Homeowners insurance is a form of property insurance that covers financial losses related to a private residence. It provides financial protection for homeowners in the event of damage to their property, personal belongings, or other liabilities arising from unforeseen events. Having homeowners insurance is essential for property owners to safeguard their investment, protect their personal belongings, and ensure peace of mind. In many cases, it is also a requirement by mortgage lenders to secure a home loan. Homeowners insurance policies typically cover dwelling protection, personal property coverage, liability protection, and additional living expenses. The coverage details and limits may vary depending on the policy and insurance provider. Dwelling coverage helps to repair or rebuild the insured home if it is damaged or destroyed by a covered event. Replacement cost policies cover the expense of rebuilding the home to its original state, while actual cash value policies factor in depreciation and pay the current market value of the home. Extended replacement cost coverage provides additional protection beyond the policy limits, usually a specific percentage above the insured amount. This coverage can be helpful in instances where construction costs have increased or when natural disasters affect many homes in an area, driving up rebuilding costs. Personal property coverage protects the personal belongings of the homeowner, such as furniture, clothing, and electronics, in case of damage or theft. Coverage limits vary, and certain high-value items may have specific sub-limits or require additional endorsements. For high-value items like jewelry, art, or antiques, homeowners can purchase a scheduled personal property endorsement, which offers broader coverage and higher limits for these specific items. Personal liability coverage protects the homeowner from financial loss if they are found legally responsible for causing injury or property damage to others. This coverage typically includes the cost of legal defense and any resulting judgments or settlements. Medical payments coverage provides for the medical expenses of visitors who are injured on the insured property, regardless of fault. This coverage is usually limited to a specific amount per person or incident. Additional living expenses (ALE) coverage helps pay for the increased cost of living when homeowners are temporarily unable to live in their home due to a covered loss. This may include expenses like hotel bills, meals, and other living costs. For homeowners who rent out part of their property, ALE coverage may also include reimbursement for lost rental income while the property is uninhabitable due to a covered loss. The most basic policy, HO-1 provides coverage for a limited number of perils, such as fire, lightning, and vandalism. This policy type is rare and not recommended for most homeowners. HO-2 policies offer broader coverage than HO-1, including additional perils like falling objects, water damage from plumbing issues, and damage caused by the weight of ice, snow, or sleet. The most common policy, HO-3 offers comprehensive coverage for the dwelling and limited coverage for personal property. It typically covers all perils except those explicitly excluded, such as earthquakes or floods. HO-4 policies are designed for renters, providing personal property and liability coverage but no dwelling protection. The most comprehensive policy available, HO-5 covers both the dwelling and personal property on an open-perils basis, meaning it covers all perils unless specifically excluded. This policy type often includes higher coverage limits and additional endorsements for high-value