Fannie Mae, a government-sponsored enterprise, plays a pivotal role in the U.S. mortgage market. When it comes to credit scores, understanding Fannie Mae's requirements is crucial for prospective homebuyers and lenders alike. For a conventional mortgage backed by Fannie Mae, the minimum credit score typically starts at 620. However, it's worth noting that a higher score might be necessary for specific loan products or to secure more favorable interest rates and terms. Moreover, other factors, such as the borrower's debt-to-income ratio, down payment size, and overall financial history, will also influence the loan's approval. While a 620 credit score is often the baseline for Fannie Mae-backed mortgages, borrowers should aim for a higher score to ensure they meet all requirements and secure the best possible loan terms. Fannie Mae uses credit scores to determine the pricing of loans. Borrowers with higher credit scores usually secure loans with more favorable interest rates. This is because a high credit score is an indicator of good financial habits, thus, less risk to the lender. Risk-Based Pricing Adjustment (RBPA) is a mechanism used by Fannie Mae where adjustments are made to the loan's interest rate based on the perceived risk. This risk is determined by several factors, one of which is the credit score. Borrowers with lower credit scores generally experience a higher RBPA, leading to a higher interest rate. The credit score significantly influences whether a loan application will be approved or not. Apart from deciding the interest rate, a lower credit score might lead to the rejection of a loan application. However, Fannie Mae does not solely depend on credit scores for this decision; other factors like income stability, total debts, and savings also play a critical role. Like Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac also has a minimum credit score requirement of 620 for most of its loans. However, the way both institutions adjust loan pricing based on credit scores might differ slightly. It's advisable to compare offers from both to get the best mortgage deal. Federal Housing Administration (FHA) loans can be more lenient, permitting credit scores as low as 500 with a 10% down payment. With a 500-579 credit score, the required down payment drops to just 3.5%. While this offers a great opportunity for those with lower credit scores, FHA loans come with their own set of criteria and additional costs, such as mortgage insurance premiums. Veterans Affairs (VA) and United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) loans do not have a strict minimum credit score requirement. Instead, they require lenders to assess the entire credit profile of a loan applicant. A long history of credit use and a lower credit utilization ratio contribute to a higher credit score. Credit utilization refers to how much of your available credit you use. Keeping this ratio below 30% can significantly improve your credit score, while a long, unblemished credit history showcases financial responsibility. To improve your credit score, consistently pay your bills on time, reduce your debts, and avoid taking on new debt. Regularly check your credit report for errors and dispute them if necessary. Furthermore, avoid closing old credit card accounts, as this can decrease your total available credit and increase your credit utilization ratio. Making payments on time is the most significant factor that contributes to your credit score. Late or missed payments can severely damage your score. Reducing overall debt not only lowers your credit utilization ratio but also paints a picture of financial responsibility, boosting your creditworthiness. Fannie Mae has introduced programs to assist borrowers with lower credit scores. For example, the HomeReady® program targets low-to-moderate-income borrowers, allowing a lower minimum credit score under certain conditions. Fannie Mae continuously revises its policies to provide more inclusive opportunities for potential homebuyers with low credit scores. By considering alternative credit data like rental history and utility payments, it seeks to expand homeownership to a more diverse range of borrowers. Fannie Mae's central role in the U.S. mortgage landscape makes understanding its credit score requisites paramount for potential homeowners and lenders. With the baseline credit score set at 620, factors such as loan pricing, Risk-Based Pricing Adjustments, and comprehensive credit evaluation interplay in the final loan decision. While Fannie Mae's requirements are comparable with Freddie Mac and distinct from more lenient institutions like the FHA, the ultimate focus remains on broader financial profiles over mere credit scores. Emphasizing credit history longevity and prudent credit utilization, prospective borrowers can bolster their scores through timely bill payments and judicious debt management. Importantly, Fannie Mae's initiatives like HomeReady® and consideration of alternative credit data underline its commitment to address credit score inequality, striving to make homeownership more accessible to all.Fannie Mae Credit Score Requirements Overview
How Fannie Mae Uses Credit Scores Works
Loan Pricing and Credit Score
Risk-Based Pricing Adjustment
Impact of Credit Score on Loan Approval
Differences Between Fannie Mae and Other Mortgage Lenders' Credit Score Requirements
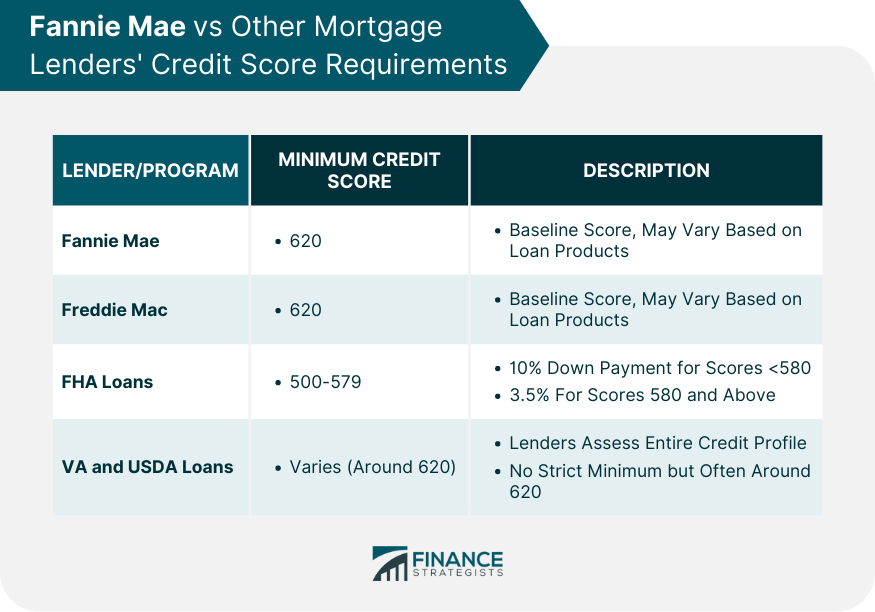
Comparison With Freddie Mac
Comparison With FHA Loans
Comparison With VA and USDA Loans
How to Improve Your Credit Score for Fannie Mae Approval
Importance of Credit History and Credit Utilization
Strategies for Improving Credit Scores
Impact of Paying Bills on Time and Reducing Debt
Fannie Mae's Role in Addressing Credit Score Inequality
Programs Aimed at Helping Low Credit Score Borrowers
Policy Changes to Create More Opportunities for Low-Credit-Score Home Buyers
Conclusion
Fannie Mae Credit Score Requirements FAQs
The minimum credit score generally required for a Fannie Mae loan is 620. However, specific loan programs and other factors such as property type and down payment size may require a higher score.
Fannie Mae uses credit scores to determine a borrower's risk level and to adjust the loan pricing. A high credit score often results in more favorable loan terms, while a lower score could lead to a higher interest rate or even loan rejection.
Fannie Mae's minimum credit score requirement is typically similar to Freddie Mac's and many VA and USDA lenders, which is often around 620. However, FHA loans can be more lenient, allowing credit scores as low as 500 with a 10% down payment.
Consistently paying your bills on time, reducing your debts, avoiding new debt, and keeping your credit utilization ratio below 30% can help improve your credit score. Checking your credit report regularly and disputing any errors can also help.
Fannie Mae has implemented programs such as HomeReady® to assist low-to-moderate-income borrowers who might not have high credit scores. It is also considering alternative credit data such as rental history and utility payments to provide more opportunities for potential homebuyers with lower credit scores.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











