Financing concession refers to an arrangement where a private party, termed as the concessionaire, is awarded rights to finance, manage, and potentially upkeep a public asset or service for a predetermined span. Born from the need to bridge public requirements with private capital and expertise, these agreements have increasingly become pivotal in sectors such as infrastructure development, transportation, and energy. The arrangement offers numerous benefits like risk-sharing, rapid project execution, and enhanced innovation. However, it's essential to navigate challenges like contract complexities and aligning public-private interests. In essence, financing concessions represent a symbiotic collaboration, channeling private resources for public good. Concessions are typically long-term arrangements, often lasting several decades. The precise duration is generally dictated by the anticipated return on investment and the nature of the project. Terms of the concession, such as revenue-sharing mechanisms, responsibilities, and early termination conditions, are meticulously detailed to ensure clarity for all parties involved. The concessionaire usually makes a significant financial commitment upfront. This commitment can take various forms, including direct investment, loans, or guarantees. The objective is to ensure the concessionaire has a vested interest in the success and sustainability of the project. While each concession agreement is unique, most include some profit-sharing mechanism. Revenue models often consider user fees, lease payments, or a combination of both. Properly structured models balance the need for the concessionaire to recoup investments and earn a profit with public affordability concerns. Financing concessions are often intertwined with other models, such as Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs). While PPPs focus on collaboration between public and private entities for service delivery, financing concessions emphasize the financial aspect of such associations. A fusion of PPPs with financing concessions often results in projects where the public sector designs and monitors, while the private sector finances, builds, and operates. Such models effectively spread risks and responsibilities between the parties. Under BOT, a private entity is contracted to design, finance, and construct a facility. After an agreed-upon operational period, during which the private entity recoups its investment through user fees or other revenues, the asset is transferred back to the public sector. In LDO arrangements, the public sector leases an existing asset to a private entity, which then further develops and operates it. This model is popular when public assets are underutilized or need enhancement. For aging infrastructure or services that need refurbishment, the ROT model is apt. The private sector is tasked with rehabilitating and operating the asset for a set period before transferring it back to public ownership. Concessions distribute risks such as construction delays, cost overruns, and revenue shortfalls. This shared responsibility often leads to better risk management and mitigation. With private capital at the helm, projects can