An unsecured loan is a loan that is not backed by collateral or any physical assets, such as a house or a car. Instead, the creditworthiness of the borrower and the ability to repay the loan are the only factors the lender considers when deciding whether to approve the loan. Unsecured loans differ from secured loans, which require borrowers to offer some form of collateral to secure the loan. Examples of unsecured loans include credit cards, personal loans, and student loans. These loans are typically used for short-term financings, such as home improvements, medical bills, or unexpected expenses. Have questions about Unsecured Loans? Click here. To qualify for an unsecured loan, borrowers must meet certain requirements set by the lender. Here are some common eligibility factors: Credit score requirements for unsecured loans can vary significantly depending on the lender and the type of loan. Some lenders may require a minimum credit score of 650, while others may require a higher score, particularly for larger loan amounts. Borrowers with a lower credit score may still be able to obtain an unsecured loan, but they may face higher interest rates and fees or have a more limited selection of lenders to choose from. To improve their chances of qualifying for an unsecured loan, borrowers can take steps to improve their credit scores. This includes paying bills on time, reducing outstanding debt, and correcting any errors on their credit report. Lenders will typically consider the income of the borrower when evaluating their eligibility for an unsecured loan. Borrowers will need to provide proof of income, such as pay stubs or tax returns, to demonstrate their ability to repay the loan. The income requirements for unsecured loans can vary depending on the lender and the type of loan. Lenders may also look at the debt-to-income (DTI) ratio of the borrower to determine if they can repay the loan. Lenders may also consider the employment history of the borrower when evaluating their eligibility for an unsecured loan. Borrowers with a stable, long-term employment history are generally seen as lower risk than those with a job hopping or unemployment history. Borrowers who are self-employed may face additional scrutiny from lenders, as they may have a less stable income and may not have the same level of documentation as a traditional employee. The debt-to-income ratio measures the debt of the borrower compared to their income. Lenders will use this information to determine if the borrower has the ability to repay the loan. Different lenders have varying criteria for what is considered an ideal DTI ratio depending on the type and size of the loan. Typically, a DTI of 20% or less is considered low, while a DTI of 43% or lower is commonly used as a guideline for obtaining a qualified mortgage, as recommended by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). To calculate their DTI ratio, borrowers can add up their monthly debt payments, including credit cards, car loans, and other loans, and divide that by their gross monthly income. Ideally, borrowers should aim for a DTI ratio of 36% or lower to improve their chances of qualifying for an unsecured loan. In addition to credit score, income, employment history, and DTI ratio, lenders may also consider other eligibility factors when evaluating the application of the borrower for an unsecured loan. These may include the age, citizenship status, and credit history of the borrower. Lenders generally view borrowers with a longer credit history and a record of making payments on time as less risky. Younger borrowers or those with limited credit history may face more scrutiny and have difficulty qualifying for an unsecured loan. To improve their chances of qualifying for an unsecured loan, borrowers can take steps to establish and build their credit history, such as opening a credit card account and making payments on time. They can also seek the advice of a financial advisor or credit counselor for guidance on improving their credit and overall financial situation. There are several places where borrowers can get unsecured loans. Here are some common options: Banks and credit unions offer personal loans and lines of credit that are typically unsecured. These loans may have lower interest rates and fees than other types of unsecured loans, but they can be more difficult to qualify for. Online lenders have become increasingly popular in recent years, as they offer a convenient way to apply for loans from the comfort of your home. Online lenders typically have looser credit requirements than traditional lenders, but they may charge higher interest rates and fees. Peer-to-peer lending platforms connect borrowers with investors who are willing to fund their loans. These loans are typically unsecured, and the interest rates and fees can vary depending on the platform and the creditworthiness of the borrower. Credit cards are a form of unsecured credit that can be used for short-term financing needs. Credit card issuers typically have looser credit requirements than other lenders but may charge higher interest rates and fees. Obtaining an unsecured loan can be a relatively straightforward process, but it is important for borrowers to take a few steps to ensure they get the best deal from their lender. Here are five steps that borrowers can follow when applying for an unsecured loan. Before applying for an unsecured loan, it is important for borrowers to check their credit score to get an idea of their likelihood of approval and the interest rates they might qualify for. Most lenders prefer borrowers with a credit score of at least 610 to 640, but those with a FICO score of 720 or higher are more likely to get the most competitive rates. Borrowers can use a free online service to check their credit scores and identify areas where they can improve their credit scores before submitting their loan application. When applying for an unsecured loan, borrowers