A secured personal line of credit is the same as a regular line of credit except that it is secured by some form of collateral, usually a car or a home. A home equity line of credit, or HELOC, is an example. Because of the securitization, these LOCs generally offer more favorable terms. A personal secured line of credit is a type of loan where a borrower is given access to a specific amount of funds by a lender, which they can draw from whenever they need. In this setup, the line of credit is "secured," meaning it is backed by collateral—an asset or assets that the borrower offers as security for the loan. The borrower isn’t charged interest until they draw from the line of credit. The collateral could be a house, a car, investments, or other assets. If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender can take possession of the collateral to recoup the money lent. A personal line of credit functions similarly to a credit card. However, unlike a credit card, which is unsecured, a personal line of credit is secured by an asset. Once the lender approves your line of credit, you can borrow as much money as you need, up to your credit limit. You're only charged interest on the amount of money you've actually borrowed, not the entire credit limit. The flexibility of a personal line of credit allows for money to be borrowed as needed, rather than in a lump sum. This means a borrower can choose when and how much to draw from the line of credit, subject to the agreed-upon limit. Monthly payments will then be calculated based on the amount borrowed. The credit limit in a personal line of credit refers to the maximum amount of money a borrower can draw from their line of credit. This limit is usually determined based on the borrower's creditworthiness and the value of the collateral. Borrowers have the freedom to use as much or as little of this limit as they need. The interest rate on a personal line of credit is the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the borrowed amount. It is typically lower than that of unsecured loans because the risk to the lender is reduced by the presence of collateral. However, the rate can be variable, which means it can change over the life of the line of credit. Collateral is a borrower's pledge of specific assets to a lender, to secure repayment of a loan. For a personal line of credit, this could be a home, car, savings account, or other valuable assets. If the borrower is unable to repay the loan, the lender has the right to seize the collateral and sell it to recover the loaned funds. Repayment terms are conditions set by the lender that dictate how the borrowed funds should be repaid. These terms specify the duration for repayments, the minimum payment amount, and the consequences of missing payments. For PSLOCs, payments typically include both a portion of the borrowed principal and the accrued interest. Borrowers can access funds from a personal line of credit whenever they need, up to their credit limit. This access can be via checks, online transfers, or even through a dedicated credit card. Unlike term loans, the borrower doesn't receive a lump sum upfront but instead draws funds as required. This means that as the borrower repays the borrowed funds, the amount available for future borrowing replenishes. So, if the borrower fully repays the drawn amount, they once again have access to the full credit limit. One of the major advantages of personal line of credit is that they often come with lower interest rates and fees compared to unsecured lines of credit or credit cards. This is because the lender's risk is mitigated by the collateral, which could be seized in the event of non-repayment. Personal line of credit provide flexibility in both borrowing and repayment. Borrowers can draw as much money as they need, when they need it, up to the credit limit. They also have flexibility in repayment—typically, they can choose to pay more than the minimum required payment, which can reduce the interest costs over the long term. With a personal line of credit borrowers may be able to secure a higher credit limit compared to unsecured lines of credit. This is because lenders are more comfortable offering larger amounts when the loan is secured by collateral. Before applying for a personal line of credit it's important to evaluate your creditworthiness. This includes assessing your credit score, income, employment stability, and overall financial health. Lenders use this information to determine your ability to repay the loan. It's crucial to accurately estimate how much money you need before applying for a personal line of credit. Borrowing more than required can lead to unnecessary interest payments. Similarly, you must consider what collateral you're willing and able to offer. Remember, if you default on your loan, you risk losing the asset used as collateral. Understanding the risks and potential consequences is essential before applying for a personal line of credit. The most significant risk is losing your collateral if you fail to repay the loan. To apply for a personal line of credit you'll need to provide certain documents and information. This may include proof of identity, proof of income, details of your collateral, and other financial information. Each lender will have specific requirements, so it's important to check with your chosen lender. During the application process, lenders will perform a credit check to assess your credit history and financial behavior. They will also consider their underwriting criteria, such as your income, employment status, and the value of your collateral. These checks help lenders evaluate your ability to repay the loan. Once your application is submitted, the lender will evaluate it. This can take a few days to a few weeks, depending on the lender. They will then make a decision based on your creditworthiness and their underwriting criteria. If approved, you will be notified about your credit limit, interest rate, and other terms of the line of credit. A personal secured line of credit is a flexible financial tool that allows individuals to access funds based on the equity they have in an asset, such as a home or vehicle. This type of credit line offers borrowers a higher borrowing limit and lower interest rates compared to unsecured lines of credit. Borrowers are granted a credit limit that they can draw from as needed. The borrower's asset serves as collateral, providing security for the lender. As the borrower repays the borrowed amount, the available credit replenishes, allowing for ongoing access to funds. Key features and terms of personal secured lines of credit include adjustable interest rates, minimum monthly payments, and the ability to borrow repeatedly up to the credit limit. Borrowers should carefully review the repayment terms and obligations to ensure they can meet the financial commitment associated with a secured line of credit.What Is a Personal Secured Line of Credit?
