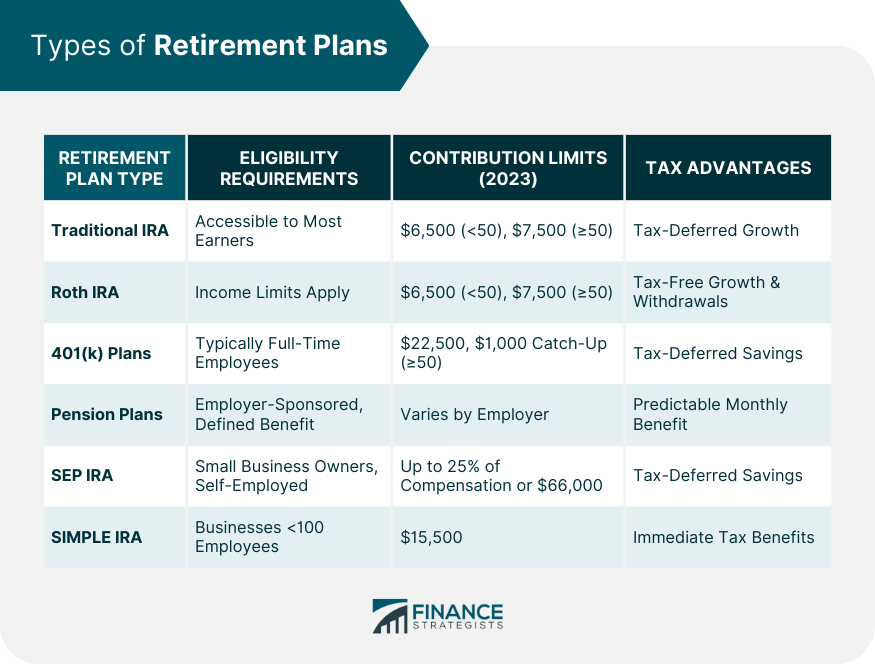
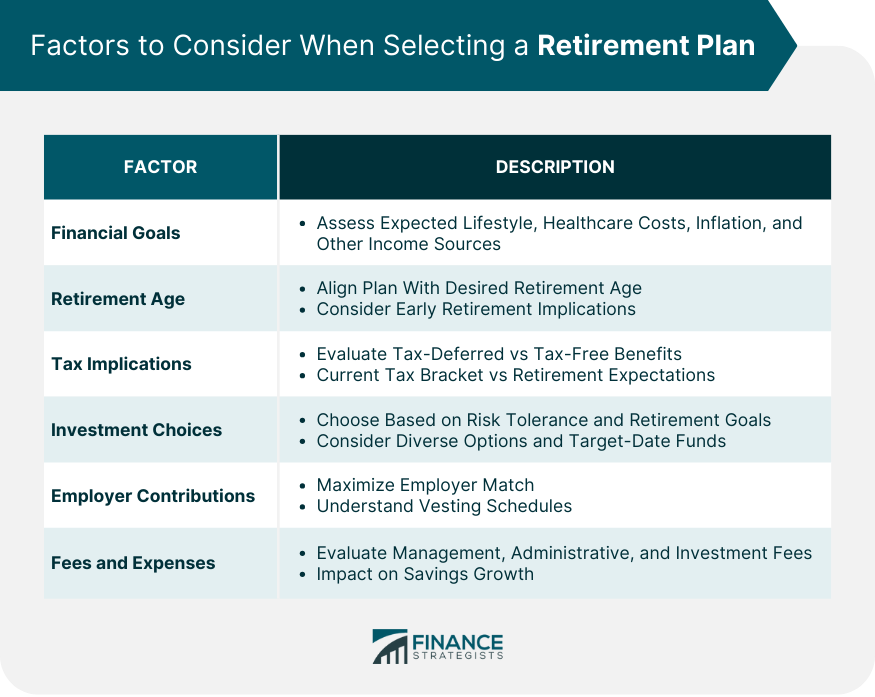
Retirement plans are pivotal in building financial stability for the future. They are designed to accumulate funds that can provide a steady income post-retirement, offering various benefits that cater to different financial situations and goals. A retirement plan is a financial arrangement designed to replace employment income upon retirement. These plans are crucial as they ensure that individuals have a stable source of income when they are no longer working. The right retirement plan not only provides financial security but also offers peace of mind, knowing that your future is secure. Understanding the importance of these plans is the first step in preparing for a financially stable retirement. There are several types of retirement plans, each with unique characteristics and advantages. Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), 401(k) plans, pensions, SEP IRAs, and SIMPLE IRAs are among the most common. Traditional IRAs are accessible to most earners and their spouses, offering a straightforward way to save for retirement. They are especially advantageous for individuals in higher tax brackets during their working years, as they provide tax-deferred growth, reducing your taxable income during the years you contribute. The IRS sets annual contribution limits for traditional IRAs, which are subject to change. For 2023, the contribution limit for a traditional IRA is $6,500 for those under age 50 ($7,500 for those 50 and older). Staying informed about these limits is crucial to maximize your retirement savings. Additionally, individuals aged 50 and over are eligible for catch-up contributions, allowing them to save more as they near retirement. One of the main attractions of traditional IRAs is their tax-deferred growth. You won't pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw the funds, typically during retirement when you may be in a lower tax bracket. This can result in significant tax savings over the life of the account. Understanding withdrawal rules is critical to avoid penalties and unexpected taxes. Withdrawals from traditional IRAs are taxed as ordinary income, and early withdrawals generally incur a penalty. However, there are exceptions for specific circumstances, such as buying a first home or paying for education expenses. Roth IRAs have income limits, which makes them suitable for individuals within certain income brackets. This type of IRA is beneficial for those who anticipate being in a higher tax bracket during retirement, as it offers tax-free growth and withdrawals. Roth IRAs have the same annual contribution limits for traditional IRA, which may change over time. Staying updated with these limits is essential to make the most of your Roth IRA. Contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, meaning there's no tax deduction in the contribution year. The most significant advantage of a Roth IRA is that earnings grow tax-free, and qualified withdrawals in retirement are not taxed. This can be particularly beneficial if tax rates are higher in the future or if your income in retirement puts you in a higher tax bracket. Roth IRAs offer more flexibility with withdrawals compared to traditional IRAs. You can withdraw your contributions at any time without penalty or tax. However, to withdraw earnings tax-free, the account must be at least five years old, and you must be 59 ½ years old unless you meet specific exceptions. 401(k) plans are employer-sponsored retirement savings plans, typically available to full-time employees. Some employers may require a certain period of service before you're eligible to participate. These plans are particularly beneficial if your employer offers matching contributions. 