Fannie Mae, formally known as the Federal National Mortgage Association, serves as a cornerstone in the U.S. housing finance system. Founded in 1938, this government-sponsored enterprise plays a pivotal role in facilitating homeownership and affordable rental housing. By buying mortgages from lenders and either holding them or securitizing them, Fannie Mae ensures that lenders have the liquidity to offer more mortgages to consumers. This mechanism has created a ripple effect, promoting the availability and affordability of mortgages throughout the country. Conforming loan limits, defining the maximum mortgage Fannie Mae can handle, balance promoting homeownership with risk mitigation. Compliance with these limits ensures mortgage market fluidity and competitive rates, underpinning a consistent supply of cost-effective financing. A conforming loan limit represents the highest mortgage amount that Fannie Mae (or its counterpart, Freddie Mac) can purchase. If a loan exceeds this limit, it's designated as a jumbo loan and isn't eligible for purchase by these government-sponsored entities. Conforming limits help standardize the home-buying process and protect the financial system from extreme volatility by capping exposure. Moreover, these limits ensure that large, riskier loans do not dominate the market, thereby maintaining financial stability. The Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA) establishes Fannie Mae's loan limits for 2024, defining the maximum conventional loans that Fannie Mae can acquire. These conforming loan limit values come in two forms: baseline loan limits and high-cost area loan limits. Effective from January 1, 2024, the limits will rise, impacting whole loans delivered and mortgage loans delivered into Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) with pool issue dates. Let's first look at the baseline loan limits for 2024, which applies to the Contiguous States, District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, Alaska, Guam, Hawaii, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Source: Fannie Mae The high-cost area loan limits vary by county or equivalent areas and can be found on both Fannie Mae's and FHFA's websites. Source: Fannie Mae Interestingly, several states, including Alaska and Hawaii, as well as Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, will not have any high-cost areas in 2024. This demonstrates how regional variations in the housing market and economic conditions can impact these limits, reflecting the balance Fannie Mae strikes between promoting home ownership and managing financial risks. The Housing Price Index (HPI) directly affects the establishment of conforming loan limits. As an indicator of home price changes, when HPI rises, it generally signifies that home prices are increasing. Consequently, Fannie Mae might elevate the loan limits to ensure potential homeowners aren't priced out of the market. This adjustment is crucial to promote homeownership across different economic strata of society. Economic trends, including employment rates, GDP growth, and inflation, influence the health of the housing market. A robust economy often correlates with higher home prices, potentially prompting an elevation in loan limits. Conversely, a sluggish economy might temper any drastic increases. These factors are consistently monitored to ensure the conforming loan limits reflect current economic realities. Regulatory shifts, instigated by legislative or executive actions, can modify how conforming loan limits are set. Laws aimed at housing affordability or financial system stability can either raise or lower these limits, depending on the perceived needs of the market. This interaction between regulatory decisions and loan limits highlights the role of policymakers in shaping the housing finance landscape. Local real estate market trends, like increased demand in urban areas or suburban growth, can indirectly influence conforming loan limits. High demand in a region can escalate home prices, nudging Fannie Mae to reconsider its established caps in that locality. Understanding these trends can assist potential homeowners and lenders in anticipating possible changes in loan limits. The 2024 conforming loan limits have seen an increase compared to previous years. This hike is reflective of the robust housing market dynamics, signifying the health of the real estate sector and Fannie Mae's commitment to align its operations with evolving housing prices. The growth in these limits enhances the borrowing capacity for potential homeowners, ultimately promoting