How Personal Secured Lines of Credit Work
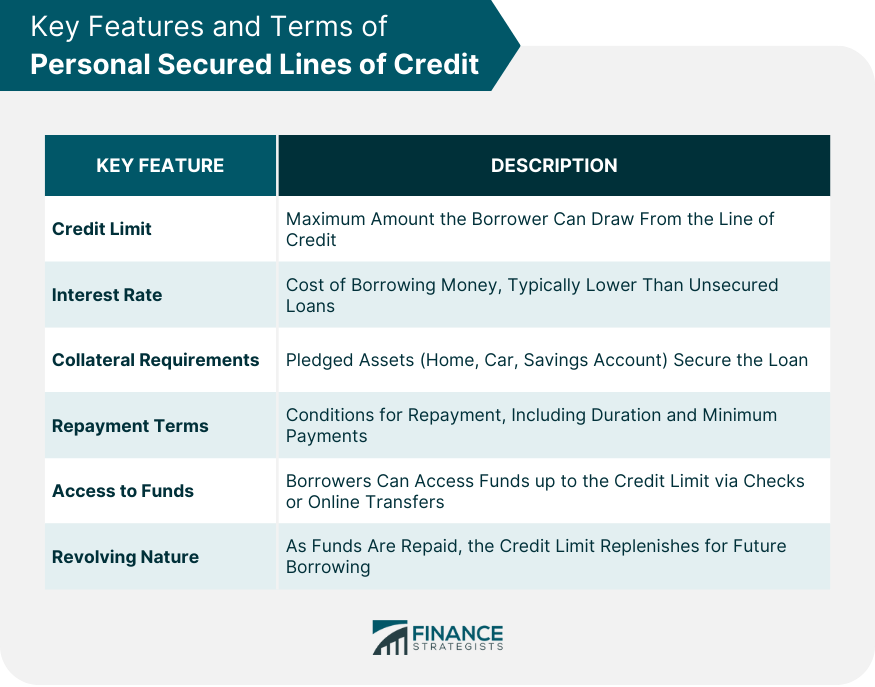
Key Features and Terms of Personal Secured Lines of Credit
Credit Limit
Interest Rate
Collateral Requirements
Repayment Terms
Access to Funds
Revolving Nature
Advantages of Personal Secured Lines of Credit
Lower Interest Rates and Fees
Flexibility in Borrowing and Repayment
Potential for Higher Credit Limits
Factors to Consider Before Applying for a Personal Secured Line of Credit
Assessing Your Creditworthiness
Determining the Amount Needed and Suitable Collateral
Evaluating the Risks and Consequences
Application and Approval Process for a Personal Secured Line of Credit
Required Documentation and Information
Credit Checks and Underwriting Criteria
Timeline and Decision Making Process
Conclusion
Personal Secured Line of Credit FAQs
A personal secured line of credit is a loan that uses an asset (such as real estate, jewelry, or vehicles) as collateral to borrow money with lower interest rates than unsecured loans and higher borrowing limits.
Individuals who have good credit history and can provide the necessary collateral are typically qualified for a personal secured line of credit.
You can use your funds from your personal secured line of credit in any way you wish, such as paying off debts, making investments, starting a business, etc.
The repayment period for a personal secured line of credit typically ranges from one to five years, depending on the lender’s terms and conditions.
Yes, there may be certain fees associated with taking out a personal secured line of credit such as origination or closing fees, annual account maintenance fees, late payment charges, etc. It is best to review the fee structure with your lender before signing up for the loan.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