should ensure that any new debt payments fit within their budget. Even though there is no collateral at risk, late payments can still impact their credit score. Most lenders consider the DTI ratio of the borrower when evaluating their loan application, which represents the percentage of the income of the borrower that goes toward monthly outstanding debt payments. Ideally, borrowers should have a DTI of 36% or less to qualify for a new unsecured loan, but this requirement varies by lender. Once borrowers have assessed their finances, they can look for lenders offering the most competitive APRs and flexible repayment terms. Many lenders offer prospective borrowers a quick and easy online prequalification process, which allows borrowers to see what kind of APRs and loan terms they are likely to qualify for without submitting their application. By prequalifying, borrowers can compare loan offers and find the best deal. Before submitting a formal application, borrowers should research the application process of their chosen lender and gather any necessary documentation. Although not always necessary, providing any required documents like tax returns or W-2s before applying can speed up the application, approval, and funding process. Finally, borrowers can complete a loan application and submit it online or in-person. Many lenders now offer a completely online application process, as well as quick approval times and same- or next-day funding. However, the exact application process varies by lender, and borrowers may need to discuss their loan with someone over the phone or in-person. By following these steps, borrowers can secure the best possible deal on an unsecured loan. Once a borrower has been approved for an unsecured loan, they will need to manage the repayment of the loan. Here are some things to keep in mind: The repayment terms for an unsecured loan will vary depending on the lender and the type of loan. Some loans may have fixed interest rates and monthly payments, while others may have variable interest rates and flexible repayment options. Interest rates for unsecured loans can be higher than those for secured loans, as the lender is taking on more risk. Borrowers should compare interest rates from multiple lenders to find the best rate. Late payment fees can add up quickly and make it difficult to repay the loan. Borrowers should make every effort to make their payments on time and avoid late fees. Some lenders may charge prepayment penalties if the borrower pays off the loan early. Borrowers should check the loan agreement to see if there are any prepayment penalties and factor this into their repayment plan. If a borrower is struggling to manage their unsecured loan payments, they may be able to refinance or consolidate their loans. Refinancing involves taking out a new loan with better terms to pay off the existing loan, while consolidation involves combining multiple loans into one. While unsecured loans can be a useful tool for borrowing money, there are risks and considerations to keep in mind. Here are some things to consider: One of the biggest risks associated with unsecured loans is the possibility of defaulting on the loan. If a borrower is unable to make their payments on time, the lender may commission a collection agency to collect the debt or take legal action against the borrower. This can result in additional fees, damage to the credit score of the borrower, and even legal action. Borrowers should always ensure they can afford the loan payments before taking out an unsecured loan. Another risk of unsecured loans is the potential impact on the credit score of the borrower. If borrowers fail to make their payments on time, their credit scores can be negatively impacted. This can make it more difficult to qualify for credit in the future, as lenders may view the borrower as a higher risk. It is important for borrowers to make timely payments and manage their debt responsibly to maintain a healthy credit score. In addition to the risk of default and impact on credit score, there are other risks to consider when taking out an unsecured loan. For example, borrowers should be aware of the potential for fraud, particularly with online lenders. It is important to verify the legitimacy of the lender before submitting any personal or financial information. Borrowers should also be aware that unsecured loans typically come with higher interest rates and fees compared to secured loans. Lastly, borrowers should be cautious not to fall into a cycle of debt, where they continually borrow money to pay off existing debt, ultimately leading to financial instability. Unsecured loans offer borrowers a way to borrow money without having to put up collateral or security. However, they also come with risks and considerations that borrowers should be aware of before taking out a loan. To qualify for an unsecured loan, borrowers will need to meet certain eligibility requirements, such as credit score, income, and employment history. Borrowers can get unsecured loans from various sources, including banks, credit unions, online lenders, peer-to-peer lending platforms, and credit cards. When applying for an unsecured loan, borrowers should be prepared to provide personal and financial information and documentation to verify their income and identity. Managing the repayment of an unsecured loan involves making regular payments on time and avoiding late fees and prepayment penalties. Finally, borrowers should consider the risks and considerations of taking out an unsecured loan, including the potential for default, the impact on their credit score, and other risks such as fraud and high-interest rates and fees. It may be beneficial to seek the advice of a financial advisor to determine if an unsecured loan is a right choice. With responsible borrowing and expert guidance, an unsecured loan can help borrowers achieve their short-term financial goals.What Is an Unsecured Loan?
