Weather insurance is a specialized form of insurance that provides coverage against losses incurred due to unexpected and adverse weather conditions. The insurance policy pays out when pre-agreed weather parameters, such as a certain level of rainfall or temperature thresholds, are met or exceeded. Unlike traditional insurance, there is no need to prove any physical damage to claim the insurance, making the process significantly straightforward. The main purpose of weather insurance is to mitigate the financial uncertainties and risks associated with unpredictable weather fluctuations. This form of insurance is particularly beneficial to industries heavily reliant on weather, such as agriculture, energy production, and event management. As the impacts of climate change intensify, weather insurance is becoming an increasingly crucial tool for financial risk management. The advent of weather insurance can be traced back to the late 19th century when crop insurance was introduced to shield farmers from the financial impacts of unpredictable weather. Over the years, the scope and sophistication of weather insurance have evolved significantly. Today, it caters to a variety of industries, from construction to retail, demonstrating its vital role in managing weather-related financial risks. Weather insurance operates on the principle of indemnifying policyholders based on specific, predetermined weather parameters or triggers, not on demonstrated losses or damages. These parameters can include a variety of measurable weather conditions, such as rainfall amount, temperature, wind speed, or snowfall. For instance, an event organizer might take out insurance against a certain level of rainfall occurring on the day of an outdoor concert. If the specified level of rainfall occurs, the policy is triggered, and the insurer pays out the agreed sum, regardless of whether the event is canceled or not. There's no need to demonstrate physical loss or financial damage, making the claims process quicker and simpler. This proactive approach helps policyholders manage weather-related financial risks effectively, providing stability and peace of mind. Event cancellation insurance provides protection against financial loss due to the cancellation, interruption, or rescheduling of an event due to adverse weather conditions. It is commonly used in industries such as entertainment, sports, and hospitality. This type of insurance safeguards businesses against revenue losses resulting from weather-related disruptions. For instance, a ski resort might take out revenue protection insurance to cover losses if the winter season sees less snowfall than expected. Weather derivatives are financial instruments used by companies to hedge against the risk of weather-related losses. They are typically used by energy companies, which can suffer significant revenue losses due to weather fluctuations. This insurance is designed to protect farmers and agricultural businesses from losses due to adverse weather conditions that affect crop production, such as drought, excessive rainfall, or frost. This insurance is designed to cover the energy industry, compensating for financial losses when weather conditions interrupt energy production, like a lack of wind for wind farms or a lack of sunshine for solar power plants. A weather insurance policy is structured around specific weather parameters and triggers. These parameters, such as rainfall levels or temperature thresholds, define the conditions under which a policy will pay out. Payouts or indemnities refer to the sum insured or the amount of money the insurer agrees to pay when the policy is triggered. The policyholder and insurer agree upon the payout amount when the policy is purchased. Premiums are the cost of purchasing the insurance policy. They are generally calculated based on the risk assessment of the weather event covered and the potential payout amount. Exclusions are conditions or circumstances under which the policy won't pay out. For instance, a policy might exclude certain severe weather events like hurricanes or floods. Policyholders need to understand these exclusions thoroughly. The first step in purchasing weather insurance involves a comprehensive risk assessment, determining the potential financial impact of various weather events on the business or individual. Choosing the right provider involves researching and comparing different insurance companies offerings, considering factors like coverage options, premium rates, customer service, and claims handling process. Once a provider is chosen, the policy terms, including the weather parameters, payout amount, and premium, are negotiated and finalized in the contract. Weather data used in weather insurance primarily comes from official meteorological sources, like the National Weather Service in the U.S., supplemented by data from private weather data providers and satellite data. Insurers use advanced statistical and machine learning algorithms to analyze historical weather data and predict future weather patterns. These insights are essential for accurately pricing premiums and understanding potential risks. Climate change is causing increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. This has a direct impact on whether insurance, necessitating adjustments in risk assessment models, premium calculations, and policy terms. Weather insurance is subject to regulations by national and state insurance regulatory bodies. These authorities oversee policy terms, premium rates, and claims practices, ensuring fairness and transparency. It's crucial to understand the legal aspects of weather insurance contracts, like the legal obligations of policyholders and insurers, dispute resolution mechanisms, and policy termination conditions. Regulatory trends in the insurance industry, such as digital transformation mandates, transparency requirements, and climate change considerations, significantly influence the design and delivery of weather insurance products. Weather insurance is an essential tool for financial risk management in the face of increasingly unpredictable weather patterns. This specialized insurance provides coverage across various industries, including agriculture, energy production, and event management. It pays out claims according to predetermined weather conditions. With a broad spectrum of types like event cancellation, revenue protection, weather derivatives and hedges, crop weather insurance, and energy production interruption insurance, it offers protection suited to specific needs. Essential components of such policies include parameters, triggers, payouts, premiums, and exclusions. Purchasing such insurance involves risk assessment, provider selection, and contract finalization. Weather data forms the bedrock of this sector, with climate change playing a critical role. Governed by laws and regulations, the weather insurance market, currently experiencing growth, is set to evolve further with technological advancements, though it must also tackle climate change-induced challenges.What Is Weather Insurance?