items. Designed specifically for condominium unit owners, HO-6 policies cover personal property, liability, and portions of the dwelling not covered by the condominium association's insurance policy. HO-7 policies are tailored for mobile and manufactured homes, providing similar coverage to an HO-3 policy but adapted for the unique risks associated with these types of residences. HO-8 policies are designed for older homes that may not meet current building codes or have a higher replacement cost than their actual cash value. These policies typically provide modified coverage for the dwelling and personal property, with some limitations. Geographical location plays a significant role in determining insurance premiums, as areas prone to natural disasters, crime, or higher rebuilding costs will have higher rates. Older homes or those in poor condition may have higher insurance premiums due to the increased risk of damage or the need for costly repairs. Higher coverage limits and lower deductibles result in higher premiums, as the insurance company assumes more financial responsibility in the event of a claim. Homeowners with a history of multiple claims may face higher premiums, as insurance companies consider them to be a higher risk. Homes with security systems, smoke detectors, or other safety features may qualify for discounts on their insurance premiums, as they are less likely to experience losses. Many insurance companies offer discounts for bundling multiple policies, such as home and auto insurance, or for policyholders who have been with the company for an extended period. Homeowners should evaluate their specific needs and potential risks, such as the value of their belongings, the likelihood of natural disasters in their area, and their liability exposure. It's essential to compare different policy types and coverage options to ensure the chosen policy meets the homeowner's unique needs. Consider the financial stability and credit rating of potential insurance providers, as this can impact their ability to pay claims. Evaluate the customer service reputation of insurance companies, including their responsiveness and ease of communication during the claims process. Research how potential insurance providers handle claims, as this can impact the speed, efficiency, and fairness of claim payouts. Compare quotes from multiple insurance providers to find the best rates and coverage for your specific situation. Notify your insurance company as soon as possible. Document the damage and take photos or videos. Make temporary repairs to prevent further damage. Keep detailed records of repair costs and additional living expenses. Cooperate with the insurance adjuster and provide any requested documentation. Maintain an inventory of personal belongings and their estimated value, as this can expedite the claims process and help ensure accurate reimbursement. An adjuster will assess the damage and determine the claim payout. It's essential to be honest and cooperative during this process to ensure a fair settlement. To maximize the claim payout, homeowners should: Provide thorough documentation of damages and losses. Obtain multiple repair estimates from reputable contractors. Keep detailed records of additional living expenses incurred. Review the policy carefully to understand the coverage limits and exclusions. If a homeowner disagrees with the insurance company's claim decision, they can: Request a second inspection by a different adjuster. Hire a public adjuster to assess the damage independently. Enter into mediation or arbitration with the insurance company. Seek legal advice or pursue a lawsuit if necessary. Homeowners insurance is a