401(k) plans, named after the tax code that governs them, are tax-advantaged, defined-contribution retirement accounts typically offered by employers. They enable employees to save a portion of their pre-tax salary, reducing their annual income tax bill. While these plans are primarily designed to foster retirement savings by providing tax incentives, under certain conditions, they can also be used for other purposes like education expenses. However, despite the temptation to use these funds for immediate needs, it's vital to remember that the main purpose of a 401(k) is for retirement. Tapping into it prematurely may address current financial requirements but could potentially jeopardize future financial stability. Therefore, careful planning is needed before redirecting 401(k) funds for non-retirement purposes. Under certain conditions, you can use your 401(k) for education expenses. However, the process isn't as straightforward as merely taking money out of a traditional savings account. If you're under the age of 59½, any withdrawal you make from your 401(k) is generally subject to income tax plus a 10% early withdrawal penalty. There are, however, some exceptions to this rule, including certain allowable hardship withdrawals and loans. There are two main ways to use your 401(k) for education expenses without incurring the standard penalties: through hardship withdrawals and loans. Hardship withdrawals from a 401(k) are permissible when there's an immediate and substantial financial necessity, such as education expenses. Nevertheless, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) mandates that these withdrawals should only occur after all other distribution and loan avenues have been exhausted. This method, while accessible, should be a last resort due to the potential impact on your retirement savings. A more flexible option for accessing your 401(k) for education costs is taking a loan against your retirement account. The loan limit is typically the lesser of $50,000 or half of your vested account balance. A significant advantage of this option over hardship withdrawals is that the money repaid, including interest, is re-contributed to your account, thereby mitigating some of the impact on your future retirement funds. Using a 401(k) loan for education expenses may allow you to avoid the 10% early withdrawal penalty and potentially save on taxes. If the loan is repaid within the specified period (usually five years, unless it's used to buy a primary home), the only cost is the interest — which goes back into your account. The funds from a 401(k) loan can be used for any purpose, including education costs. This includes tuition, fees, and other associated expenses for higher education. As long as you can demonstrate that the expenses are necessary and meet the loan terms, you can use a 401(k) loan to help finance an education. If your 401(k) is performing well, it can be an attractive source of funding, especially