Fannie Mae, short for the Federal National Mortgage Association, stands as a significant entity in the American mortgage landscape. Their purpose is to ensure liquidity, stability, and affordability in the housing market. They purchase mortgages from lending institutions, effectively setting industry-wide standards and ensuring lenders can issue more loans to borrowers. By providing consistent liquidity, Fannie Mae helps to stabilize the housing market, especially in turbulent times. Their pivotal role offers a balance between consumer needs and the industry's growth. Recovering from foreclosure can seem daunting. However, knowledge of waiting periods, especially those set by pivotal entities like Fannie Mae, provides a semblance of clarity. A clear path can help homeowners rebuild their future with defined steps and expectations. Knowing these periods allows for strategic planning, equipping borrowers with a roadmap to homeownership once again. Sudden Job Loss: Unemployment can drastically reduce a household's income, making it challenging to meet monthly mortgage payments. While some might have savings to tide them over for a few months, prolonged unemployment can lead to defaults. Debilitating Health Issues: Unexpected health problems can lead to substantial medical bills and loss of income. If one is not adequately insured, these costs can be overwhelming, pushing homeowners to the brink of foreclosure. Divorce: A divorce can result in financial instability as a single income might not suffice to cover the mortgage payment, especially if alimony or child support is involved. Adjustable Rate Loans: If homeowners have an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM), monthly payments can rise significantly, leading to financial strain and potential defaults. Excessive Debt Obligations: Some borrowers have substantial amounts of other debts like credit card bills, student loans, and car payments. These can divert funds away from the mortgage, leading to potential foreclosure. Diminished Credit Scores: A foreclosure remains on the credit report for seven years and can significantly lower one's credit score, affecting future borrowing capabilities. Emotional Toll: Losing a home can be emotionally devastating, as homes often hold memories and sentimental value. Strains in Familial Relationships: The stress and emotional toll can strain familial relationships, possibly leading to further complications in personal lives. Rental and Employment Challenges: A tarnished credit report can impact rental applications and, in some professions, employment opportunities. Potential Deficiency Judgments: If the sale of the home doesn't cover the outstanding loan amount, the lender might pursue a deficiency judgment, requiring the borrower to pay the difference. Missed Payments: The process begins when a borrower fails to make consecutive mortgage payments. After the first missed payment, the lender may contact the borrower, and a late fee might be charged. Pre-Foreclosure: After 90 days of missed payments, the lender records a public notice with the County Recorder's Office, indicating the borrower has defaulted on the mortgage. During this period, the borrower can work out an arrangement with the lender or pay the outstanding amount and fees. Notice of Sale: If the default isn't corrected within three to six months, the lender will schedule a foreclosure sale and publish a notice in local newspapers. Auction: The property is then auctioned to the highest bidder, which can be a third party or the lender. If the property isn't sold at auction, it becomes a bank-owned property or real estate owned (REO). Post-Foreclosure: If the property becomes REO, the lender usually tries to sell it through a real estate agent or in bulk sales to investors. The borrower might still face a deficiency judgment if the sale proceeds don't cover the loan balance. Fannie Mae mandates a seven-year