crucial component of responsible homeownership, as it protects one of the most significant investments most people will ever make. Adequate coverage ensures financial protection in the event of unexpected losses or liabilities. It's essential for homeowners to review their insurance coverage regularly, particularly when making significant home improvements or acquiring valuable items. This ensures that their policy remains up-to-date and provides adequate protection. Homeowners should stay informed about changes in the insurance industry, such as new coverage options, discounts, or legal requirements, to ensure they maintain the best possible coverage for their needs.What Is Homeowners Insurance?
Components of a Homeowners Insurance Policy
Dwelling Coverage
Replacement Cost vs Actual Cash Value
Extended Replacement Cost
Personal Property Coverage
Coverage Limits and Categories
Scheduled Personal Property Endorsement
Liability Protection
Personal Liability Coverage
Medical Payments to Others
Additional Living Expenses
Coverage for Temporary Relocation
Loss of Rental Income
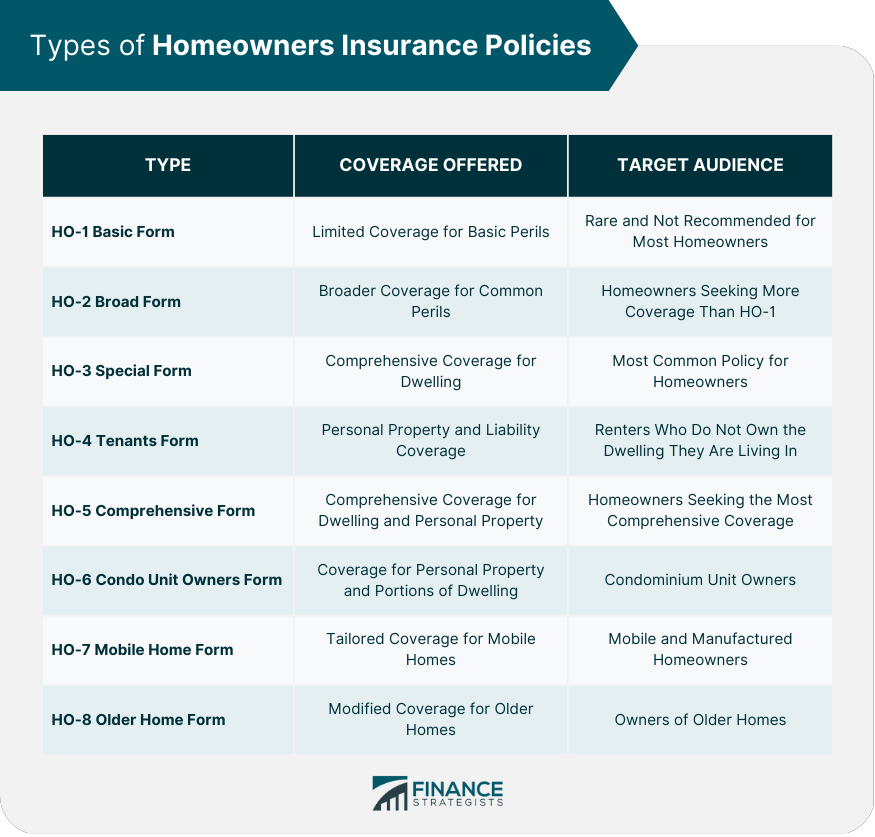
Types of Homeowners Insurance Policies
HO-1: Basic Form
HO-2: Broad Form
HO-3: Special Form
HO-4: Tenants Form (Renters Insurance)
HO-5: Comprehensive Form
HO-6: Condo Unit Owners Form
HO-7: Mobile Home Form
HO-8: Older Home Form
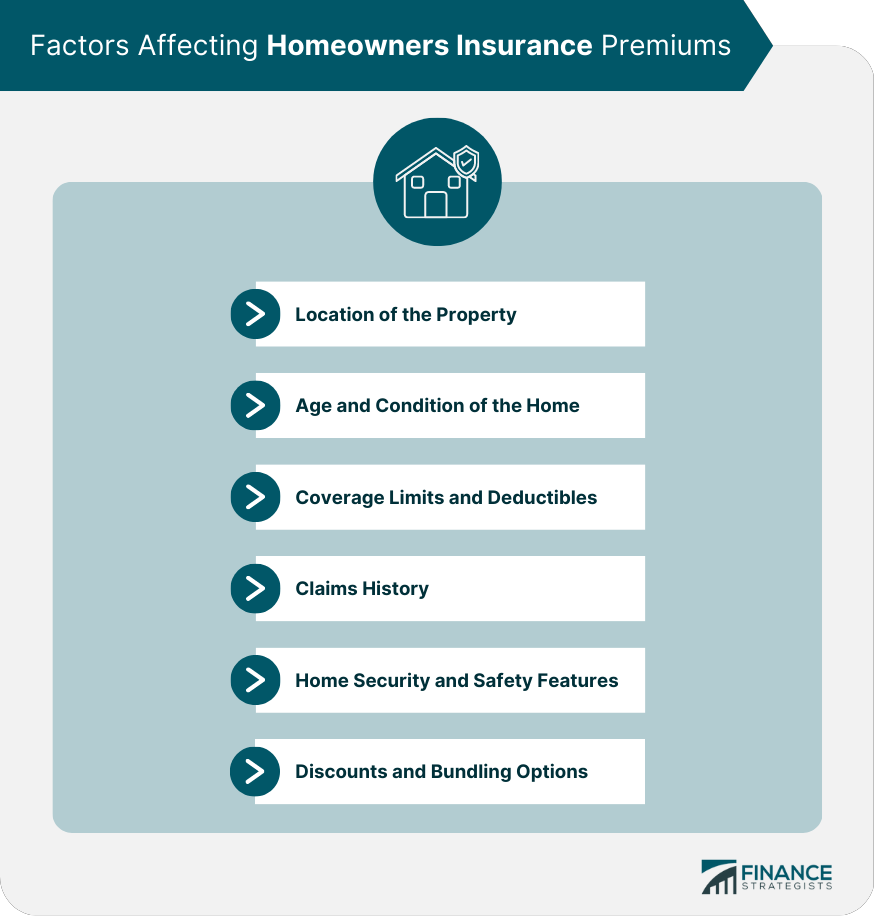
Factors Affecting Homeowners Insurance Premiums
Location of the Property
Age and Condition of the Home
Coverage Limits and Deductibles
Claims History
Home Security and Safety Features
Discounts and Bundling Options
How to Choose a Homeowners Insurance Policy
Assessing Personal Needs and Risks
Comparing Coverage Options
Evaluating Insurance Companies
Financial Strength
Customer Service
Claims Handling
Shopping for the Best Rates
Filing a Homeowners Insurance Claim
Steps to File a Claim
Documenting Damage and Losses
Working With an Insurance Adjuster
Maximizing the Claim Payout
Dispute Resolution Options
Conclusion
Homeowners Insurance FAQs
Homeowners insurance is a type of insurance policy that provides financial protection for your home and personal property. It typically covers damage or loss caused by specific perils such as fire, theft, and weather-related events like windstorms and hail. It may also provide liability coverage if someone is injured on your property.
Even if you own your home outright, it's still a good idea to have homeowners insurance to protect your investment. Homeowners insurance can cover the cost of repairs or rebuilding your home if it's damaged or destroyed, as well as protect your personal belongings.
Several factors can impact the cost of homeowners insurance, including the age and condition of your home, its location, the materials used to build it, and the level of coverage you choose. Additionally, your credit score, claims history, and deductible amount can also affect your premiums.
Yes, you can make changes to your homeowners insurance policy mid-term. For example, you might want to increase or decrease your coverage, add an endorsement, or change your deductible. However, making changes mid-term can result in a prorated refund or additional premium payment.
If you need to file a homeowners insurance claim, the first step is to contact your insurance company or agent. They'll guide you through the claims process, which typically involves providing documentation and evidence of the damage or loss, such as photos or receipts. Be sure to keep all receipts and documents related to the claim, and follow up with your insurance company if you have any questions or concerns.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