401(k) plans generally have higher annual contribution limits compared to IRAs. These limits are often adjusted for inflation, allowing you to save more each year, especially as you get closer to retirement. The 401(k) plan has a contribution limit of $22,500 for 2023, with a $1,000 catch‑up contribution limit for individuals aged 50 and over. Many employers offer a match on employee contributions to a 401(k) plan, which can significantly enhance your retirement savings. Understanding your employer's matching formula and maximizing your contribution to get the full match can greatly increase your retirement funds. Most 401(k) plans offer a range of investment options, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. This variety allows employees to tailor their investment strategies based on their individual risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. It's important to review and understand these options to ensure your investments align with your retirement objectives. Pension plans, also known as defined benefit plans, are employer-sponsored and promise a specified monthly benefit at retirement. The benefit can be based on factors such as salary history and length of employment. While not as common as they once were, pensions offer a level of security and predictability that is valuable in retirement planning. The calculation of pension benefits often involves a formula that considers the number of years worked and the salary earned during your employment. Understanding how your pension is calculated can help you estimate your retirement income and make informed financial decisions. Most pension plans have a vesting schedule, which is the amount of time you must work for the company before you are entitled to the full pension benefit. Familiarizing yourself with the vesting schedule of your pension plan is essential, especially if you're considering changing jobs or retiring early. SEP IRAs and SIMPLE IRAs are designed for small business owners and self-employed individuals. SEP IRAs are suitable for those with variable income levels, while SIMPLE IRAs are intended for businesses with fewer than 100 employees. Understanding the eligibility requirements for these plans is key to determining if they are right for your business. Both SEP and SIMPLE IRAs have higher contribution limits compared to traditional IRAs, allowing for larger tax-deferred savings. In 2023, the maximum contribution an employee can make from their salary to a SIMPLE IRA is limited to $15,500. For each employee's SEP-IRA, your annual contributions must not exceed the smaller of these two amounts: 25% of their compensation, or $66,000 for the year 2023. These plans offer flexibility and ease of use, making them attractive options for small business owners and self-employed professionals. SEP and SIMPLE IRAs provide immediate tax benefits by reducing taxable income in the year of contribution. The tax-deferred growth of investments in these accounts can significantly enhance retirement savings over time. Like other retirement plans, withdrawals from SEP and SIMPLE IRAs are subject to income tax and potential early withdrawal penalties. Understanding these rules can help you plan your retirement withdrawals strategically to minimize taxes and maximize income. Setting precise financial goals for retirement is essential for selecting the right plan. Begin by assessing your expected lifestyle in retirement. Do you envision a quiet life at home, regular travel, or perhaps starting a new business or hobby? Each lifestyle choice has different financial implications. Consider also potential healthcare costs, inflation, and unexpected expenses. Factor in your projected Social Security benefits and any other predictable income sources, such as rental income or pensions. This comprehensive financial picture will help you calculate the savings needed to support your desired retirement lifestyle. Remember, it's better to overestimate your needs to ensure a comfortable cushion. Deciding when to retire is a personal decision that significantly impacts your retirement planning. If you plan to retire early, you may not have access to certain