Automatic enrollment is a process by which employees are automatically enrolled in benefit programs, such as retirement plans or health insurance coverage, without needing to opt into these programs actively. Employers implement automatic enrollment to increase employee participation rates, simplify enrollment, and promote financial security and health coverage for their workforce. Employees are usually enrolled with pre-determined contribution rates and investment or coverage options. Still, they are given the opportunity to opt-out, change their contribution levels, or select different options if they wish. The primary purpose of automatic enrollment is to overcome the inertia and procrastination that may prevent employees from signing up for essential benefits programs. Automatic enrollment has several benefits, including: Increased employee participation rates in benefit programs Encouraging a culture of saving for retirement and promoting financial security Enhancing health insurance coverage and promoting preventive care Simplifying the enrollment process for employees and employers An automatic enrollment system enrolls eligible employees in the benefit programs by default, typically with a pre-determined contribution rate and investment or coverage option. Employees of small businesses or even large ones are informed of their enrollment and given the opportunity to make changes, such as adjusting contribution levels, selecting different investment or coverage options, or opting out of the program altogether. As we delve deeper into the topic, let us examine the key elements forming the foundation of automatic enrollment programs in retirement and health insurance plans. Default Contribution Rate: Employers set a default contribution rate for retirement plans, which is automatically deducted from the employee's paycheck unless the employee chooses to opt-out or modify the rate. Default Investment Options: Employers designate default investment options for retirement plans, usually based on an employee's age, risk tolerance, or other factors. Employees have the option to change these investments if they wish. Employee Notification and Opt-Out Options: Employers are required to notify employees of their automatic enrollment status, the default contribution rate, and investment options. Employees must be provided with the opportunity to opt out of the program or make changes to their contribution levels and investment choices. The following are retirement plans that do not have automatic enrollment: 401(k) Plans: These employer-sponsored retirement plans allow employees to save and invest a portion of their paycheck before taxes are taken out. Employers can offer automatic enrollment to encourage employees to participate in the plan and start saving for retirement. 403(b) Plans: Similar to 401(k) plans, 403(b) plans are available to employees of certain tax-exempt organizations, such as public schools, hospitals, and non-profit organizations. Automatic enrollment can be utilized in these plans as well. SIMPLE IRA Plans: These retirement plans are designed for small businesses with 100 or fewer employees. Employers can establish automatic enrollment to increase participation rates among employees. Now that we clearly understand automatic enrollment let us delve into its advantages, specifically retirement plans. Increased Employee Participation: Automatic enrollment has been shown to significantly increase participation rates in retirement plans, ensuring more employees take advantage of the benefits offered by these programs. Boosting Retirement Savings: By enrolling employees automatically, employers help them start saving for retirement earlier, allowing them to accumulate more savings over time. Tax Benefits for Employers and Employees: Both employers and employees can enjoy tax advantages through automatic enrollment in retirement plans. Having explored the advantages of automatic enrollment in retirement plans, it is essential to discuss the implementation process and key considerations for employers to establish these programs effectively. Plan Design Considerations: Employers must carefully design their automatic enrollment programs, taking into account factors such as default contribution rates, investment options, and employee notification procedures. Legal and Regulatory Requirements: Employers must comply with legal and regulatory requirements for automatic enrollment, such as the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) and Internal Revenue Service (IRS) regulations. Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance: Employers offering health insurance benefits can use automatic enrollment to simplify the process and increase the number of employees who are covered by insurance. This can lead to lower overall healthcare costs for both employers and employees. State and Federal Health Insurance Exchanges: Automatic enrollment can also be implemented in state and federal health insurance exchanges, streamlining the enrollment process for individuals seeking coverage through these marketplaces. Expanding Health Insurance Coverage: Employers can significantly increase the percentage of employees with access to healthcare coverage by automatically enrolling employees in health insurance plans. Simplifying the Enrollment Process: Automatic enrollment reduces the administrative burden associated with manual enrollment processes, making it easier for both employees and employers to manage health insurance coverage. Encouraging Preventative Care: Employees with health insurance coverage are more likely to seek preventative care, which can lead to better overall health and reduced healthcare costs. Plan Design Considerations: Similar to retirement plans, employers must carefully design their automatic enrollment programs for health insurance, taking into account factors such as default coverage options, employee notification procedures, and opt-out provisions. Legal and Regulatory Requirements: Employers must comply with legal and regulatory requirements for automatic enrollment in health insurance plans, such as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and other applicable state and federal regulations. Employee Resistance: Some employees may be resistant to automatic enrollment, viewing it as an infringement on their personal choice or financial autonomy. Employers must clearly communicate the benefits of automatic enrollment and allow employees to opt out or change their plans. Administrative Burden: Implementing automatic enrollment can create additional administrative work for employers, particularly in the initial setup and ongoing maintenance of the program. Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Employers must navigate complex legal and regulatory requirements to ensure that their automatic enrollment programs comply with all applicable laws and regulations. Clear Communication and Education: Employers should provide clear and concise communication to employees about the automatic enrollment process, including the benefits of participating, default options, and the ability to opt-out or make changes to their plans. Periodic Reviews and Updates: Employers should regularly review and update their automatic enrollment programs to ensure they continue to meet their employees' needs and comply with legal and regulatory requirements. Leveraging Technology for Efficiency: Employers can leverage technology, such as payroll and benefits administration software, to help streamline the implementation and management of automatic enrollment programs. As technology continues to advance, automatic enrollment systems are expected to become more sophisticated and user-friendly, further simplifying the enrollment process for employees and employers. Additionally, new innovations in financial planning and healthcare management may lead to the development of more personalized and effective automatic enrollment programs. The widespread adoption of automatic enrollment has the potential to significantly increase retirement savings and healthcare coverage for millions of individuals. By helping employees overcome inertia and procrastination, automatic enrollment