The Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines are a set of standardized criteria established by the Federal National Mortgage Association, commonly known as Fannie Mae. These guidelines play a pivotal role in the U.S. mortgage industry, ensuring that loans eligible for purchase by Fannie Mae meet specific quality and risk standards. By setting these guidelines, Fannie Mae aims to maintain a robust and resilient housing market, ensuring both lenders and borrowers operate within a transparent and secure framework. The criteria encompass borrower's eligibility factors, such as credit scores and debt-to-income ratios, and also property-related factors, like appraisals. Adherence to these guidelines is crucial for lenders wishing to sell their loans to Fannie Mae and provides borrowers with a clearer understanding of what's expected in the mortgage application process. One of the fundamental aspects of these guidelines is determining a borrower's eligibility. The factors often taken into account include the borrower's credit score, employment history, and overall financial health. For a loan to pass Fannie Mae's guidelines, proper documentation is paramount. This often involves verifying a borrower's income, assets, and other relevant details. Lenders typically require tax returns, W-2s, bank statements, and other pertinent records. The Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio is a critical metric in mortgage underwriting. It represents the amount of the loan compared to the value of the property. A lower LTV indicates a borrower has more equity in the home, which generally presents a lower risk to the lender. Before a loan is approved, an appraisal of the property is necessary. This ensures that the home's value aligns with the loan amount and that the lender isn't lending more money than the property is worth. A critical factor in underwriting is the Debt-to-Income (DTI) ratio. It represents a borrower's total monthly debt obligations compared to their gross monthly income. A lower DTI often indicates a borrower has a better capability to manage and repay the loan. Credit scores are a vital component. They offer a glimpse into a borrower's creditworthiness and history of managing debt. Different loan products might have varying minimum credit score requirements. Whether a property is a single-family home, multi-unit dwelling, or a condo can influence underwriting decisions. Each property type comes with its risks and considerations. Mortgage insurance often comes into play when a borrower can't make a 20% down payment. This insurance protects lenders in case