Historical Background
How Weather Insurance Works
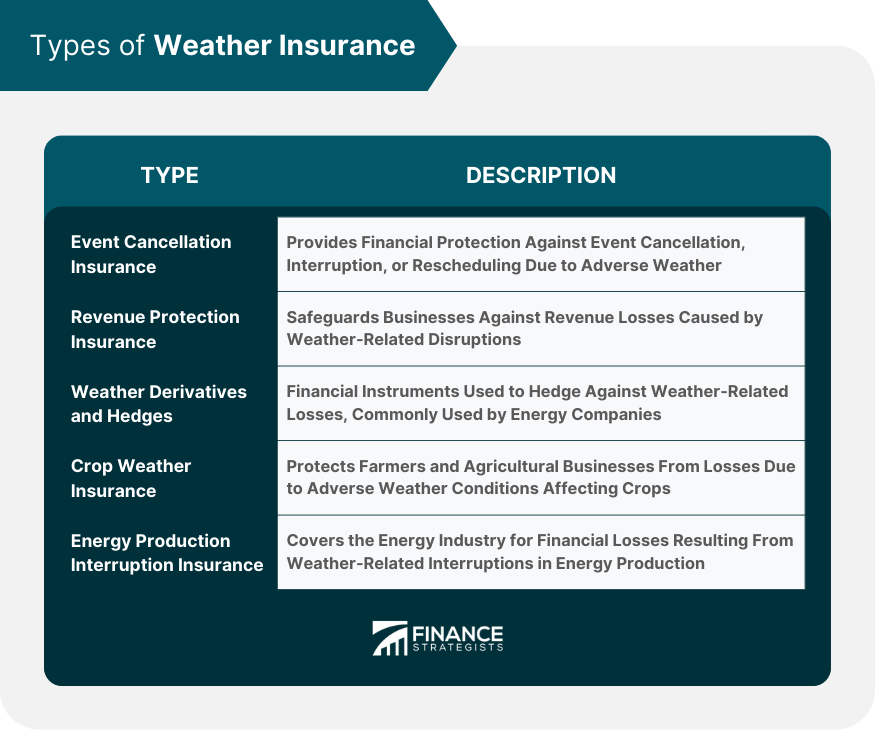
Types of Weather Insurance
Event Cancellation Insurance
Revenue Protection Insurance
Weather Derivatives and Hedges
Crop Weather Insurance
Energy Production Interruption Insurance
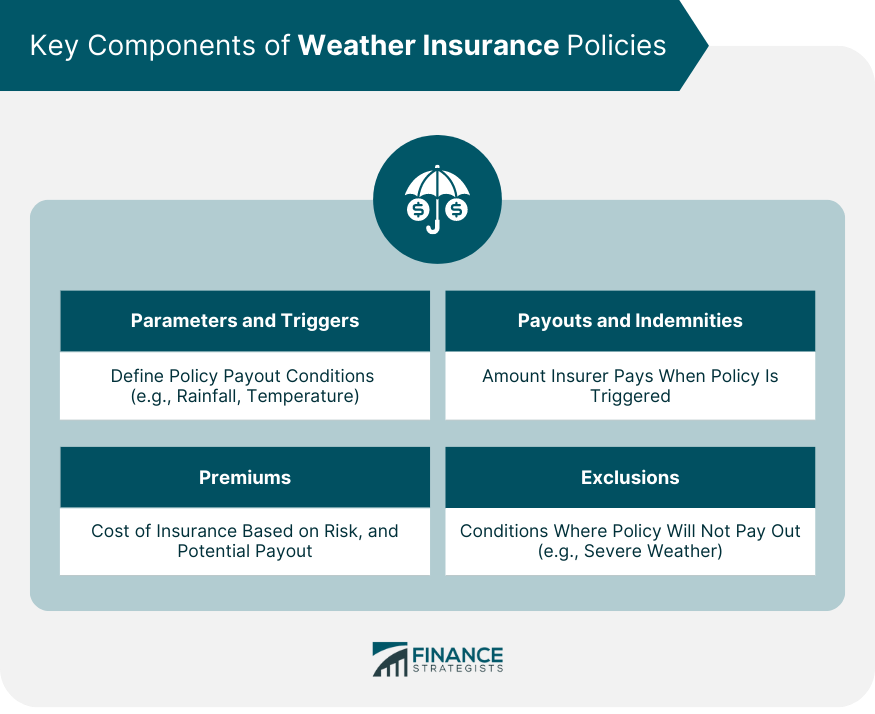
Key Components of Weather Insurance Policies
Parameters and Triggers
Payouts and Indemnities
Premiums
Exclusions
Process of Purchasing Weather Insurance
Risk Assessment
Selecting an Insurance Provider
Contract Negotiation and Finalization

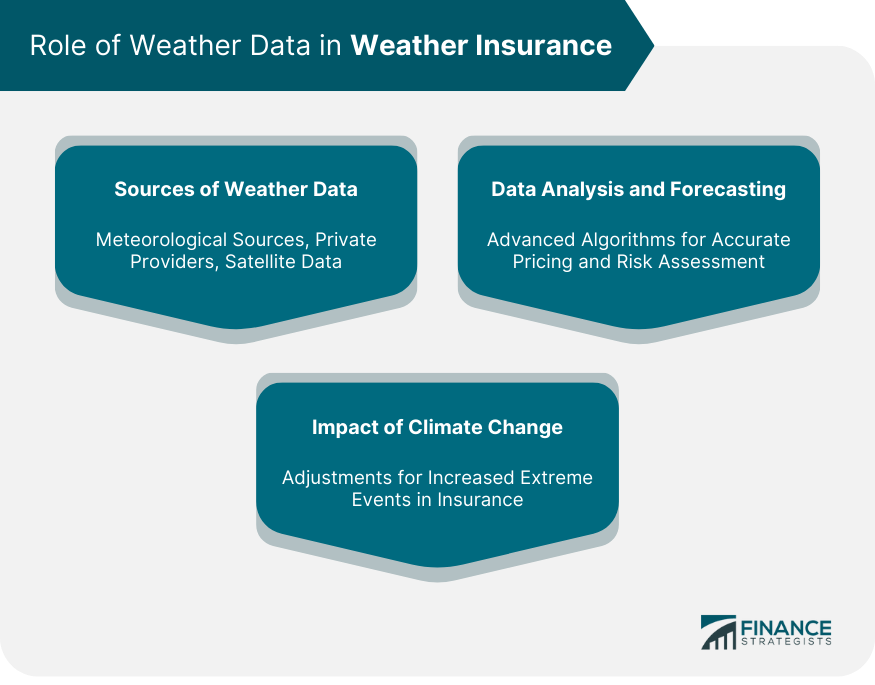
Role of Weather Data in Weather Insurance
Sources of Weather Data
Data Analysis and Forecasting
Impact of Climate Change on Weather Insurance
Regulatory Environment and Legal Aspects
Laws and Regulations Governing Weather Insurance
Legal Considerations in Policy Enforcement
Regulatory Changes and Trends
Final Thoughts
Weather Insurance FAQs
Weather insurance is a specialized insurance product that offers financial protection against losses resulting from adverse weather conditions. It is important because it mitigates the financial risks associated with weather fluctuations, ensuring operational continuity for businesses and financial protection for individuals, especially in the face of increasing climate change impacts.
There are several types of weather insurance, including event cancellation insurance, revenue protection insurance, weather derivatives and hedges, crop weather insurance, and energy production interruption insurance. These insurance types cater to various sectors heavily influenced by weather conditions.
Weather insurance operates based on specific, pre-agreed weather parameters or triggers, such as a certain amount of rainfall or temperature thresholds. If these parameters are met or exceeded, the policy pays out. There's no need to prove any physical loss or damage, which simplifies the claims process.
Weather data is pivotal to weather insurance. It is used for risk assessment, policy pricing, and claims validation. Insurers rely on official meteorological data, private weather data providers, and satellite data. Advanced data analysis and forecasting techniques are employed to understand potential risks and price policies accurately. Climate change, influencing weather patterns, directly impacts weather insurance.
The weather insurance market is expected to evolve with advancements in predictive analytics, artificial intelligence, and IoT devices for weather monitoring. However, it will also face challenges with the increased unpredictability of weather events due to climate change. It will necessitate continuous adaptation to stay relevant and effective.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