often bypass bureaucratic red tape, leading to quicker execution and timely delivery. The competitive nature of acquiring concessions drives private entities to innovate, ensuring state-of-the-art infrastructure and service delivery. By leveraging private capital, the public sector can redirect its resources to other critical areas, ensuring efficient utilization of taxpayer money. Given the long-term nature and multifaceted dynamics of such deals, crafting contracts that are foolproof and equitable can be challenging. While public sectors aim for maximum public good, private entities often prioritize profits. Striking a balance is crucial but sometimes elusive. Ensuring that the concessionaire adheres to terms and maintains service quality requires robust monitoring mechanisms, which can be resource-intensive. From unexpected operational challenges to shifts in macroeconomic scenarios, concessionaires face significant financial risks that can sometimes jeopardize their investment. Be it roads, bridges, or airports, financing concessions have enabled the rapid expansion of transportation infrastructure, improving connectivity and fostering economic growth. From renewable energy farms to traditional power plants and grids, financing concessions have facilitated private investment, addressing growing energy demands. Ensuring access to clean water and sanitation services has been made possible in many regions due to financing concessions, marking significant strides in public health. Guidelines from international bodies, like the World Bank, set the benchmark for framing financing concession contracts, ensuring transparency and equity. While the fundamental premise remains consistent, varying legal, economic, and social landscapes mean that concession regulations differ significantly across nations. From dispute resolution mechanisms to force majeure clauses, a plethora of legal considerations dictates the structure and enforceability of concession contracts. Before embarking on a concession journey, thorough feasibility studies gauge the viability of projects, while comprehensive risk assessments identify potential pitfalls. Understanding and managing public perception is critical. Engaging stakeholders ensures project acceptance and smoother execution. The complexity of financing concessions necessitates a detailed exploration of suitable financing structures and potential sources of capital. For private entities, assessing the potential return on investment is paramount. This not only dictates the financial feasibility but also the long-term sustainability of the project. Financing concessions effectively marry private investment and expertise with public needs and assets, playing a critical role in sectors like transportation, energy, and sanitation. While these models offer advantages such as risk sharing, prompt project completion, improved quality, and fiscal benefits, they also present challenges like contractual complexity, public-private interest alignment, governance hurdles, and financial risks. Different models, including PPPs with financing concessions, BOT, LDO, and ROT, cater to diverse project needs. Regulatory frameworks and international guidelines ensure transparency and equity in these arrangements. Aspiring concessionaires must conduct detailed feasibility studies, stakeholder engagement, source viable financing structures, and evaluate returns on investment. Despite the challenges, financing concessions remain a pivotal tool for global development, underpinning significant public infrastructure and service enhancement.Financing Concession Overview