waiting period after foreclosure. This span is calculated from the completion date of the foreclosure action. The seven-year period helps ensure that borrowers have ample time to recover financially and establish a more stable financial footing. It acts as a buffer, allowing borrowers to repair credit, accumulate savings, and position themselves better for future loan approvals. By marking a clear duration, Fannie Mae sets transparent expectations for all involved parties. A foreclosure remains a black mark on a credit report. It significantly diminishes credit scores, affecting loan eligibility, interest rates, and trust from future lenders. Over time, its impact wanes, but borrowers must be proactive in credit restoration to expedite the recovery process. Consistent, timely financial behaviors can gradually offset the negative impact. Moreover, lenders often view a foreclosure in context, weighing other positive financial behaviors alongside this event. Life is unpredictable. Recognizing this, Fannie Mae allows a three-year waiting period if extenuating circumstances led to foreclosure. These are significant life events beyond a borrower's control, like severe illness or loss of employment, that directly impact their financial situation. It's an acknowledgment that unforeseen hardships can befall anyone, and individuals shouldn't be indefinitely penalized for circumstances beyond their control. The shortened period offers a semblance of hope to those eager to reclaim their homeownership dreams. To qualify for the shorter waiting period, proper documentation is paramount. Proof that directly links the extenuating event to the foreclosure, such as medical bills or termination notices, is essential. Without substantial evidence, borrowers might face the standard seven-year hiatus. Clear, concise documentation not only helps in making a case for extenuating circumstances but also fosters transparency in the lending process. By doing so, borrowers and lenders establish a mutual understanding, ensuring smooth progress. The three-year exception isn't a mere reduction in time. It comes with stipulations. Borrowers must show a direct tie between foreclosure and extenuating circumstances and, once verified, undergo additional requirements if they wish to re-enter the housing market within three to seven years post-foreclosure. It's crucial to understand that this isn't a shortcut, but a provision for genuine hardship cases. By adhering to the guidelines, borrowers demonstrate responsibility and commitment towards future homeownership. Loan-to-value (LTV) ratios, combined loan-to-value (CLTV) ratios, and home equity combined loan-to-value (HCLTV) ratios play crucial roles during this period. Borrowers must adhere to certain ratio criteria, principally ensuring their loan doesn't exceed 90% of the property's value. Additionally, during this time, the only property purchases permitted are for principal residences. Maintaining these standards ensures that borrowers are financially equipped for new mortgages, minimizing the risk of default in the future. For those eyeing refinances, there's a beacon of hope. Limited cash-out refinances become accessible during this window. However, the refinancing's nature must align with the existing eligibility requirements, ensuring borrowers don't overextend their financial capacities. Refinancing can offer lower interest rates or more favorable terms, but borrowers should approach it with caution, ensuring it aligns with their long-term financial goals and capabilities. Credit recovery post-foreclosure is akin to rebuilding from scratch. Regular bill payments, reducing outstanding debts, and cautious credit utilization help nurture credit health back to vitality. Consultation with credit counselors can offer tailored strategies for individual circumstances. It's a journey that demands discipline and patience. Over time, with consistent