benefits, like Medicare or full Social Security, requiring a more substantial personal savings plan. Conversely, delaying retirement can maximize Social Security benefits and give your investments more time to grow. It's also crucial to understand the age-related rules of different retirement plans. For instance, 401(k)s and IRAs have specific ages for required minimum distributions (RMDs) and penalties for early withdrawals. Aligning your chosen retirement plan with your desired retirement age is fundamental to a successful retirement strategy. Taxes play a significant role in retirement planning. Traditional IRAs and 401(k)s offer tax-deferred savings, meaning you pay taxes upon withdrawal, ideally at a lower tax rate in retirement. In contrast, Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s provide tax-free income in retirement, although contributions are made with after-tax dollars. Your current tax bracket, potential changes in tax laws, and expected tax rate in retirement should guide your decision. For instance, if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement, a Roth account might be more beneficial. Understanding these nuances can help you choose a plan that optimizes your tax situation both now and in the future. The investment options available within a retirement plan are crucial to achieving your financial goals. A diverse range of options can help balance risk and return. For example, younger savers might prefer a portfolio weighted towards stocks for growth potential, while those closer to retirement may lean towards bonds for stability. Some plans offer target-date funds that automatically adjust the investment mix as you near retirement. It's also important to review these choices regularly and rebalance them as needed to maintain your desired risk level. Always ensure that your investment choices align with your long-term retirement goals and risk tolerance. Employer contributions can significantly enhance your retirement savings. If your employer offers a 401(k) match, aim to contribute at least enough to get the full match – it's essentially free money. Some employers also offer profit-sharing contributions or even contributions to a Roth 401(k). Understand the vesting schedule of these contributions, as it may affect your decision if you're considering changing jobs. Missing out on employer contributions is like leaving money on the table, so make sure to incorporate this aspect into your retirement planning strategy. The fees associated with a retirement plan can greatly impact the growth of your savings. High management fees, administrative fees, and investment fees can erode your investment returns over time. It's crucial to understand all the fees charged by your retirement plan and how they compare to other available options. Some plans might offer lower fees in exchange for a limited choice of investment options or vice versa. Finding a balance between reasonable fees and a robust selection of investment options is key. Regularly reviewing and understanding these fees can help you make more informed decisions and potentially save a significant amount in the long run. A strategic approach to retirement planning involves several key steps, each critical to building a secure financial future. Begin your retirement planning journey by taking a comprehensive look at your current financial situation. Assess your assets, liabilities, and existing savings. This baseline understanding is crucial for setting realistic retirement goals and choosing the most appropriate retirement plan. Define what you want your retirement to look like. Consider factors like desired lifestyle, travel plans, and any other personal goals. Having clear, specific retirement objectives will guide your savings and investment decisions. Based on your financial situation and retirement goals, select a retirement plan that best suits your needs. This selection should be influenced by factors such as tax