Key Characteristics of Financing Concession
Duration and Terms of the Concession
Financial Commitment by the Concessionaire
Profit-Sharing Arrangements and Revenue Models
Relationship With Other Financing Models

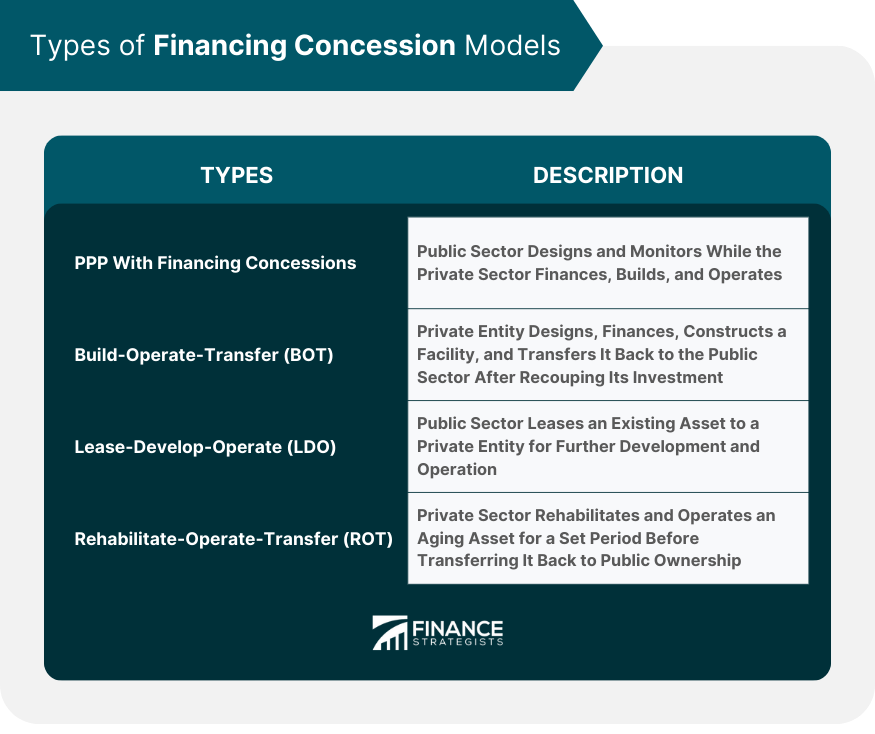
Types of Financing Concession Models
Public-Private Partnership (PPP) With Financing Concessions
Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) And Related Models
Lease-Develop-Operate (LDO)
Rehabilitate-Operate-Transfer (ROT)
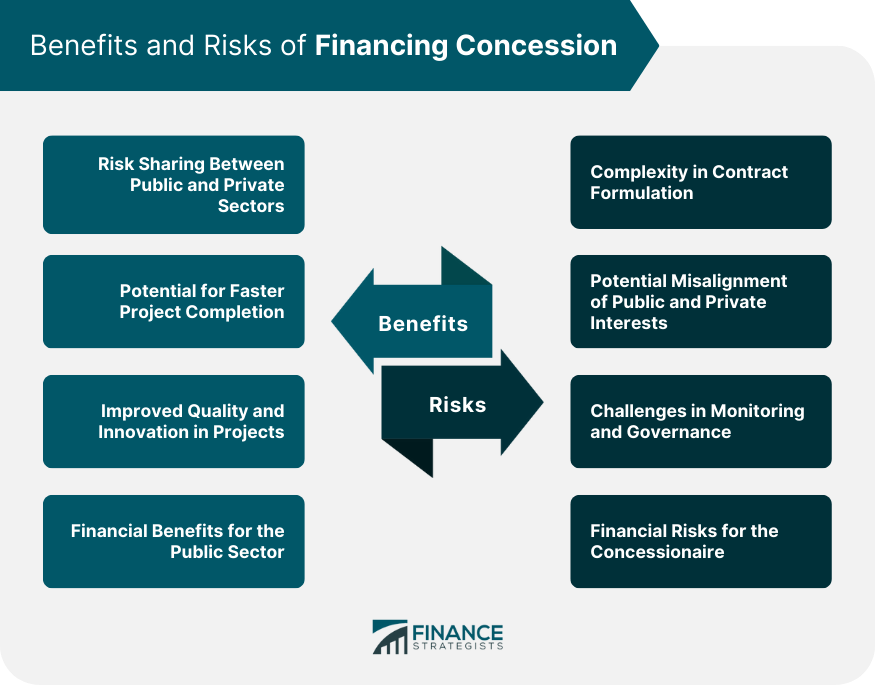
Benefits of Financing Concession
Risk Sharing Between Public and Private Sectors
Potential for Faster Project Completion
Improved Quality and Innovation in Projects
Financial Benefits for the Public Sector
Risks of Financing Concession
Complexity in Contract Formulation
Potential Misalignment of Public and Private Interests
Challenges in Monitoring and Governance
Financial Risks for the Concessionaire
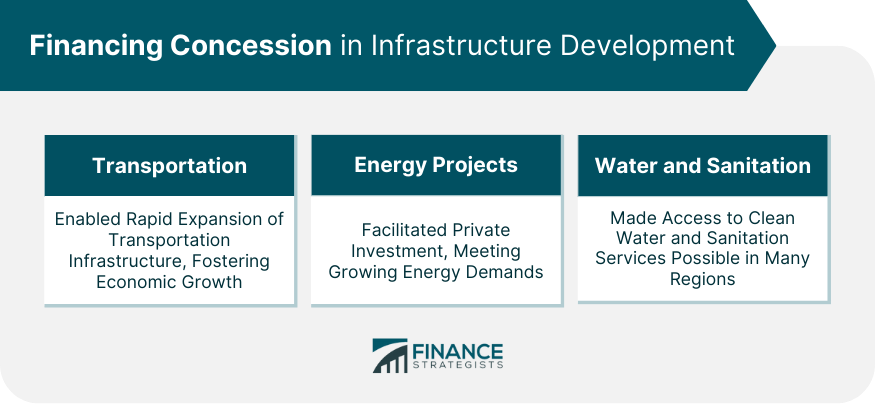
Financing Concession in Infrastructure Development
Role in Transportation
Impact on Energy Projects
Financing Concession in Water and Sanitation Infrastructure
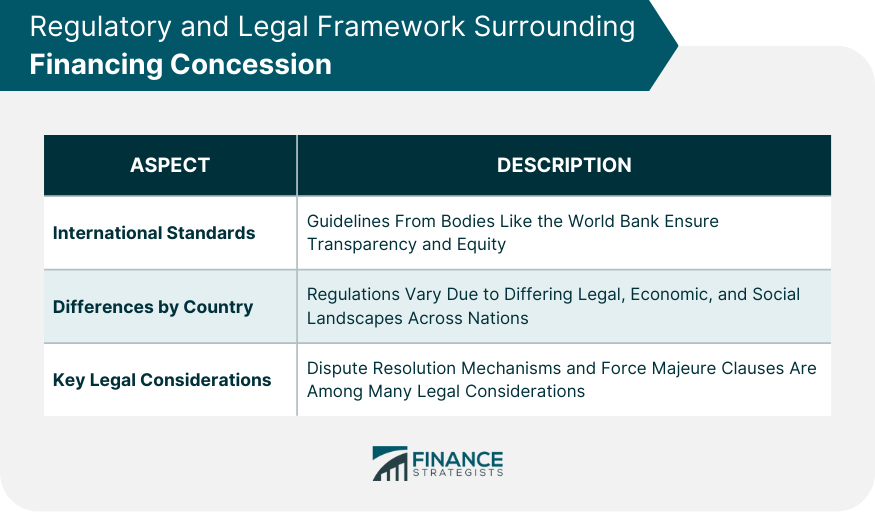
Regulatory and Legal Framework Surrounding Financing Concession
International Standards and Best Practices
Differences in Regulatory Approaches by Country
Key Legal Considerations in Concession Contracts
Evaluating Financing Concession Opportunities
Feasibility Studies and Risk Assessment
Stakeholder Engagement and Public Perception
Financing Structures and Sourcing Capital
Return on Investment and Project Viability
Conclusion
Financing Concession FAQs
A financing concession is an arrangement where a private entity, the concessionaire, is granted rights to finance, operate, and possibly maintain a public asset or service for a defined period.
While both involve collaboration between public and private entities, a financing concession emphasizes the financial aspect, granting rights to finance and operate. On the other hand, PPPs typically focus on joint collaboration for service or infrastructure delivery.
Financing concession models allow risk-sharing between public and private sectors, the potential for faster project completion, improved quality and innovation in projects, and financial benefits for the public sector.
Yes, challenges can include complexities in contract formulation, potential misalignment of public and private interests, monitoring and governance hurdles, and financial risks for the concessionaire.
Financing concession is popular in infrastructure development, especially in sectors like transportation (roads, bridges, airports), energy projects (power plants, grids), and water and sanitation infrastructure.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