can play a critical role in promoting financial security and improving public health. In light of the many benefits and potential positive impacts of automatic enrollment, employers must consider implementing such programs in their organizations carefully. As regulations and workforce needs continue to evolve, staying informed and adapting to these changes will be essential. Employers may benefit from consulting with a professional financial advisor to ensure the successful implementation of automatic enrollment and navigate the complexities involved. These experts can provide valuable guidance in designing and managing automatic enrollment programs that comply with legal and regulatory requirements while meeting your organization's unique needs. Automatic enrollment is a powerful strategy for increasing employee participation in retirement and health insurance plans, fostering financial security, and promoting overall well-being. This article has covered the essential aspects of automatic enrollment, such as its implementation in retirement and health insurance plans, the advantages it brings, and the challenges it poses for employers. Despite the many benefits of automatic enrollment, navigating its complexities, such as legal and regulatory requirements and plan design considerations, can be challenging for employers. By hiring a retirement planning professional, you can access the expertise and guidance necessary to design and manage an automatic enrollment program that is not only legally compliant but also tailored to your organization's unique needs.What Is Automatic Enrollment?
Purpose and Benefits of Automatic Enrollment
How Automatic Enrollment Works
Automatic Enrollment Process Overview
Key Elements of Automatic Enrollment
Automatic Enrollment in Retirement Plans
Types of Retirement Plans With Automatic Enrollment
Advantages of Automatic Enrollment in Retirement Plans
Employers may receive tax credits for setting up the plan, while employees benefit from tax-deferred contributions and potential tax deductions.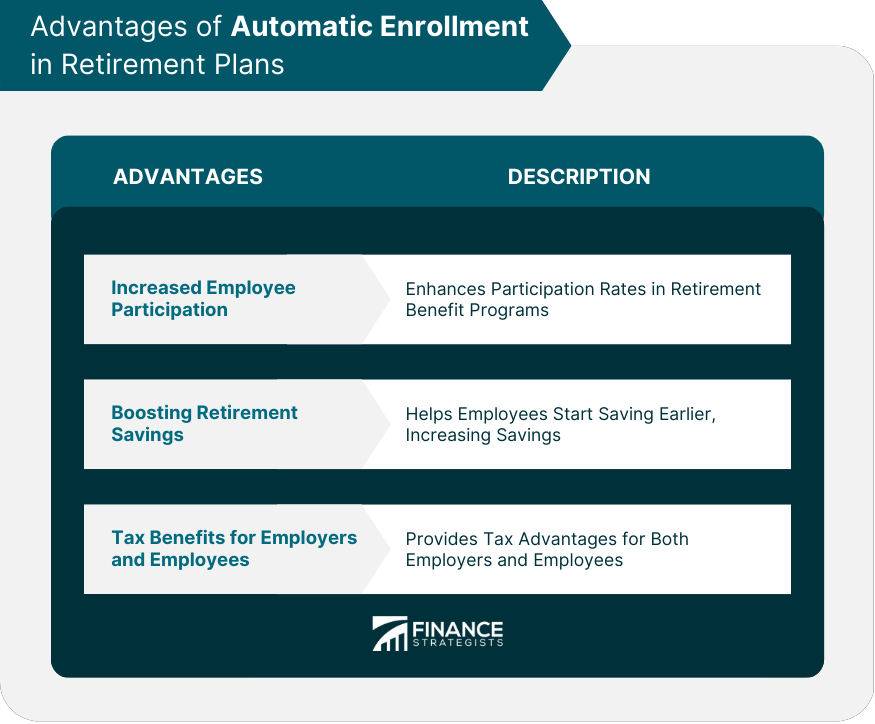
Automatic Enrollment Implementation for Retirement Plans
These requirements ensure that the automatic enrollment process is transparent, fair, and consistent with applicable laws.Automatic Enrollment in Health Insurance Plans
The Role of Automatic Enrollment in Health Insurance
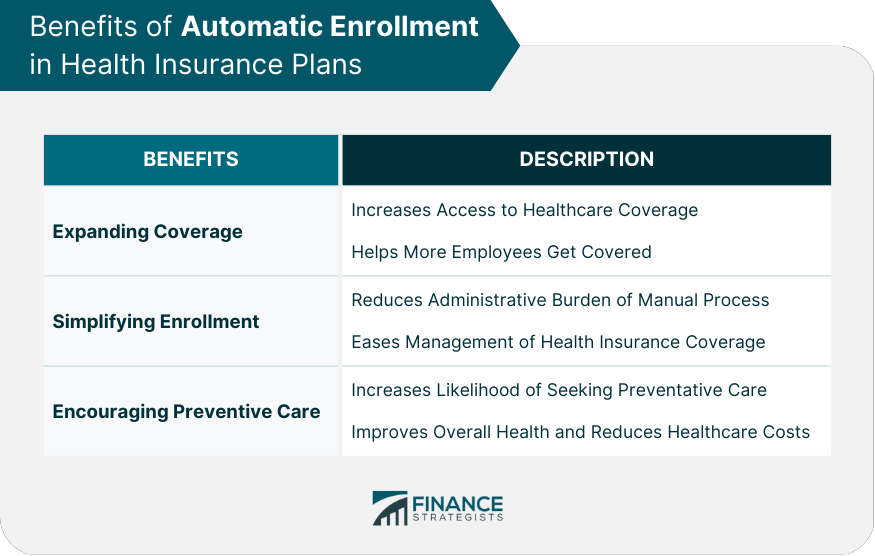
Benefits of Automatic Enrollment in Health Insurance Plans
Automatic Enrollment Implementation for Health Insurance Plans
Potential Challenges and Solutions for Automatic Enrollment
Challenges of Implementing Automatic Enrollment
Solutions and Best Practices for Automatic Enrollment
The Future of Automatic Enrollment
Innovations and Trends in Automatic Enrollment
Potential Impacts on Retirement Savings and Healthcare Coverage
Takeaway
Automatic Enrollment FAQs
Automatic enrollment aims to increase employee participation rates in benefit programs, simplify enrollment, and promote financial security and health coverage for the workforce.
In automatic enrollment for retirement plans, eligible employees are enrolled by default with a pre-determined contribution rate and default investment options. Employees can then choose to opt-out, adjust their contribution levels, or change their investment options.
Advantages of automatic enrollment in retirement plans include increased employee participation, boosted retirement savings, and tax benefits for both employers and employees.
Employers can implement automatic enrollment in health insurance plans by carefully designing their programs, considering default coverage options, employee notification procedures, and opt-out provisions while complying with legal and regulatory requirements.
Challenges of implementing automatic enrollment may include employee resistance, administrative burden, and legal compliance. Employers can address these challenges through clear communication, periodic reviews, leveraging technology, and seeking assistance from retirement planning professionals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











