Earthquake Insurance?
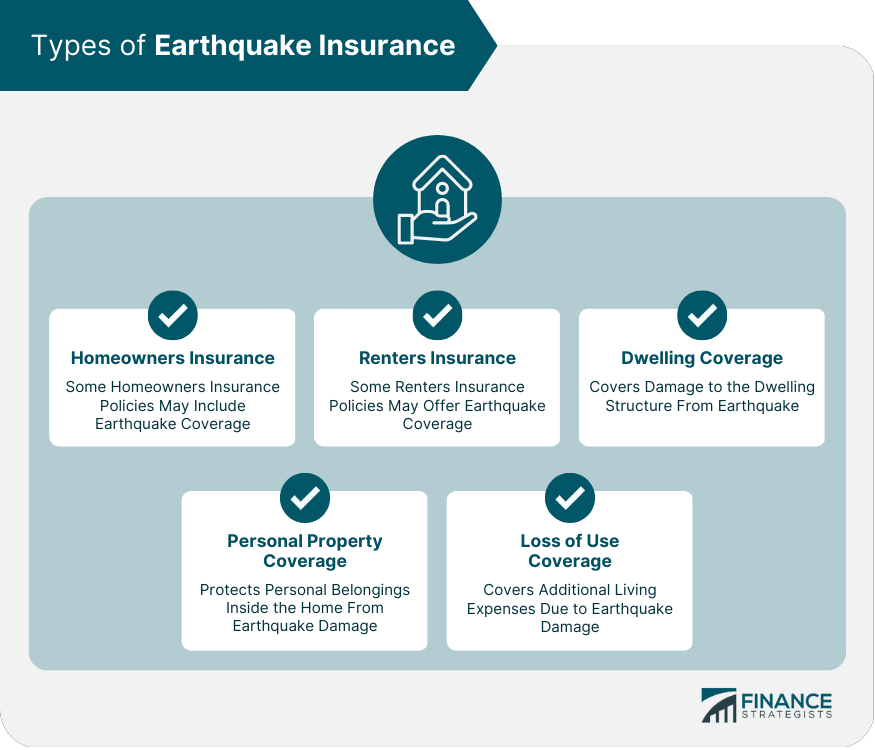
Types of Earthquake Insurance
Comprehensive Policies
Stand-Alone Policies
Key Components of Earthquake Insurance
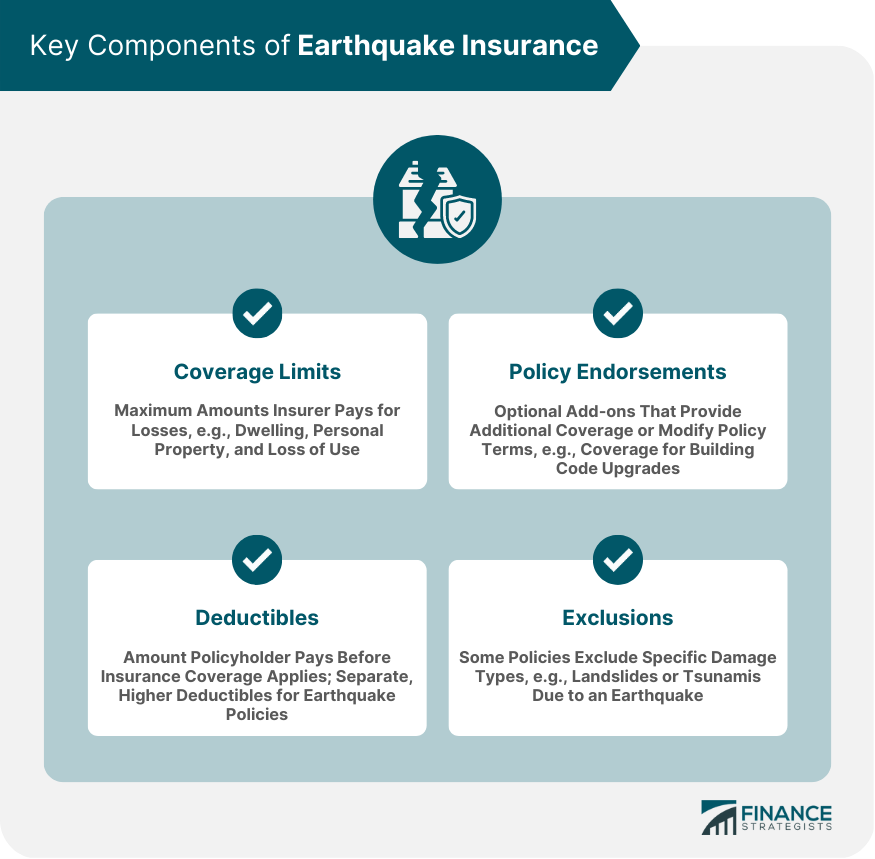
Coverage Limits
Deductibles
Exclusions
Policy Endorsements
Factors Affecting Earthquake Insurance Premiums
Geographic Location
Construction Type and Age of the Building
Foundation Type
Retrofitting and Mitigation Measures
Evaluating the Need for Earthquake Insurance
Assessing Earthquake Risk
Financial Considerations
How to Purchase Earthquake Insurance
Shopping for Policies
Tips for Choosing the Right Policy
Filing an Earthquake Insurance Claim
Steps to Take Immediately Following an Earthquake
How to Document Damages
Navigating the Claims Process
Conclusion
Earthquake Insurance FAQs
Earthquake insurance is a type of insurance that provides coverage for damage to your property caused by earthquakes. This type of insurance is typically not included in standard homeowner's insurance policies and must be purchased separately.
Anyone who lives in an area with a high risk of earthquakes should consider purchasing earthquake insurance. This includes individuals living in states such as California, Oregon, and Washington, where earthquakes are relatively common.
Earthquake insurance typically covers damage to your property caused by earthquakes, including structural damage to your home and damage to personal belongings. Some policies may also cover additional expenses, such as temporary housing and living expenses, if your home is deemed uninhabitable due to earthquake damage.
The cost of earthquake insurance varies depending on a variety of factors, including the location and value of your property, the level of coverage you choose, and your insurance provider. In general, earthquake insurance can be relatively expensive, especially in areas with a high risk of earthquakes.
Earthquake insurance is not typically required by law, but some mortgage lenders may require borrowers to purchase earthquake insurance as a condition of the loan. Additionally, some states may offer earthquake insurance programs or require insurance providers to offer earthquake coverage as an option. It is important to check your local laws and lender requirements to determine whether earthquake insurance is mandatory in your area.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