of a default, and its presence can influence underwriting decisions. By setting a universal standard, Fannie Mae's guidelines bring about uniformity. This ensures that irrespective of the lender, certain baseline criteria must be met, thereby protecting both the borrower and the lender. Thanks to these guidelines, borrowers have a clearer understanding of what is expected of them. They are better equipped to provide the necessary documents and meet the required criteria. For lenders, adhering to these guidelines offers a layer of protection. It ensures that they are not taking on undue risk and that the loans they offer are grounded in a secure and reliable framework. While standardization has its benefits, over-reliance can sometimes hinder nuanced judgment. Not all borrowers' situations fit neatly into a box, and an overemphasis on strict guidelines can potentially exclude deserving borrowers. Those with non-conventional sources of income or unconventional financial situations might find it more challenging to meet these stringent guidelines. Markets are dynamic, and sometimes, rapid changes can occur. In such instances, strict adherence to a set of guidelines might not always be in the best interest of the housing market. Freddie Mac, another government-sponsored entity, also has its set of guidelines. While there's significant overlap, there are nuances that differentiate the two. Loans insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) have different criteria, especially catering to first-time homebuyers or those with lower credit scores. For veterans and active-duty military personnel, VA loans offer unique benefits. Their underwriting guidelines differ, taking into account the unique challenges and situations faced by military personnel. Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines play an instrumental role in the U.S. mortgage landscape, offering a standardized approach to loan eligibility and assessment. This framework establishes clarity for borrowers, ensuring they know what's anticipated in the mortgage process, from credit score evaluations to property appraisals. Furthermore, they equip lenders with tools to make informed, secure decisions. Despite the invaluable benefits, such as fostering transparency and predictability, there are potential challenges, like over-reliance on standards or addressing swift market shifts. Still, when compared to other guidelines like those from Freddie Mac, FHA, or VA, Fannie Mae's guidelines maintain their distinct importance. Recognizing the nuances and overarching principles of these guidelines enables a more cohesive understanding of the mortgage ecosystem.Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines Overview
