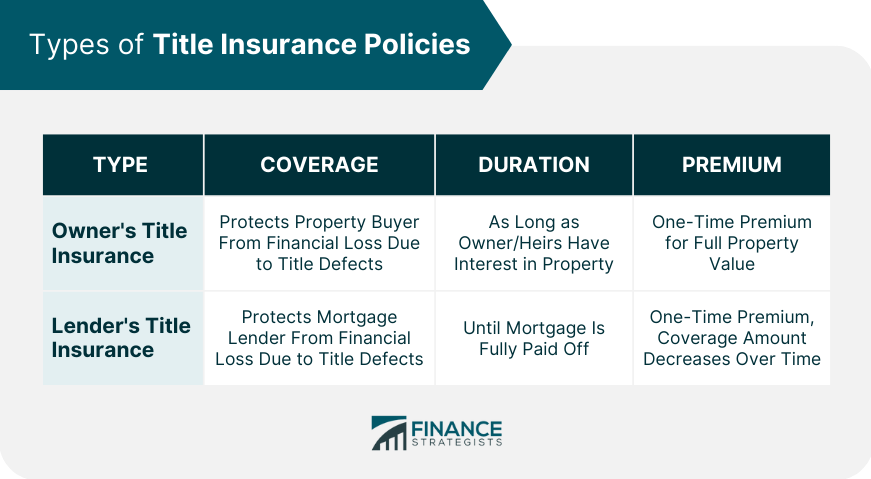
Title insurance is a unique form of indemnity insurance that protects property owners and lenders against financial loss due to defects in a property's title. It ensures that the title being transferred is free from any encumbrances, liens, or other issues that might impact the owner's rights to the property. The primary purpose of title insurance is to provide peace of mind to property buyers and lenders by guaranteeing that the title is clear and marketable. It helps avoid costly and time-consuming legal battles that can arise from disputes over property ownership or other issues related to the title. Title insurance plays a critical role in real estate transactions by ensuring the legitimacy of the property's title. It helps buyers avoid potential legal and financial problems that can arise from undiscovered title defects or claims. Lenders also require title insurance as a condition for issuing mortgages. This protects the lender's investment by ensuring the property's title is clear, which in turn protects the buyer and enhances the overall integrity of the real estate market. An owner's title insurance policy protects the property buyer from financial losses due to title defects. It covers issues like unpaid liens, fraud, or errors in public records that might affect the owner's rights to the property. Owner's title insurance is typically purchased at the time of closing and lasts for as long as the owner or their heirs maintain an interest in the property. It is a one-time premium that provides coverage for the full value of the property, with limitations and exclusions specified in the policy. Lender's title insurance, on the other hand, protects the mortgage lender from financial losses due to title defects. It ensures the lender's security interest in the property is valid and enforceable, safeguarding their investment. Like owner's title insurance, lender's title insurance is purchased at closing and paid as a one-time premium. However, the coverage amount typically corresponds to the outstanding mortgage balance and decreases over time as the loan is repaid. The policy remains in effect until the mortgage is fully paid off. Title companies play a crucial role in the title search and examination process. They research the property's history, review public records, and identify any potential title issues that might affect the property's ownership. The title company's main responsibility is to ensure that the property's title is clear and marketable. This involves conducting a thorough title search, preparing a title commitment or preliminary report, and ultimately issuing the title insurance policy. The title search process involves a detailed review of public records and documents related to the property. This includes land records, deeds, mortgages, liens, judgments, and other relevant information that might impact the property's title. By examining these records, title companies can identify potential title issues, such as unpaid liens, errors in public records, or disputes over property boundaries. This information is used to create a title commitment or preliminary report, which outlines any defects or concerns that need to be addressed before the property can be transferred. Liens and encumbrances are common title issues that can affect property ownership. A lien is a legal claim against a property, usually resulting from unpaid debts or taxes. Encumbrances, on the other hand, are restrictions or limitations on a property's use, such as easements or building restrictions. Both liens and encumbrances can impact the property's marketability and create financial liabilities for the owner. Title insurance helps protect the property owner and lender from these potential issues by ensuring that any existing liens or encumbrances are resolved before the property is transferred. This helps prevent future disputes and legal battles that might arise from unresolved claims against the property. Errors in public records are another common title issue that can have serious consequences for property owners. These errors can include inaccuracies in property descriptions, incorrect legal descriptions, or mistakes in recording deeds and other documents. Title insurance protects property owners from financial losses resulting from these errors by covering the cost of correcting them. This ensures that the property's title is clear and accurate, which in turn helps maintain the integrity of the real estate market and protect property owners' rights. Boundary disputes can occur when property owners have conflicting claims over the location of property lines or boundaries. These disputes can be the result of inaccurate surveys, errors in public records, or disagreements over historic property lines. Title insurance can help property owners address and resolve boundary disputes by covering the costs associated with legal representation, negotiation, and, if necessary, litigation. This provides peace of mind to property owners, ensuring their property rights are protected and potential disputes are resolved. Fraudulent activity and forgeries are also potential title issues that can have serious consequences for property owners. Examples include forged deeds, fraudulent transfers, and identity theft. Title insurance helps protect property owners from the financial losses associated with fraudulent activity and forgeries by providing coverage for the costs of rectifying these issues. This can include legal fees, court costs, and other expenses necessary to resolve disputes and clear the property's title. To clear liens and encumbrances, property owners or title companies must work with the relevant parties to resolve the outstanding issues. This can involve paying off debts, negotiating with lienholders, or obtaining releases for encumbrances. Title insurance can help cover the costs associated with clearing liens and encumbrances, ensuring that the property's title is clear and marketable. This is essential for maintaining the integrity of the real estate market and protecting property owners' rights. Correcting errors in public records is essential for ensuring the accuracy and validity of a property's title. This can involve working with local government agencies, such as the county recorder's office, to amend or update property records. Title insurance can help cover the costs associated with correcting errors in public records, providing peace of mind to property owners and lenders. This ensures that the property's title is clear and accurate, which in turn helps maintain the integrity of the real estate market. Addressing boundary disputes can