efforts, borrowers can witness a significant improvement in their credit scores, opening doors to better financial opportunities. Conventional mortgages might be off the table temporarily, but alternative financing options exist. FHA loans, private lenders, or even rent-to-own agreements can pave paths back to homeownership, albeit often at higher interest rates or with more stringent terms. Each alternative comes with its set of advantages and challenges, requiring thorough research and consideration. Nonetheless, they offer hope and feasible pathways for those eager to reestablish homeownership. Professional guidance can be a game-changer. Mortgage brokers and counselors, equipped with industry insights and a wealth of experience, can navigate borrowers through the maze of post-foreclosure options, ensuring informed decisions at every turn. These experts can provide clarity on the best courses of action, tailored to individual situations. With their guidance, navigating the complex world of post-foreclosure financing becomes significantly more manageable. While Fannie Mae's policies are influential, they aren't the only ones in the arena. Freddie Mac, FHA, and others have their own stipulations regarding post-foreclosure re-entry. A comparative understanding can illuminate the best path forward for prospective borrowers. Each agency, while operating with similar core principles, might have nuances that could better align with a borrower's specific circumstances. Thus, knowledge of various policies can prove invaluable. By setting clear standards, Fannie Mae's policies create ripples throughout the housing market. Their waiting periods influence lending practices, property prices, and even buyer sentiment, forming an interconnected web of cause and effect. Lenders often frame their policies in sync with Fannie Mae's guidelines, leading to industry-wide practices. This uniformity can offer stability, especially in volatile market conditions. Time brings change. Over the years, Fannie Mae's foreclosure policies have evolved, reflecting the changing economic climate and lessons learned from past housing crises. A glimpse into these changes provides context and insights into future policy directions. Historical perspectives shed light on how policies adapt to societal needs and economic realities, offering a window into the resilience and flexibility of the housing market. Knowledge is empowerment. Familiarizing oneself with Fannie Mae's specific compliance requirements ensures borrowers remain within legal boundaries, paving a smoother road to property acquisition post-foreclosure. Compliance goes beyond mere adherence; it embodies a borrower's commitment to responsible homeownership. This understanding can also shield borrowers from potential pitfalls, ensuring smoother transactions in their journey back to homeownership. Foreclosure doesn't strip borrowers of all rights. Protections exist, ensuring fair treatment and preventing undue discrimination. From credit reporting rights to protections against predatory lending, borrowers retain a shield against potential injustices. Being well-informed about these rights empowers borrowers to stand against unfair practices, ensuring they're treated with the dignity and fairness they deserve. Foreclosure might close one chapter, but it doesn't end the homeownership story. Preparation is pivotal. This includes credit restoration, financial planning, and gaining a comprehensive understanding of the housing market nuances. By setting clear goals and equipping themselves with necessary knowledge, borrowers can position themselves for a successful re-entry into homeownership. Each step taken in preparation reduces potential hurdles in the future. Every borrower's goal post-foreclosure is a successful mortgage application. From timely bill payments to reducing debts and maintaining steady employment, specific strategies enhance chances of