Reinsurance ceded refers to the process where an insurance company transfers a portion of its risk to another insurer or reinsurer through a reinsurance agreement. By ceding risk, the primary insurer reduces its exposure to potential losses and spreads the risk across multiple entities. The reinsurer assumes a portion of the primary insurer's liabilities and agrees to compensate them for covered claims. Reinsurance ceded allows insurance companies to manage their capital, stabilize their financial position, and protect against catastrophic losses. It plays a crucial role in the insurance industry by providing additional capacity and support to insurers, enabling them to underwrite policies with confidence. There are two main types of reinsurance ceded: proportional and non-proportional. In proportional reinsurance ceded, the ceding company and the reinsurer agree to share risks and premiums on a predetermined percentage basis. This type of reinsurance allows for a more predictable distribution of risks and rewards between the parties involved. In non-proportional reinsurance ceded, the reinsurer only assumes responsibility for risks exceeding a specified threshold or attachment point. This type of reinsurance is less predictable, as the reinsurer's liability depends on the severity and frequency of claims made. The process of reinsurance ceded involves two parties: the ceding company and the reinsurer. The ceding company transfers a portion of its risks to the reinsurer in exchange for a share of the insurance premiums. This allows the ceding company to reduce its overall risk exposure and maintain stable financial performance. The reinsurer assumes the risks transferred by the ceding company and collects a share of the insurance premiums. This allows the reinsurer to diversify its risk portfolio and generate additional revenue. Reinsurance ceded plays a crucial role in managing the risks associated with insurance policies. One of the primary functions of reinsurance ceded is to transfer risk from the ceding company to the reinsurer. This transfer allows the ceding company to reduce its overall risk exposure, which can help stabilize its financial performance and protect it from large, unexpected losses. Reinsurance ceded also enables both the ceding company and the reinsurer to diversify and reduce their risk exposure. By ceding a portion of its risks, the ceding company can maintain a more balanced risk portfolio, while the reinsurer can spread its risks across multiple ceding companies and types of insurance. By transferring risks to a reinsurer, a ceding company can maintain more predictable financial results. This stability can help the ceding company meet regulatory requirements, maintain its credit rating, and attract investors. Reinsurance ceded allows ceding companies to increase their underwriting capacity. By reducing their overall risk exposure, ceding companies can underwrite more policies without exceeding their risk tolerance. Reinsurance ceded has a significant impact on the primary insurance market and the insurance industry as a whole. Reinsurance ceded enables primary insurers to offer coverage for more significant risks and provide more comprehensive policies to their clients. This increased capacity can lead to more competitive pricing and a broader range of insurance products for consumers. Several trends and developments in the reinsurance industry have shaped the practice of reinsurance ceded. These include the growth of alternative risk transfer mechanisms, such as Insurance-Linked Securities (ILS) and catastrophe bonds, which provide additional capacity for reinsurers. Additionally, advancements in technology and data analytics