implications, investment choices, and the potential for employer contributions. Each plan has its unique benefits and limitations, so choose one that aligns closely with your individual retirement strategy and financial situation. Consistency is key in retirement planning. Establish a habit of making regular contributions to your chosen retirement plan. Consider setting up automatic transfers to simplify the process and ensure that you consistently save. Regular contributions, even in small amounts, can compound over time, leading to significant growth in your retirement savings. Retirement planning is not a set-it-and-forget-it process. It requires ongoing attention and adjustments. Review your retirement plan at least annually to ensure it remains in line with your goals. Life changes, such as a new job, marriage, or the birth of a child, might necessitate adjustments to your plan. Additionally, changes in the financial market or new tax laws can impact the effectiveness of your retirement strategy. Regular reviews and adjustments will help you stay on track and adapt to any changes in your personal circumstances or the broader economic environment. Selecting the best retirement plan is a crucial step towards ensuring financial security and peace of mind in your later years. Understanding the various options, including Traditional and Roth IRAs, 401(k) plans, pensions, SEP IRAs, and SIMPLE IRAs, is essential. Each plan offers unique benefits, tax advantages, and contribution limits, catering to different financial situations and goals. When choosing a retirement plan, consider factors such as your financial goals, retirement age, tax implications, investment choices, employer contributions, and associated fees and expenses. A strategic approach involves assessing your current financial status, defining retirement goals, selecting the appropriate plan, making regular contributions, and regularly monitoring and adjusting your plan. By carefully considering these aspects and staying informed about changes in contribution limits and tax laws, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your retirement aspirations and financial circumstances, leading to a stable and fulfilling retirement.Understanding Retirement Plans: The Foundation of Financial Security
Evaluating the Best Retirement Plans
Traditional IRA
Eligibility Requirements
Contribution Limits
Tax Advantages
Withdrawal Rules
Roth IRA
Eligibility Requirements
Contribution Limits
Tax Advantages
Withdrawal Rules
401(k) Plans
Eligibility Requirements
Contribution Limits
Employer Match Details
Investment Options
Pension Plans
How They Are Structured
Benefit Calculations
Vesting Schedules
SEP IRA and SIMPLE IRA
Eligibility Requirements
Contribution Limits
Tax Benefits
Withdrawal Regulations
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Retirement Plan
Financial Goals
Retirement Age
Tax Implications
Investment Choices
Employer Contributions
Fees and Expenses
Step-By-Step Approach to Retirement Planning
Assess Current Financial Status
Define Retirement Goals
Select the Appropriate Retirement Plan
Make Regular Contributions
Monitor and Adjust the Plan

Final Thoughts
Best Retirement Plans FAQs
Roth IRAs are often considered the best retirement plan for tax benefits, offering tax-free growth and withdrawals.
Employer contribution is a key factor in choosing the best retirement plan; plans like 401(k)s with employer match can significantly boost retirement savings.
SEP IRAs and SIMPLE IRAs are typically the best retirement plans for self-employed individuals, offering higher contribution limits and tax benefits.
Roth IRAs are generally the best retirement plan for flexibility with early withdrawals, as contributions can be withdrawn tax and penalty-free.
The best retirement plan for investment choices depends on individual risk tolerance and goals. A plan offering a diverse range of investment options is ideal.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