when compared to high-interest credit cards or private student loans. While you will lose out on potential gains while the money is withdrawn, you will be repaying the loan with interest, which is funneled back into your account. If you can't pay back a 401(k) loan within the specified period, it becomes classified as a distribution. This means the remaining balance is subject to income taxes and possibly a 10% early withdrawal penalty if you're under 59½. Also, if you leave your job (or are let go) while you have an outstanding 401(k) loan, the remaining balance usually becomes due much sooner. When you borrow from your 401(k), you're effectively reducing the amount of money that's invested for your retirement. Even if you pay back the loan, the overall amount may be less than if you had left the money untouched due to missed investment gains during the loan period. Although 401(k) contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, both the principal and interest on a 401(k) loan must be repaid with after-tax dollars. This effectively means you'll pay taxes twice on the same money: once when you repay the loan and again when you withdraw the funds in retirement. A 529 plan is a tax-advantaged savings plan designed specifically for education expenses. These plans can be a more efficient way to save for education, offering tax-free growth and tax-free withdrawals for qualified education expenses. They also have high contribution limits, and anyone can contribute to a plan, making them a great option for family members or friends who want to help. Scholarships and grants offer another way to finance education without dipping into retirement savings. They are often need-based or merit-based and don't have to be repaid. The application process can be competitive, but the potential benefits are significant. Student loans are another common way to pay for education. While these do need to be repaid with interest, federal student loans often have lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options than other types of debt. Plus, unlike with a 401(k) loan, there's no risk to your retirement savings. Before using your 401(k) for education, consider the expected return on investment (ROI) for the educational pursuit. Will this education lead to a significantly higher income or new opportunities that outweigh the depletion of your retirement savings? If the potential ROI is not high, it might be wise to seek other financing methods. Your proximity to retirement is a key factor. If retirement is close, using your 401(k) funds might be risky, as it reduces the time for your investments to rebound and grow. However, if you're further from retirement, you may have more time to replace the funds and recover from any potential investment losses. The current performance and future prospects of your 401(k) investments should also be taken into account. If your investments are doing well, withdrawing from the fund may mean