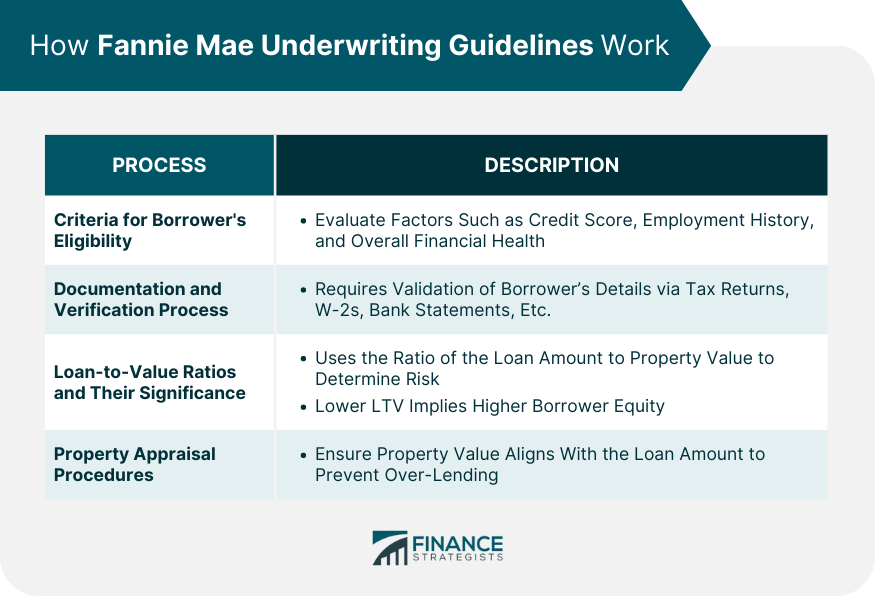
How Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines Work
Criteria for Borrower's Eligibility
Documentation and Verification Process
Loan-to-Value Ratios and Their Significance
Property Appraisal Procedures
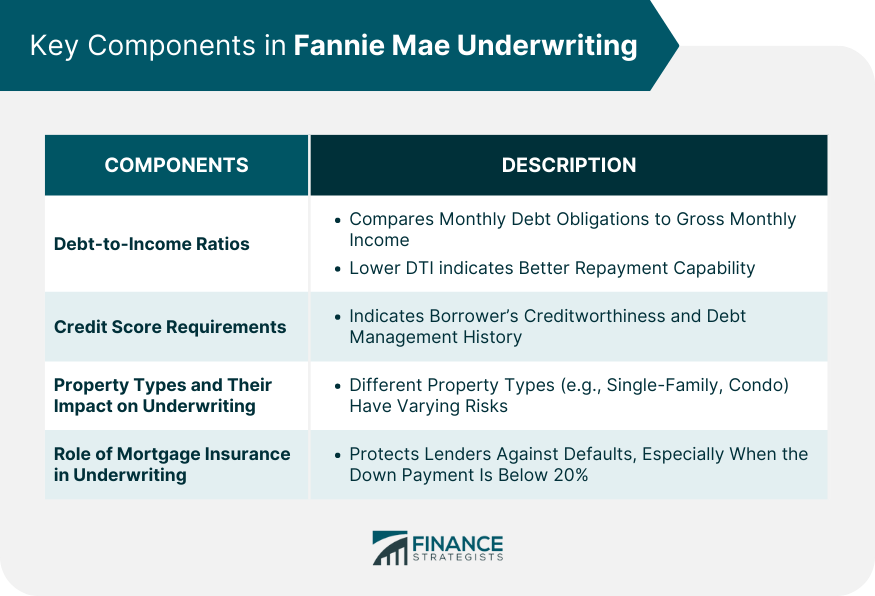
Key Components in Fannie Mae Underwriting
Debt-to-Income Ratios
Credit Score Requirements
Property Types and Their Impact on Underwriting
Role of Mortgage Insurance in Underwriting
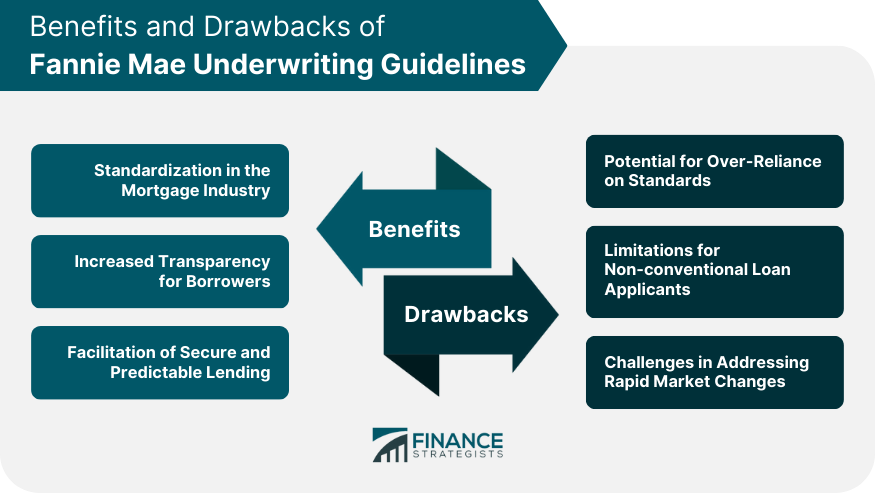
Benefits of Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines
Standardization in the Mortgage Industry
Increased Transparency for Borrowers
Facilitation of Secure and Predictable Lending
Drawbacks of Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines
Potential for Over-Reliance on Standards
Limitations for Non-conventional Loan Applicants
Challenges in Addressing Rapid Market Changes
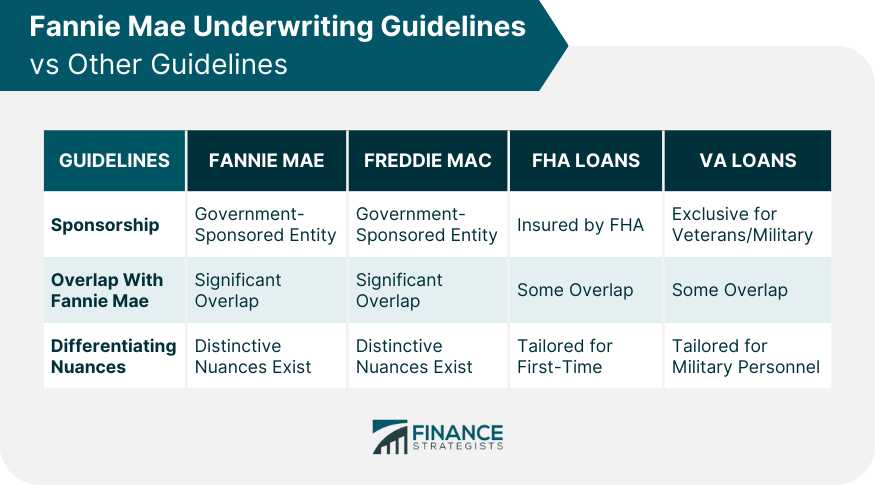
Comparing Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines to Other Guidelines
Freddie Mac Underwriting Guidelines
FHA Loan Guidelines
VA Loan Guidelines
Conclusion
Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines FAQs
Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines are a set of standards and criteria that loans must meet for them to be eligible for purchase by Fannie Mae, ensuring quality and a high likelihood of repayment.
These guidelines bring about transparency, predictability, and clarity for lenders and borrowers. They ensure that the loans Fannie Mae buys are standardized and of good quality.
The guidelines use the LTV ratio as a critical metric, representing the amount of the loan compared to the value of the property. A lower LTV means the borrower has more equity in the home, indicating a lower risk for lenders.
DTI ratio is a significant factor in underwriting, showing a borrower's total monthly debt obligations against their gross monthly income. A lower DTI indicates a borrower's better ability to manage and repay the loan, according to Fannie Mae Underwriting Guidelines.
While Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and FHA all have their underwriting standards, each caters to different segments of the market with specific criteria. Fannie Mae's guidelines focus on ensuring loan quality for its purchases, while Freddie Mac and FHA might have variations in criteria, especially catering to specific borrowers or property types.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