Qualifying for an Unsecured Loan
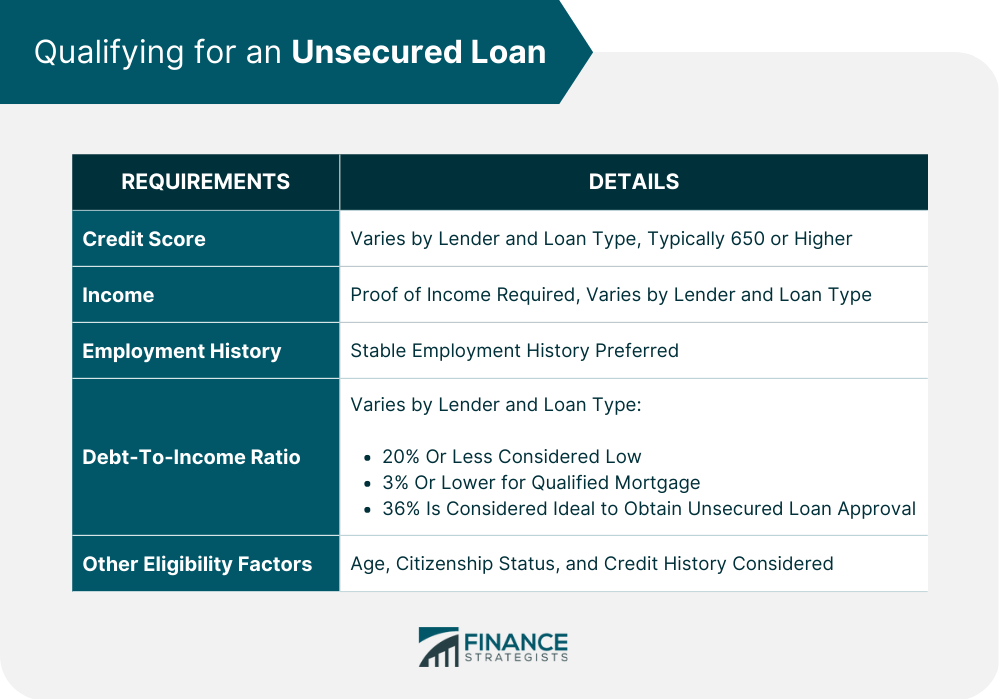
Credit Score Requirements
Income Requirements
Employment History Requirements
Debt-To-Income (DTI) Ratio
Other Eligibility Factors
Where to Get Unsecured Loans
Banks and Credit Unions
Online Lenders
Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms
Credit Cards

How to Apply for an Unsecured Loan
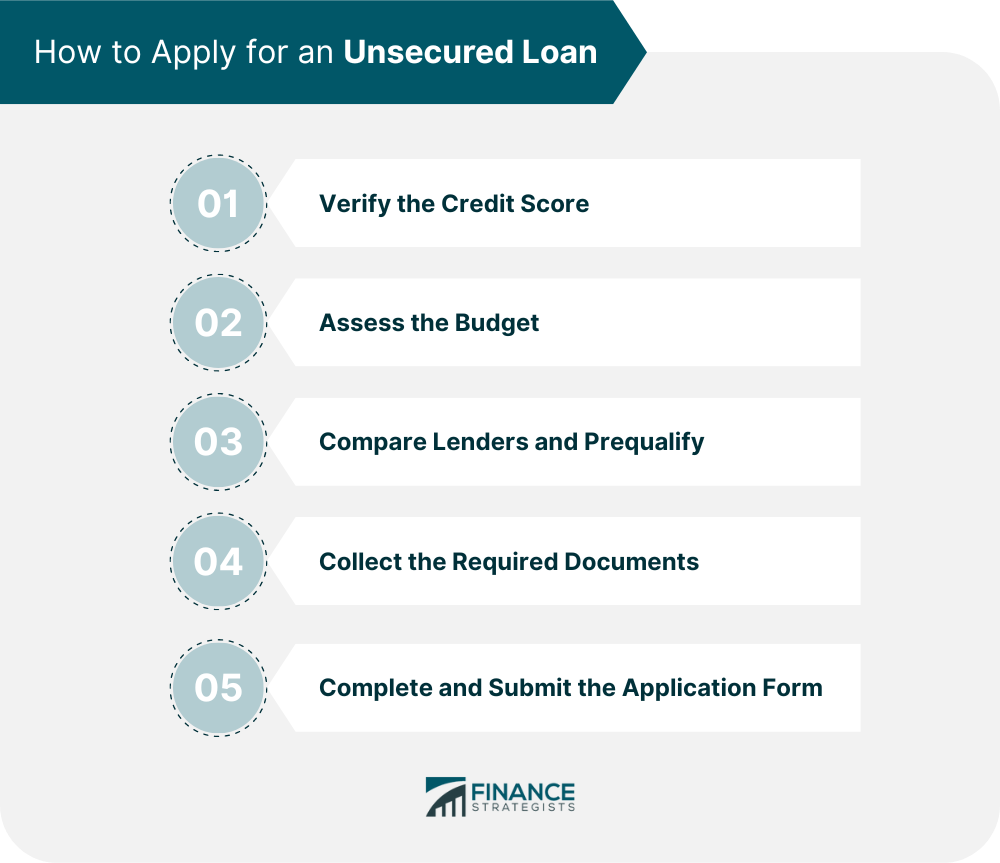
Step 1: Verify the Credit Score
Step 2: Assess the Budget
Step 3: Compare Lenders and Prequalify
Step 4: Collect the Required Documents
Step 5: Complete and Submit the Application Form
Managing Unsecured Loan Repayment
Repayment Terms
Interest Rates
Late Payment Fees
Prepayment Penalties
Options for Refinancing or Consolidating Unsecured Loans
Risks and Considerations on Unsecured Loans
Default and Collection
Impact on Credit Score
Other Risks to Consider
Final Thoughts
Unsecured Loan FAQs
An unsecured loan is a loan that is not backed by collateral or any physical assets. Instead, the lender considers the creditworthiness of the borrower and the ability to repay the loan.
Examples of unsecured loans include credit cards, personal loans, and student loans.
To qualify for an unsecured loan, borrowers typically need to meet certain eligibility requirements, such as having a good credit score, stable income, and a low debt-to-income ratio.
Unsecured loans can be obtained from various sources, including banks, credit unions, online lenders, and peer-to-peer lending platforms.
To manage the repayment of an unsecured loan, borrowers should make regular payments on time and avoid late fees and prepayment penalties. They may also be able to refinance or consolidate their loans if they struggle to make payments.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