accessibility to homeownership. Historically, Fannie Mae has recognized the variances in housing costs across different regions, leading to the implementation of high-cost area limits. The 2024 figures have also witnessed an escalation from their predecessors, particularly in the contiguous states, District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico. This progression is indicative of increasing real estate prices in these areas, demonstrating Fannie Mae's responsiveness to regional housing market trends. Over the years, the loan limit adjustments for two-to-four unit properties have been responsive to the demand and prices in the multi-unit property market. The 2024 numbers further this trend, marking an increase from the previous limits. This allows potential investors and homeowners to access more significant financing for these properties, fueling the multi-unit housing market. The method of calculating the conforming loan limits has remained consistent, using the Housing Price Index as a guiding factor. However, given the unprecedented economic fluctuations in recent years, Fannie Mae's approach in 2024 embodies a more comprehensive analysis, integrating various economic indicators and housing market trends. This nuanced calculation further underlines Fannie Mae's adaptability and proactive stance in navigating the ever-evolving housing landscape. For borrowers, the conforming loan limits directly affect their borrowing capacity. A higher limit can allow potential homeowners to venture into pricier markets or secure better properties. Conversely, when limits are stringent, some borrowers might find themselves restricted or leaning towards non-conforming jumbo loans. Hence, these limits significantly shape the choices and opportunities available to borrowers. Lenders use these limits as a benchmark. Mortgages within the conforming limits are less risky as they can be sold to Fannie Mae. This encourages lenders to offer competitive interest rates for conforming loans, making them an attractive option for borrowers. As a result, the loan limits influence not only the products offered by lenders but also the overall health and competition within the lending industry. The most evident difference between conforming and non-conforming loans is the loan amount. Conforming loans adhere to Fannie Mae's set limits, while non-conforming loans, often called jumbo loans, exceed these set thresholds. Understanding this difference is crucial as it impacts the borrower's options, interest rates, and down payment requirements. Conforming loans often have more lenient borrower eligibility criteria, owing to the protection that Fannie Mae's backing provides. Jumbo loans, on the other hand, might have stricter credit score requirements, larger down payment needs, and comprehensive documentation. Thus, the borrower's financial profile and capacity significantly influence the choice between conforming and non-conforming loans. Historically, conforming loans tend to offer more favorable interest rates than jumbo loans. This is due to the perceived higher risk associated with larger loan amounts in non-conforming loans. Additionally, the terms of repayment and loan conditions might differ between the two. These differences impact the overall cost of borrowing and the affordability of monthly repayments. Conforming loans are frequently bought, bundled, and sold in the secondary mortgage market by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. This liquidity ensures the continuous availability of funds for mortgages. Non-conforming loans, however, do not enjoy this standardized secondary market. Instead, they might be held by the originating bank or sold to specialized investors, indicating the distinct roles these loans play in the broader financial system. Before diving into the mortgage process, it's essential to comprehend the specifics of your borrowing needs. This not only pertains to the amount you intend to borrow but also the type of property you're eyeing, its location, and how it aligns with the 2024 conforming loan limits. Assessing these elements can provide clarity, ensuring you don't overshoot the limits and inadvertently step into jumbo loan territory. Furthermore, having a keen understanding of your borrowing requirements allows you to craft a budget, making the home search more directed and fruitful. Once you've pinned down your borrowing needs, juxtapose your financial qualifications with the loan limits. This includes evaluating your credit score, income, and existing debts. Ensuring you fit snugly within the