An Automatic Contribution Arrangement (ACA) is a type of retirement savings plan that enables employers to enroll their employees automatically in a retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or similar defined contribution plan. ACA plans are becoming increasingly popular because they help employees save for retirement without taking action, while employers benefit from administrative ease and increased employee satisfaction. ACA plans are often paired with automatic escalation, which increases the employee's contribution rate automatically over time. The main objective of an ACA is to encourage retirement savings among employees by automatically enrolling them in a plan. This helps employees overcome the inertia that often prevents them from initiating their retirement planning. By making it easier for employees to save, ACA plans can help reduce the number of employees who retire without sufficient savings to support their retirement lifestyle. Additionally, ACA plans can also help employers attract and retain employees by offering a valuable benefit that enhances their financial well-being. To understand the specifics of how ACA plans work, let's take a closer look at the enrollment process. The enrollment process for an ACA plan is straightforward. When an employee is hired, they are automatically enrolled in the employer's retirement plan, such as a 401(k), unless they choose to opt out of the plan. If an employee decides to opt out, they can do so within a specified timeframe, typically 30 days. If the employee does not opt out, their contributions will begin automatically, and they will receive a default contribution rate, which is usually set at 3% of their salary. ACA plans have contribution rates and limits that are set by the employer. The contribution rate is the percentage of an employee's salary that is contributed to the retirement plan. The default contribution rate is typically set at 3%, but this can vary depending on the employer's preferences. The contribution limit is the maximum amount of money that an employee can contribute to their retirement plan in a given year. The contribution limit for 2024 is $23,000 for employees under the age of 50 and $30,500 for employees over the age of 50. Employers may also choose to offer matching contributions, which means they will match a portion of an employee's contributions up to a certain percentage. ACA plans offer employees various investment options, including mutual funds, target-date funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Employees can select the investment option that aligns with their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and retirement goals. Employers may also offer a default investment option, which is typically a target-date fund based on the employee's age. Vesting refers to an employee's ownership of the contributions made to their retirement plan. With ACA plans, vesting schedules are determined by the employer and can vary depending on the employer's policies. A vesting schedule determines how long an employee must work for the employer before they are entitled to the full amount of their employer's contributions. One of the most significant benefits of the ACA is that it increases retirement savings. When employees are automatically enrolled in a retirement plan, they are more likely to start saving earlier and contribute more to their retirement savings. The automatic enrollment feature helps employees overcome the initial barriers of inertia and indecision, encouraging them to save for retirement actively. ACA plans encourage retirement preparedness by automatically enrolling employees in a retirement plan. This allows employees to build their retirement savings earlier and helps them maintain a disciplined savings approach over time. With the automatic escalation feature, the employee's contribution rate increases automatically over time, which helps to ensure that they are contributing a sufficient amount to their retirement plan. ACA plans can also help employers reduce the administrative burden associated with managing a retirement plan. By automatically enrolling employees in a plan, employers can reduce the amount of time and effort needed to educate employees about retirement planning, answer questions, and manage the enrollment process. Additionally, the automatic escalation feature helps simplify managing an employee's contribution rate over time. Like any retirement savings plan, ACA has potential drawbacks that employers and employees should be aware of. One potential drawback of ACA plans is that employees may have limited control over their retirement savings. Since the employer selects the plan and investment options, employees may need the ability to customize their retirement plan to align with their specific investment goals and objectives. Another potential drawback of ACA plans is that employees may experience a decrease in their take-home pay. Since contributions are automatically deducted from their paycheck, employees may have less money to use for their immediate needs and expenses. Finally, ACA plans may be less flexible than other retirement plans, such as IRAs or Roth IRAs. Employees may not have the same flexibility to withdraw their contributions or make changes to their investment options. Comparing ACA plans with other retirement plans