involve negotiation, mediation, or litigation to resolve conflicting claims over property lines. This can be a complex and time-consuming process, often requiring the expertise of surveyors, attorneys, and other professionals. Title insurance can help cover the costs associated with addressing boundary disputes, providing protection for property owners and lenders. This ensures that property rights are protected and potential disputes are resolved, maintaining the integrity of the real estate market. Remedies for fraudulent activity and forgeries can involve legal action to rectify the issues and clear the property's title. This may include seeking court judgments, working with law enforcement, or engaging in negotiations with affected parties. Title insurance can help cover the costs associated with these remedies, providing protection for property owners and lenders from the financial losses associated with fraudulent activity and forgeries. This ensures that property rights are protected and potential disputes are resolved. Title insurance premiums can vary depending on several factors, including the property's value, location, the insurer's underwriting guidelines, and the level of coverage chosen. Additional factors may include the property's risk profile, which takes into account the historical likelihood of title issues or claims in the area. While title insurance premiums can vary from one policy to another, they generally represent a small percentage of the property's value. This makes title insurance a relatively affordable investment in the long-term security of property ownership. Unlike other types of insurance, title insurance premiums are typically paid as a one-time fee at closing. This means there are no ongoing or recurring payments to maintain the policy, making title insurance a cost-effective option for property owners and lenders. The one-time premium provides coverage for the entire duration of the policy, which lasts as long as the owner or their heirs maintain an interest in the property (for owner's title insurance) or until the mortgage is fully paid off (for lender's title insurance). Title insurance differs from other types of insurance, such as homeowners or auto insurance, in several ways. First, it covers past events, specifically title issues that may have arisen before the property was purchased, while other types of insurance cover future events. Second, title insurance premiums are paid as a one-time fee, while other insurance policies typically require ongoing or recurring payments. Despite these differences, title insurance is an important part of a comprehensive insurance strategy for property owners and lenders, providing essential protection against potential financial losses due to title defects or claims. When choosing a title insurance company, there are several factors to consider. These include the company's reputation, financial stability, the level of coverage offered, and the cost of the policy. It's also important to consider the quality of the title search and examination process, as well as the company's customer service and responsiveness to claims. In addition, it's essential to ensure that the title insurance company is licensed to operate in your state, as licensing requirements can vary by jurisdiction. Comparing title insurance providers is an important step in the process of selecting a policy. This involves researching and evaluating different companies based on factors such as reputation, coverage options, and pricing. Consumers can seek recommendations from real estate professionals, lenders, or friends and family who have recently purchased property. Additionally, online reviews and ratings can provide valuable insights into the experiences of other property owners with specific title insurance companies. When purchasing title insurance, consumers have certain rights and responsibilities. These include the right to choose their title insurance provider, to review the title commitment or preliminary report, and to ask questions about the policy's terms and conditions. Consumers also have a responsibility to be informed about the title insurance process and to understand the coverage offered by their policy. This includes being aware of any limitations or exclusions, as well as knowing the steps to take in the event of a title issue or claim. Title insurance is a critical component of real estate transactions, providing essential protection for property owners and lenders against potential financial losses due to title defects or claims. By ensuring the legitimacy of a property's title, title insurance helps maintain the integrity of the real estate market and safeguards the rights of property owners. While title insurance involves some potential risks, such as the limitations and exclusions of a policy, the benefits far outweigh these concerns. Title insurance provides peace of mind to property owners and lenders, ensuring that their property rights are protected and that potential disputes are resolved efficiently.What Is Title Insurance?
Types of Title Insurance Policies
Owner's Title Insurance
Lender's Title Insurance
Title Search and Examination Process
Role of Title Companies
Public Records and Document Review
Common Title Issues and Defects
Liens and Encumbrances
Errors in Public Records
Boundary Disputes
Fraudulent Activity and Forgeries
Resolving Title Issues
Clearing Liens and Encumbrances
Correcting Errors in Public Records
Addressing Boundary Disputes
Remedies for Fraudulent Activity and Forgeries
Title Insurance Premiums and Costs
Factors Influencing Premiums
One-time vs Recurring Fees
Comparison With Other Types of Insurance
Choosing a Title Insurance Company
Factors to Consider
Comparing Providers
Consumer Rights and Responsibilities
Conclusion
Title Insurance FAQs
Title insurance is a type of insurance that protects homeowners and lenders from financial loss due to problems with the title to the property.
Title insurance protects you from financial loss in case of any problems with the title to your property that may arise after you purchase it.
There are two types of title insurance: owner's title insurance, which protects the homeowner, and lender's title insurance, which protects the mortgage lender.
A title examination is conducted by a title company or attorney to determine if there are any liens, claims, or other issues with the title that could affect ownership.
Common issues covered by title insurance include fraudulent title claims, undiscovered liens, and errors in public records or surveys that could affect the title to your property.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