loan limits, while also meeting the lending criteria, can ease the borrowing process, potentially offering more favorable loan terms. Remember, even if you're eligible for a high loan amount, it's prudent to borrow only as much as you can comfortably repay. Down payments and loan-to-value ratios (LTV) play a pivotal role in determining the kind of loan you qualify for. In the context of conforming loan limits, you might find that a larger down payment helps you stay within the confines of these limits, especially in high-cost areas. Alternatively, a favorable LTV can make you a more appealing borrower, potentially smoothing out the loan approval process. In 2024, it's vital to understand the intricacies of down payments and LTV in relation to conforming loan limits, ensuring you maximize your borrowing potential while safeguarding your financial health. Navigating the world of conforming loan limits can be intricate, which is where mortgage brokers and financial advisors come into the picture. These professionals, armed with expertise and experience, can guide you through the maze, ensuring you're aligned with the 2024 conforming loan limits. Mortgage brokers, especially, have a pulse on the market, understanding the nuances of various lending institutions and the products they offer. Collaborating with them can illuminate the path, helping you procure a loan that harmonizes with your financial circumstances and homeownership aspirations. Similarly, financial advisors can provide strategic insights, assisting in budgeting, down payment planning, and overall financial preparedness, ensuring a seamless borrowing experience. In 2024, the conforming loan limits set by Fannie Mae, underpinned by economic conditions and housing market trends, signify an upward adjustment from previous years, reflecting a robust housing market. These limits not only influence the borrowing capacity for potential homeowners and the lending practices of financial institutions, but also encapsulate regional variances in housing costs. As Fannie Mae continues to balance homeownership promotion and financial risk management, the loan limits serve as vital indicators for borrowers, lenders, and policymakers alike. Understanding these conforming loan limits, alongside the nuanced differences between conforming and non-conforming loans, is crucial for prospective borrowers to navigate the financial landscape effectively. This knowledge enables crafting a comprehensive borrowing strategy, taking into consideration factors like borrowing needs, financial qualifications, and the role of down payments and loan-to-value ratios.Overview of Fannie Mae
Understanding Fannie Mae Conforming Loan Limits in 2024
Definition of Conforming Loan Limits
Fannie Mae Conforming Loan Limits in 2024
First Mortgage Conforming Loan Limit Values
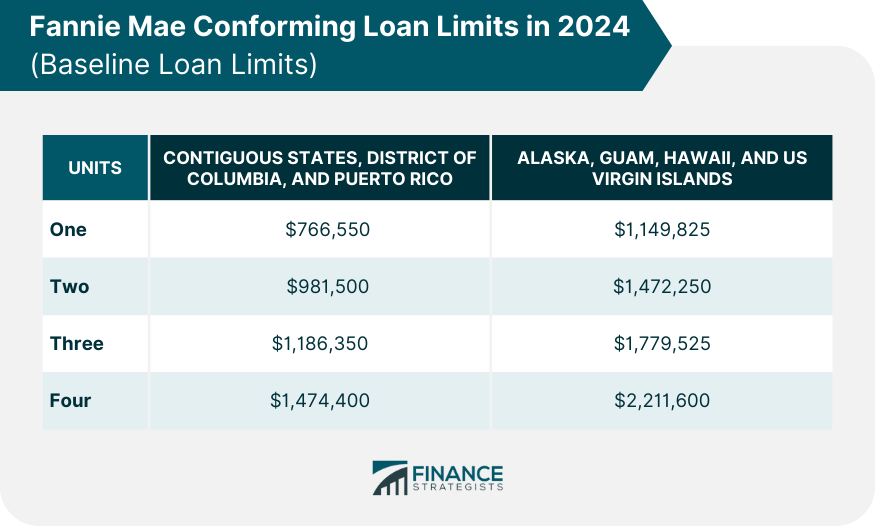
High-Cost Area Loan Limits

Factors Influencing Fannie Mae Conforming Loan Limits
Housing Price Index
Economic Conditions
Regulatory Changes
Real Estate Market Trends

Comparison of 2024 Conforming Loan Limits With Previous Years
Changes in Loan Limit Amounts
Variations in High-Cost Area Limits
Shifts in Loan Limit Adjustments for Two-To-Four Unit Properties
Changes in Conforming Loan Limit Calculation Methods
Implications of Fannie Mae Conforming Loan Limits
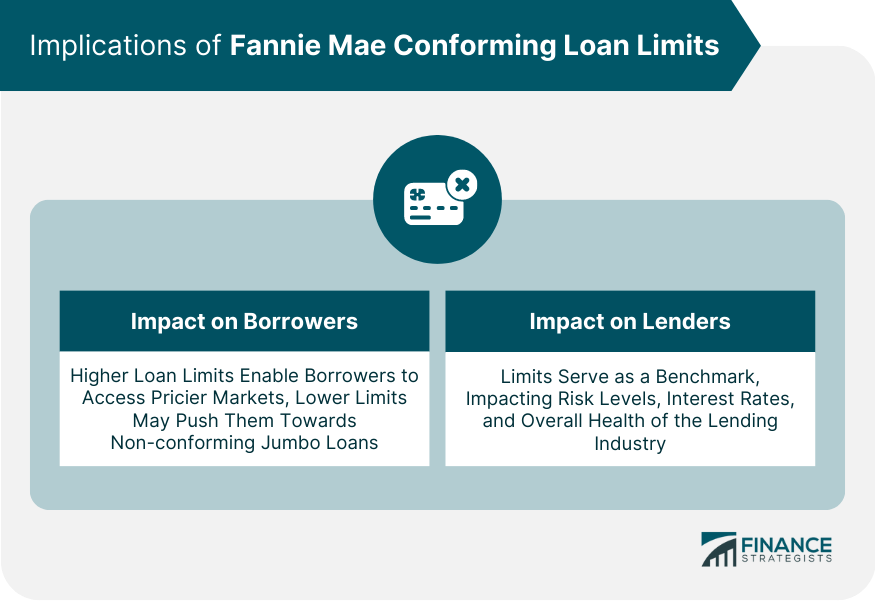
Impact on Borrowers
Impact on Lenders
Conforming vs Non-Conforming Loans: Detailed Comparison
Loan Limit Amounts
Borrower Eligibility
Mortgage Rates and Terms
Secondary Mortgage Market

How to Navigate Fannie Mae Conforming Loan Limits in 2024
Strategies for Potential Borrowers
Understand Borrowing Needs
Evaluate Qualifications Against Loan Limits
Plan For Down Payments and Loan-To-Value Ratios
Role of Mortgage Brokers and Financial Advisors
Bottom Line
Fannie Mae Conforming Loan Limits FAQs
They dictate the maximum mortgage size Fannie Mae can purchase or securitize, ensuring a balanced and fluid mortgage market.
The 2024 limits are adjusted based on home prices, economic conditions, the Housing Price Index, regulatory changes, and real estate trends.
These limits affect borrowing capacity, and adhering to them often results in more favorable interest rates and loan terms.
Conforming loans adhere to Fannie Mae's set limits, whereas non-conforming (jumbo) loans exceed these thresholds.
Understand your borrowing needs, evaluate qualifications against the limits, plan for down payments, and consider consulting mortgage brokers or financial advisors.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