is essential to determine which option is best suited for your needs. A Traditional IRA is an individual retirement account that allows individuals to contribute pre-tax dollars to a retirement account. Unlike ACA plans, individuals are responsible for opening and funding their own Traditional IRA, and there is no automatic enrollment feature. Additionally, Traditional IRAs may offer more flexibility than ACA plans in terms of investment options and withdrawal policies. A Roth IRA is another type of individual retirement account that allows individuals to contribute after-tax dollars to a retirement account. Like Traditional IRAs, there is no automatic enrollment feature, and individuals are responsible for opening and funding their own Roth IRA. However, Roth IRAs may offer more flexibility than ACA plans in terms of withdrawal policies and tax advantages. A 401(k) is a defined contribution retirement plan that allows employees to contribute pre-tax dollars to a retirement account. Employers may also offer matching contributions up to a certain percentage. Like ACA plans, 401(k) plans have automatic enrollment features, and employees can select from a range of investment options. However, 401(k) plans may be more complex to manage than ACA plans, and employers may have more administrative responsibilities associated with managing a 401(k) plan. To ensure the successful implementation of ACA plans, employers and employees must consider specific factors carefully. Employers have several responsibilities when it comes to managing an ACA plan. They must select the retirement plan and investment options that will be offered to employees. They must communicate the plan details and enrollment process to employees. Then they must manage the employee contribution rates and vesting schedules. Finally, employers must ensure they comply with all legal and regulatory requirements for managing a retirement plan. Employees should carefully consider the benefits and drawbacks of an ACA plan before deciding whether to participate. They should review the plan details, including the contribution rate, investment options, and vesting schedule. Employees should also consider their long-term retirement goals and whether the ACA plan aligns with their investment objectives and risk tolerance. While ACA plans are designed to encourage retirement savings, employees can opt out of the plan if they choose to do so. Employers must provide employees with clear instructions on how to opt out of the plan. Employees should carefully consider the benefits and drawbacks of opting out before making a decision. Automatic Contribution Arrangements are an effective way to help employees save for retirement and assist employers in attracting and retaining top talent. The automatic enrollment feature and contribution rate escalation help employees overcome the barriers of indecision and inertia and encourage retirement preparedness. While ACA plans have some potential drawbacks, such as limited employee control and a possible decrease in take-home pay, their benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. Employers and employees should carefully consider the plan details and their long-term retirement goals before making a decision. To ensure maximum benefits, hiring a retirement planning expert who can provide personalized advice and guidance is advisable. Take charge of your retirement planning today by hiring one and securing a financially stable retirement future.What Is an Automatic Contribution Arrangement (ACA)?
Purpose of Automatic Contribution Arrangement (ACA)
How Automatic Contribution Arrangement (ACA) Works
Enrollment Process
Contribution Rates and Limits
Investment Options
Vesting
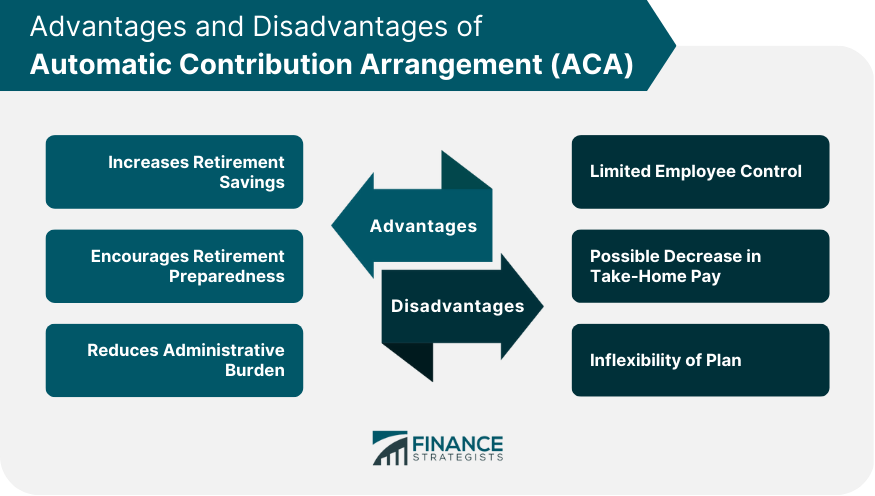
Advantages of Automatic Contribution Arrangement (ACA)
Increases Retirement Savings
Encourages Retirement Preparedness
Reduces Administrative Burden
Potential Disadvantages of ACA
Limited Employee Control
Possible Decrease in Take-Home Pay
Inflexibility of Plan
Comparison to Other Retirement Plans
Traditional IRA
Roth IRA
401(k)
Considerations for Employers and Employees
Employer Responsibilities
Employee Considerations
Opt-Out Options
Conclusion
Automatic Contribution Arrangement (ACA) FAQs
An Automatic Contribution Arrangement (ACA) is a retirement savings plan that allows employers to enroll their employees automatically in a retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or similar defined contribution plan.
The benefits of an ACA plan include increased retirement savings, encouragement of retirement preparedness, and a reduction in administrative burden for employers.
The potential drawbacks of an ACA plan include limited employee control over retirement savings, a possible decrease in take-home pay, and the plan's inflexibility.
An ACA plan works by automatically enrolling employees in a retirement plan when they are hired, with a default contribution rate. Employers select the plan and investment options and manage employee contribution rates and vesting schedules.
Employees should carefully consider the benefits and drawbacks of an ACA plan before deciding whether to opt out. Opting out means missing out on the automatic enrollment and contribution rate escalation features that encourage retirement savings.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