have improved the modeling and understanding of risks, leading to more accurate pricing and better risk management. Regulatory frameworks for reinsurance ceded vary across jurisdictions, but some key regulatory initiatives include: Solvency II a European Union directive that regulates the capital requirements and risk management practices of insurance and reinsurance companies. It aims to ensure that insurers have sufficient capital to cover their risks and promote financial stability in the industry. In the United States, the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) has developed a model law that establishes standards for the regulation of reinsurance ceded. This model law is designed to protect policyholders and ensure the financial stability of the insurance industry. Other countries have their regulatory frameworks for reinsurance ceded, which can vary significantly. These frameworks may include requirements for capital adequacy, risk management, and disclosure. When entering into a reinsurance ceded agreement, several factors should be considered by the ceding company. The financial strength of the reinsurer is essential, as it impacts their ability to pay claims and fulfill their obligations under the reinsurance agreement. Ceding companies should evaluate the pricing and contract terms offered by the reinsurer, including the level of risk transfer, the sharing of premiums, and the terms for handling claims. The ceding company should assess the reinsurer's claims management and administration capabilities to ensure that claims are processed efficiently and effectively. Regular monitoring of the performance of a reinsurance ceded agreement is crucial for both the ceding company and the reinsurer. KPIs can be established to measure the effectiveness of reinsurance ceded agreement, including loss ratios, risk-adjusted returns, and claims handling efficiency. Both parties should establish a regular reporting and review process to assess the performance of the reinsurance ceded agreement and make adjustments as needed. Reinsurance ceded is not without its challenges and criticisms. The practice of reinsurance ceded may create a moral hazard, as the ceding company may take on more significant risks than it would otherwise, knowing that the reinsurer will assume some of the losses. Reinsurance ceded can lead to concentration risk if multiple ceding companies transfer their risks to a single reinsurer, which may become overexposed to certain risks or market segments. Counterparty risk arises when one party in a reinsurance ceded agreement fails to fulfill its obligations. This risk can be mitigated through careful evaluation of the reinsurer's financial strength and diversification of the ceding company's reinsurance partners. Transparency and disclosure in reinsurance ceded agreements can be limited, as the specific terms of these agreements are often confidential. This lack of transparency may make it difficult for regulators and other stakeholders to assess the risks involved in these transactions and the overall financial health of the involved parties. Reinsurance ceded is a process where insurers transfer risk to reinsurers, reducing exposure and obtaining support for covered claims. It plays a crucial role in managing risks, allowing insurers to stabilize their financial position and protect against catastrophic losses. Proportional reinsurance ceded involves sharing risks and premiums based on predetermined percentages, while non-proportional reinsurance ceded covers risks exceeding a specified threshold. Reinsurers assume risks transferred by ceding companies, diversifying their portfolios, and generating additional revenue. Reinsurance