missing out on potential earnings. If the performance is mediocre, it might seem less risky to use these funds, but remember that market conditions can change. Examine all available education financing resources before tapping into your retirement savings. Other options might include grants, scholarships, work-study programs, or student loans. These options could be a more financially prudent route than potentially jeopardizing your future retirement security. Using a 401(k) for education expenses can be advantageous. It can provide a tax-deferred way to save for education, and it can help you reach your retirement savings goals. The convenience and flexibility offered by 401(k) withdrawals or loans for education are undeniably appealing. Yet, it's crucial to remember that these choices come with potential pitfalls, such as early withdrawal penalties, long-term impacts on your retirement nest egg, and double taxation. As such, alternatives like 529 plans, scholarships, grants, and student loans should be explored before tapping into your retirement savings. Given the high stakes and long-term implications of this decision, professional advice from a financial planner or advisor can be invaluable. To ensure your financial future remains secure, seek retirement planning services that can offer tailored strategies for your unique circumstances.Understanding 401(k) Plans
Using a 401(k) for Education Expenses
401(k) Withdrawals for Education Costs
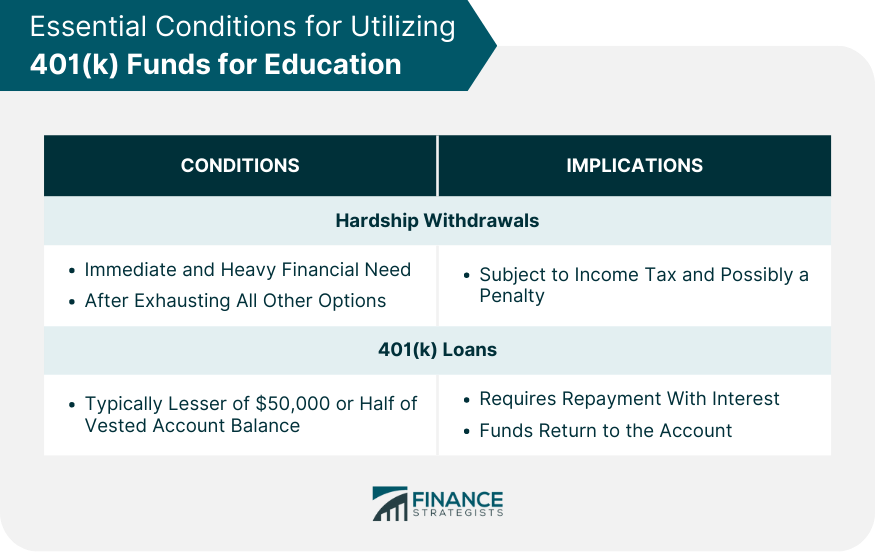
Essential Conditions for Utilizing 401(k) Funds for Education
Hardship Withdrawals
401(k) Loans
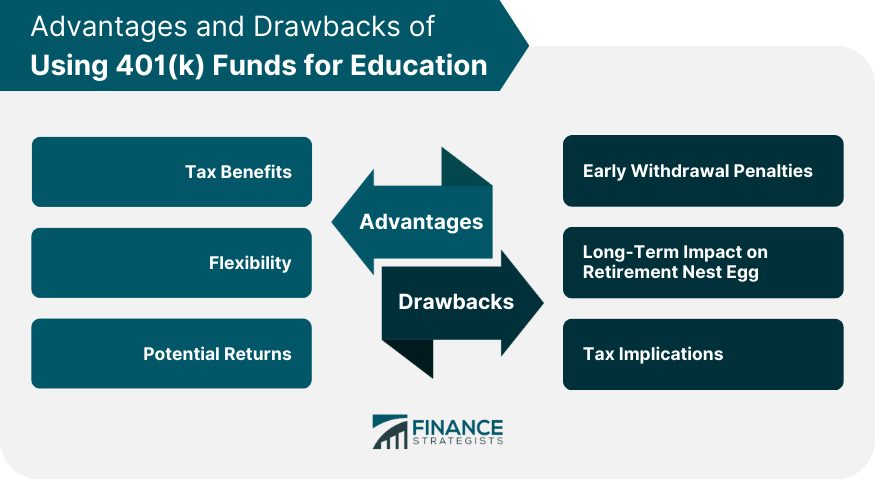
Advantages of Using 401(k) Funds for Education
Tax Benefits
Flexibility
Potential Returns
Risks and Drawbacks of Using 401(k) Funds for Education
Early Withdrawal Penalties
Long-Term Impact on Retirement Nest Egg
Tax Implications
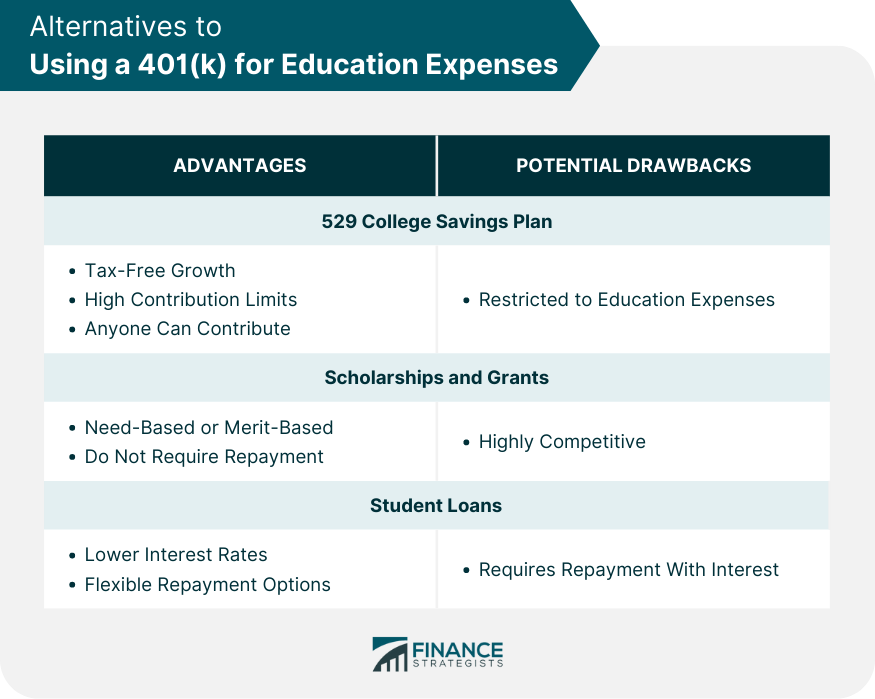
Alternatives to Using a 401(k) for Education Expenses
529 College Savings Plan
Scholarships and Grants
Student Loans
Is Using a 401(k) for Education Right for You?
Key Factors to Consider in the Decision-Making Process
Potential Return on Education Investment
Time Until Retirement
Performance of 401(k) Investments
Availability of Other Education Financing Resources
Bottom Line
Can 401(k) Be Used for Education FAQs
Yes, under certain conditions like hardship withdrawals or loans, you can use your 401(k) for education expenses.
If you take a 401(k) loan for education, you may avoid a 10% early withdrawal penalty and potentially save on taxes.
Drawbacks include potential early withdrawal penalties, a decrease in retirement savings, and double taxation upon repayment.
Alternatives include 529 College Savings Plans, scholarships and grants, and student loans.
Consider factors like potential education returns, time until retirement, 401(k) performance, and seek advice from a financial advisor.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