gaining Fannie Mae's nod of approval. Building a healthy savings account, seeking professional advice, and staying informed about changing mortgage policies can further boost a borrower's prospects. It's about showcasing financial responsibility and readiness for a new mortgage commitment. Not all properties are created equal, especially in Fannie Mae's eyes. Understanding the nuances of property types and their respective eligibility requirements ensures borrowers align their aspirations with feasible targets, streamlining their journey back to homeownership. Whether considering a single-family home, a multi-unit property, or a condo, each property type has its eligibility criteria. Being aware of these can prevent unwelcome surprises and set clear expectations for borrowers. After a foreclosure, re-entering the housing market can be challenging. Fannie Mae, a linchpin in the American mortgage arena, has established clear guidelines to assist borrowers in this journey. With a standard seven-year waiting period post-foreclosure, Fannie Mae ensures that borrowers have sufficient time to regain financial stability. However, in instances of uncontrollable hardships like severe illness or job loss, this period is reduced to three years. To qualify for this reduction, substantial evidence linking the hardship to foreclosure is essential. This policy aims to balance the need for responsible lending with empathy towards genuine hardships. Moreover, these waiting periods are influential, shaping broader lending practices and offering stability in the housing market. As borrowers navigate this post-foreclosure landscape, understanding these guidelines, consulting professionals, and adhering to Fannie Mae's stipulations can provide a clearer path to homeownership, facilitating informed and strategic decisions.Overview of Fannie Mae and Waiting Periods
Understanding Foreclosure
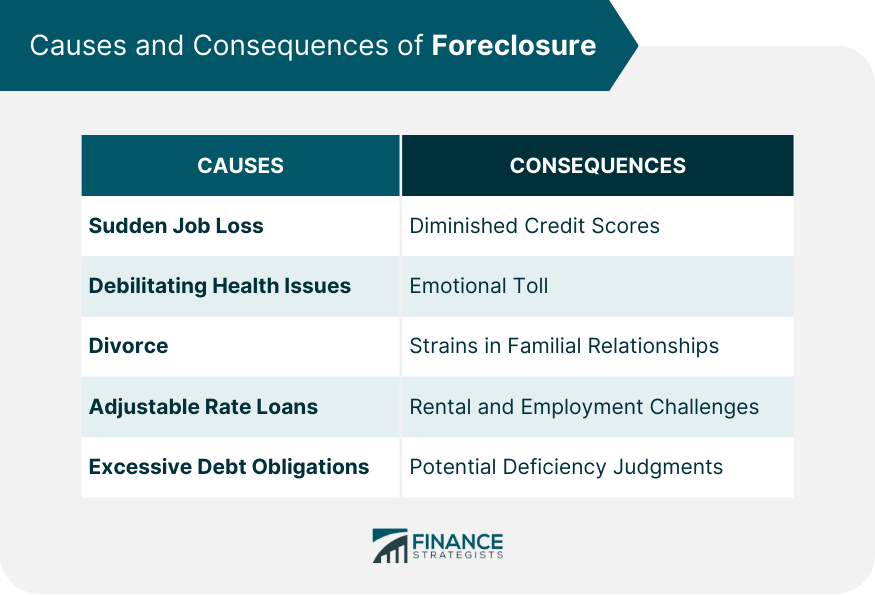
Causes and Consequences of Foreclosure
Causes
Consequences
Foreclosure Process: A Brief Overview

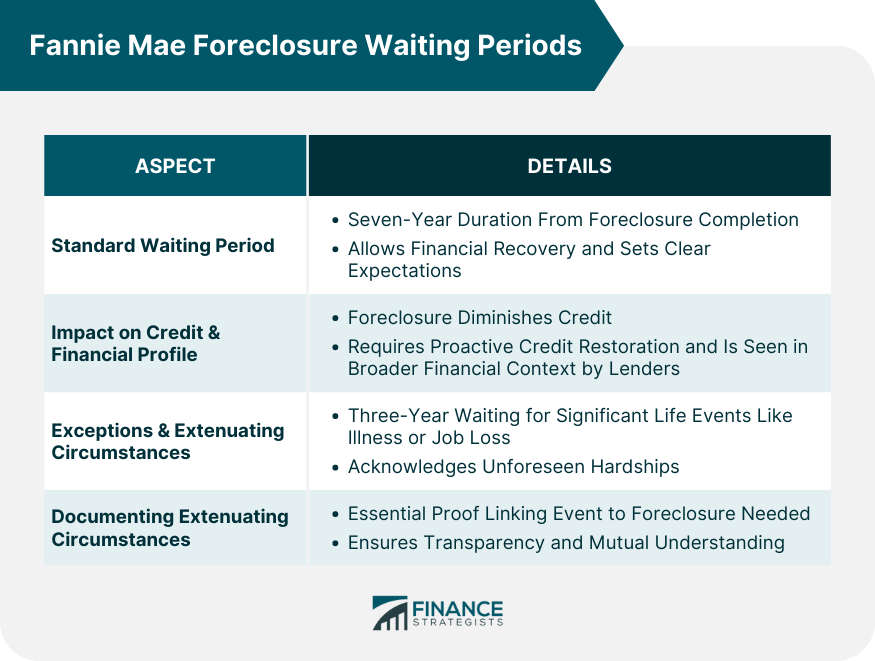
Fannie Mae Foreclosure Waiting Periods
Standard Waiting Period: Duration and Significance
Impact on Borrowers' Credit and Financial Profile
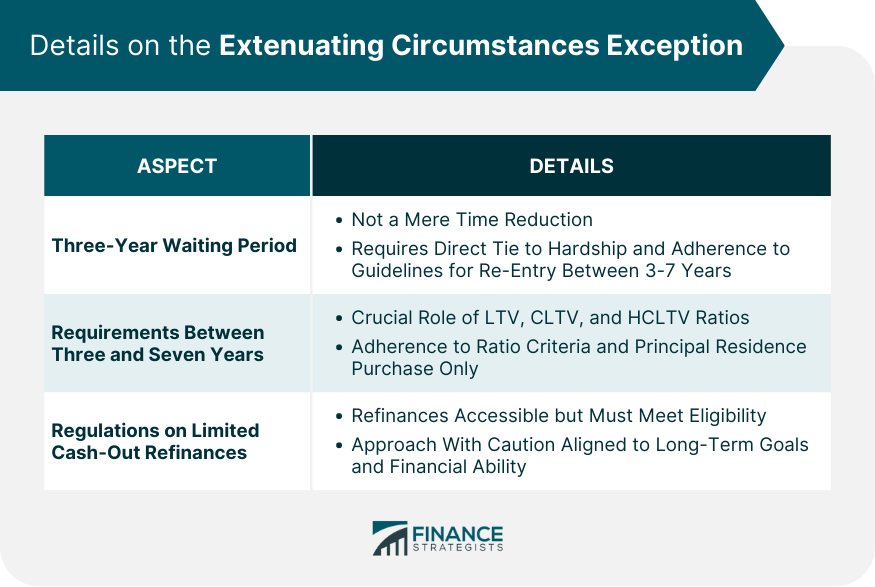
Exceptions and Extenuating Circumstances: Criteria for Identification
Documenting Extenuating Circumstances
Details on the Extenuating Circumstances Exception
Definition of the Three-Year Waiting Period
Requirements Between Three and Seven Years
Regulations on Limited Cash-Out Refinances
Navigating the Post-Foreclosure Landscape
Restoring Credit Health
Considering Alternative Financing Options
Consulting Mortgage Brokers and Counselors
Comparative Analysis of Foreclosure Waiting Periods
Comparison With Other Mortgage Agencies’ Policies
How Fannie Mae’s Policy Impacts the Housing Market
Historical Perspective: Changes in Fannie Mae’s Foreclosure Policies Over Time
Legal and Regulatory Considerations of the Fannie Mae Waiting Period for Foreclosure
Understanding Fannie Mae's Compliance Requirements
Rights and Protections for Consumers Post-Foreclosure

Practical Implications for Borrowers
Preparation for Post-Foreclosure Home Buying
Enhancing Chances of Mortgage Approval With Fannie Mae
Navigating Property Types and Eligibility
Bottom Line
Fannie Mae Waiting Period for Foreclosure FAQs
Fannie Mae mandates a seven-year waiting period post-foreclosure.
Fannie Mae's policies influence lending practices, property prices, and buyer sentiment, offering market stability.
Yes, with proven extenuating circumstances, the waiting period can be reduced to three years.
By restoring credit, reducing debts, maintaining steady employment, and staying informed on mortgage policies.
Familiarity ensures borrowers remain within legal boundaries and paves a smoother road to property acquisition post-foreclosure.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











