War damage insurance is a policy that safeguards individuals and businesses against the devastating effects of war-related destruction. It offers financial protection in times of turmoil and conflict, ensuring that affected parties can recover and rebuild their lives and properties. This form of insurance recognizes the unpredictable nature of warfare and its potential to inflict substantial harm. By providing coverage for damages resulting from armed conflicts, including bombings, looting, and vandalism, war damage insurance seeks to mitigate the financial burdens that arise in these dire circumstances. Its purpose is to offer peace of mind and a safety net amidst the chaos of war. Commercial war damage insurance is designed to protect businesses from the financial consequences of war-related events. This type of coverage typically includes property insurance and business interruption insurance. Property insurance provides coverage for damage to commercial buildings and their contents caused by war-related events, such as acts of war, terrorism, and civil unrest. This can include coverage for physical damage, theft, and vandalism. Business interruption insurance is designed to cover the loss of income and additional expenses resulting from the interruption of a business due to a war-related event. This type of coverage is essential for businesses that may be forced to temporarily cease operations or relocate due to war-related events. Personal war damage insurance is designed to protect individuals from the financial consequences of war-related events. This type of coverage typically includes homeowners insurance and renters insurance. Homeowners insurance provides coverage for damage to a person's home and personal property caused by war-related events, such as acts of war, terrorism, and civil unrest. This can include coverage for physical damage, theft, and vandalism. Renters insurance is similar to homeowners insurance but is designed specifically for individuals who rent their homes. This type of coverage provides protection for personal property and additional living expenses in the event of war-related events. Specialty war damage insurance is designed to cover unique risks associated with specific industries or assets. Examples of this type of coverage include aviation insurance and marine insurance. Aviation insurance provides coverage for aircraft and aviation-related risks, including war-related events that can result in damage to aircraft or liability arising from war-related events. Marine insurance covers vessels and cargo against the risks associated with war-related events, including damage to ships and cargo, as well as liability arising from war-related events. War damage insurance typically provides coverage for the following war-related events: Acts of War: This includes armed conflict between nations, military operations, and invasions. Terrorism: This refers to acts of violence committed for political, religious, or ideological reasons that are intended to create fear and coerce governments or societies. Insurrection and Civil Unrest: This includes riots, rebellions, and uprisings against established governments or social order. War damage insurance policies may exclude certain types of events or circumstances from coverage. Common exclusions include: Nuclear, Biological, and Chemical Warfare: Many policies specifically exclude damage caused by the use of nuclear, biological, or chemical weapons. Pre-existing Damage: Insurance policies generally do not cover damage that existed before the war-related event occurred. Acts of Sabotage: Some policies may exclude damage resulting from intentional acts of destruction carried out by individuals or groups for political or ideological reasons. War damage insurance policies typically have limits on the amount of coverage provided, as well as deductibles that must be paid before the insurance company will cover a loss. Policyholders should carefully review their coverage limits and deductibles to ensure they have adequate protection in the event of a war-related event. Several factors influence the cost of war damage insurance premiums. Some of the key factors include: Location and Geography: Areas with a higher likelihood of experiencing war-related events, such as regions with ongoing conflicts or geopolitical tensions, typically have higher premium rates. Type of Property: The nature of the property being insured, including its size, construction, and use, can influence premium rates. For example, commercial properties or properties with higher replacement costs may have higher premiums. Historical War Risk: The historical occurrence of war-related events in a region can also impact premium rates. Areas with a history of war-related events are often seen as higher-risk, resulting in higher premiums. There are several strategies policyholders can use to lower their war damage insurance premiums: Risk Mitigation Strategies: Implementing security measures, such as surveillance systems, access controls, and emergency response plans, can help reduce the risk of war-related events and potentially lower premiums. Bundling Policies: Combining war damage insurance with other insurance policies, such as property insurance or business interruption insurance, may result in discounted premiums. Negotiating With Insurers: Working with an experienced insurance broker or agent can help policyholders negotiate better coverage terms and premium rates. When a war-related event results in a loss, policyholders must promptly report the claim to their insurance company. This typically involves: Documentation: Gathering evidence of