ceded enhances risk management, stabilizes financial performance, and enhances underwriting capacity. It impacts the primary insurance market by enabling coverage for significant risks and driving industry trends. Regulatory frameworks like Solvency II and NAIC model law regulate reinsurance ceded. Evaluating reinsurer financial strength, pricing, and claims management is essential. Monitoring performance and addressing challenges like moral hazard, concentration risk, counterparty risk, and transparency issues are crucial for successful reinsurance ceded agreements.Definition of Reinsurance Ceded
Types of Reinsurance Ceded
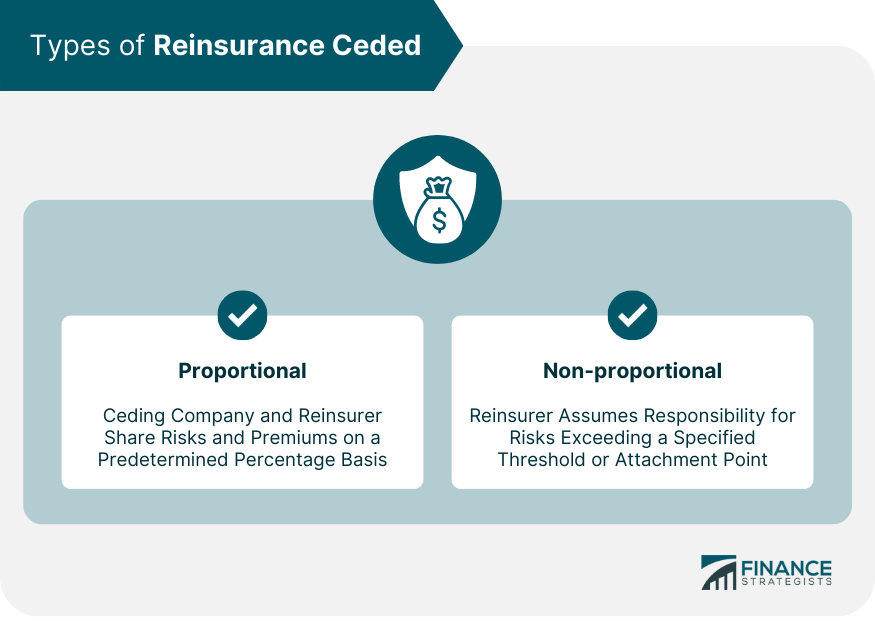
Proportional Reinsurance Ceded
Non-proportional Reinsurance Ceded
How Reinsurance Ceded Works
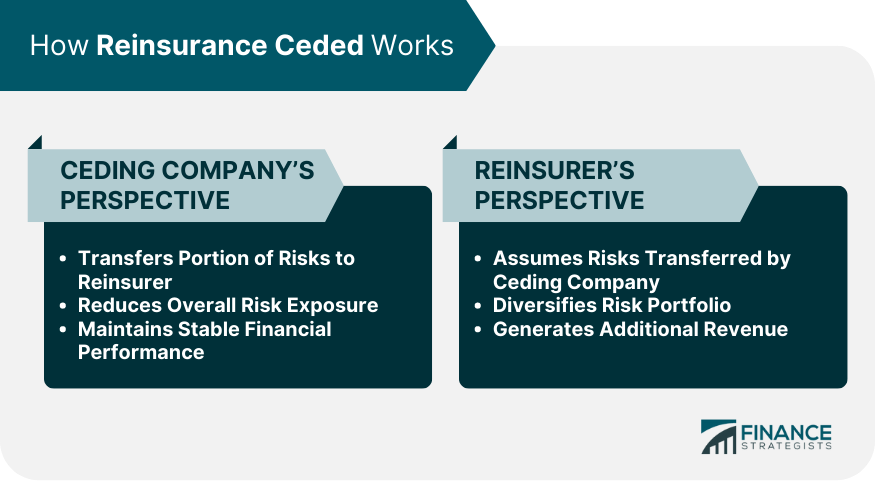
Ceding Company's Perspective
Reinsurer's Perspective
Role of Reinsurance Ceded in Risk Management
Risk Transfer in Reinsurance Ceded
Risk Diversification and Reduction
Stabilizing Financial Performance
Enhancing Capacity for Underwriting

Reinsurance Ceded and the Insurance Industry
Impact on the Primary Insurance Market
Industry Trends and Developments in Reinsurance Ceded
Regulation of Reinsurance Ceded
Solvency II
NAIC Model Law
Other Regulatory Frameworks
Evaluating Reinsurance Ceded Agreements
Factors to Consider in Ceding Insurance
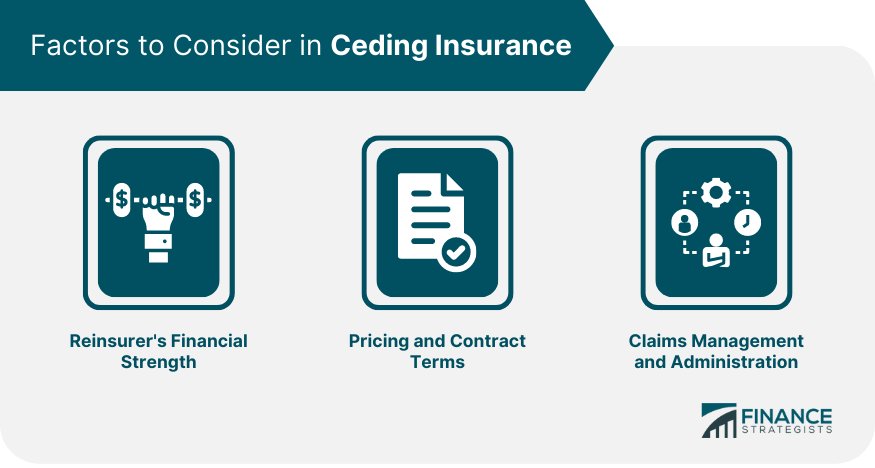
Reinsurer's Financial Strength
Pricing and Contract Terms
Claims Management and Administration
Monitoring Reinsurance Ceded Performance
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Regular Reporting and Reviews
Challenges and Criticisms of Reinsurance Ceded

Potential for Moral Hazard
Concerns About Concentration Risk
Counterparty Risk in Reinsurance Ceded
Transparency and Disclosure Issues
Bottom Line
Reinsurance Ceded FAQs
Reinsurance Ceded is the process where a ceding company transfers a portion of its insurance policies or risks to a reinsurer to reduce its overall risk exposure. It plays a crucial role in risk management, stabilizing financial performance, and enhancing underwriting capacity for insurance companies, ultimately benefiting both insurers and consumers.
There are two main types of Reinsurance Ceded: proportional and non-proportional. Proportional reinsurance ceded involves sharing risks and premiums on a predetermined percentage basis, while non-proportional reinsurance ceded requires the reinsurer to assume responsibility for risks exceeding a specified threshold or attachment point.
Reinsurance Ceded helps manage risks by transferring a portion of the ceding company's risks to the reinsurer. This risk transfer reduces the ceding company's overall risk exposure, promotes risk diversification and reduction, stabilizes financial performance, and enhances the capacity for underwriting, ultimately benefiting the entire insurance industry.
Some challenges and criticisms of Reinsurance Ceded include the potential for moral hazard, concerns about concentration risk, counterparty risk, and transparency and disclosure issues. These challenges can be mitigated through careful evaluation and monitoring of reinsurance ceded agreements and adherence to regulatory requirements.
Insurance companies can evaluate Reinsurance Ceded agreements by considering factors such as the reinsurer's financial strength, pricing, contract terms, and claims management and administration capabilities. Regular monitoring can be achieved through the establishment of key performance indicators (KPIs) and a reporting and review process, ensuring the effectiveness of the reinsurance ceded agreement and making adjustments as needed.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