the damage, such as photographs, videos, and written descriptions, is crucial for supporting the claim. Claim Filing Deadlines: Insurance policies often have strict deadlines for reporting claims, so policyholders should be aware of these requirements to ensure their claim is processed in a timely manner. After a claim has been reported, the insurance company will typically conduct a loss assessment, which may involve: Inspections: An insurance adjuster or other professional may visit the property to inspect the damage and determine the cause. Damage Estimates: The insurance company will estimate the cost of repairing or replacing the damaged property, based on the policy's coverage limits and deductibles. Once the loss assessment is complete, the insurance company will determine the claim settlement, which may involve: Actual Cash Value vs Replacement Cost: Depending on the policy, the insurance company may pay the actual cash value (depreciated value) or replacement cost (full cost of repairing or replacing the damaged property) of the loss. Deductibles and Co-insurance: Policyholders may be responsible for paying a deductible or co-insurance amount before the insurance company covers the remaining loss. Dispute Resolution: If the policyholder disagrees with the insurance company's settlement offer, they may have the option to enter into a dispute resolution process, such as mediation or arbitration. War damage insurance is subject to various international laws and treaties that govern the insurance industry, such as the International Convention on War Damage Insurance and the Geneva Conventions. These agreements aim to protect policyholders and ensure fair treatment in the event of a war-related event. Some countries offer government-sponsored war risk insurance programs to supplement or replace private insurance coverage. These programs typically provide coverage for specific industries or types of risks that may be difficult to insure in the private market. War damage insurance providers must comply with local insurance regulations, which can vary by country or jurisdiction. Policyholders should ensure their insurance provider is properly licensed and compliant with applicable regulations to avoid potential coverage disputes or legal issues. War damage insurance protects against war-related destruction. Types include commercial property insurance, business interruption insurance, homeowners insurance, renters insurance, aviation insurance, and marine insurance. Coverage includes acts of war, terrorism, and civil unrest. Exclusions may apply for nuclear, biological, and chemical warfare, pre-existing damage, and acts of sabotage. Pricing factors include location, type of property, and historical war risk. Premiums can be reduced through risk mitigation strategies, policy bundling, and negotiating with insurers. The claims process involves reporting the claim, conducting a loss assessment, and settling the claim. Legal aspects include international laws, government-sponsored programs, and compliance with local regulations. To ensure comprehensive coverage and financial security in the face of war-related events, it is highly recommended to seek the guidance of professional insurance brokers or agents who can help navigate the complex world of war damage insurance.Definition of War Damage Insurance
Types of War Damage Insurance
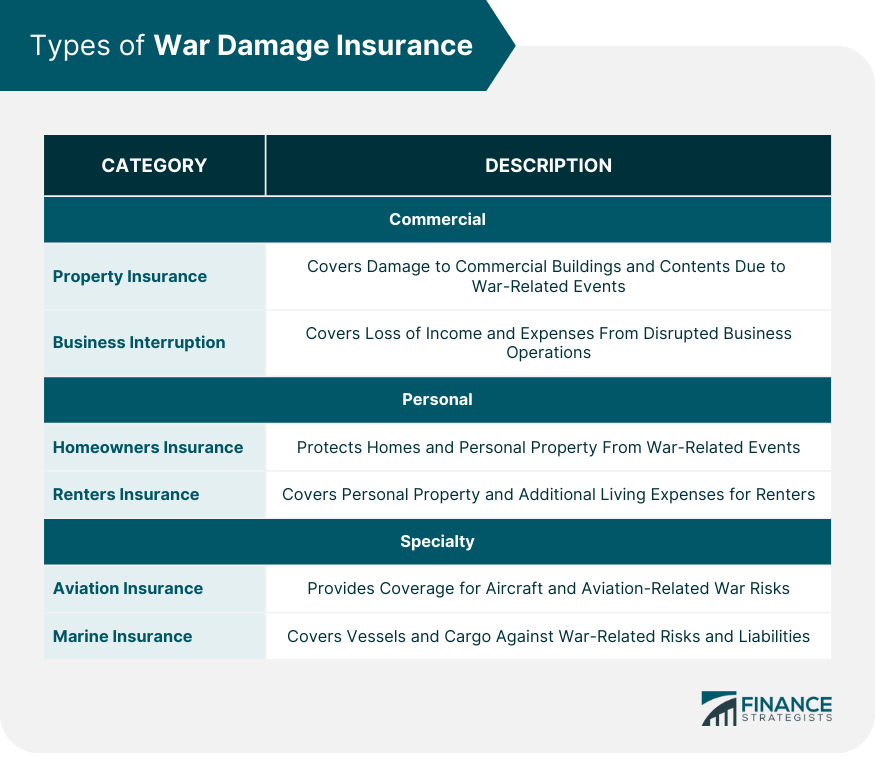
Commercial War Damage Insurance
Property Insurance
Business Interruption Insurance
Personal War Damage Insurance
Homeowners Insurance
Renters Insurance
Specialty War Damage Insurance
Aviation Insurance
Marine Insurance
War Damage Insurance Coverage
Covered Perils
Exclusions
Policy Limits and Deductibles
War Damage Insurance Pricing
Factors Influencing Premium Rates

How to Reduce Premiums

Claims Process for War Damage Insurance
Reporting a Claim
Loss Assessment
Claim Settlement
Legal and Regulatory Aspects of War Damage Insurance
International Laws and Treaties
Government-Sponsored War Risk Insurance Programs
Compliance With Local Regulations
Bottom Line
War Damage Insurance FAQs
War Damage Insurance is a specialized type of coverage designed to protect businesses, individuals, and organizations from the financial consequences of war-related events, such as acts of war, terrorism, and civil unrest. It is important because it helps mitigate the financial impact of these events, fostering global stability and promoting economic recovery after conflicts.
The main types of War Damage Insurance include commercial war damage insurance (property insurance and business interruption insurance), personal war damage insurance (homeowners insurance and renters insurance), and specialty war damage insurance (aviation insurance and marine insurance).
War Damage Insurance generally covers acts of war, terrorism, and insurrection or civil unrest. However, policies may exclude specific events or circumstances, such as nuclear, biological, and chemical warfare, pre-existing damage, or acts of sabotage.
The cost of War Damage Insurance is influenced by factors such as location and geography, type of property, and historical war risk. Implementing risk mitigation strategies, bundling policies, and negotiating with insurers can help reduce premium rates.
The claims process for War Damage Insurance involves reporting the claim (with documentation and adhering to filing deadlines), loss assessment (including inspections and damage estimates), and claim settlement (considering actual cash value vs. replacement cost, deductibles, co-insurance, and dispute resolution).
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











