A Roth IRA is a type of individual retirement account (IRA) where you contribute or save money for retirement after you have paid taxes on it. Since a Roth IRA is funded by post-tax dollars, you will not have to pay taxes on your contributions or earnings when you withdraw after retirement. A Roth IRA is the direct opposite of a traditional IRA, which is funded by pre-tax dollars. In this case, taxes are deferred until you withdraw your contributions or earnings after retirement. If you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in the future, a Roth IRA can be a good savings vehicle because of its tax-free withdrawals. However, there are also income limitations to opening a Roth IRA, so not everyone will be eligible for this type of retirement account. Have questions about Roth IRA Contribution Limits? Click here.
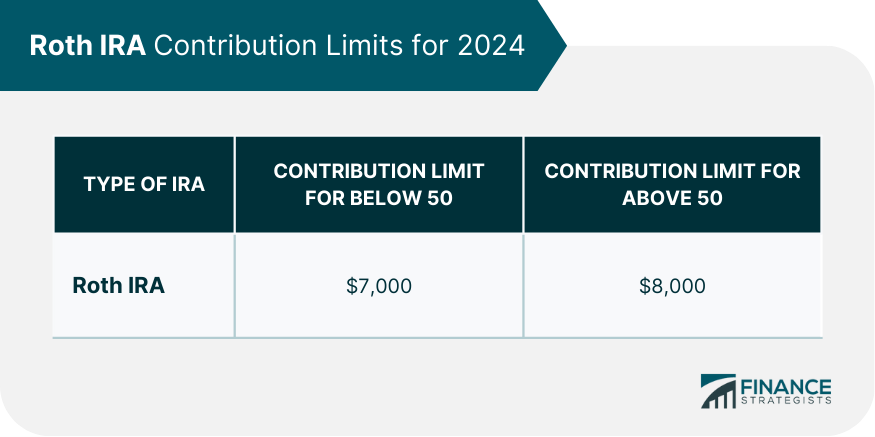
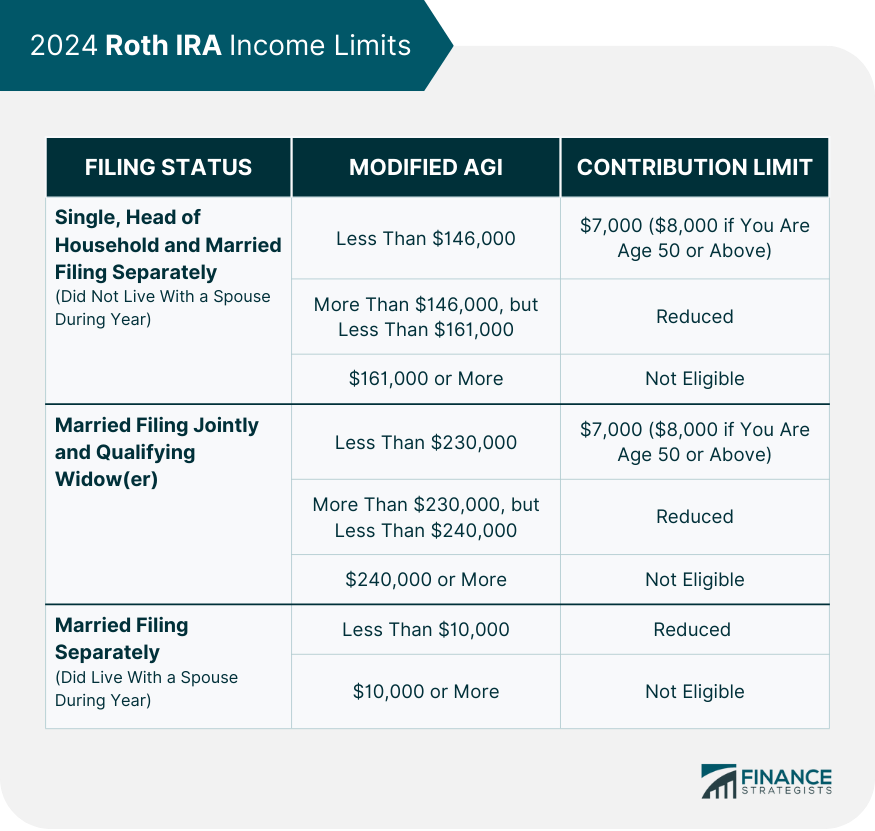
The contribution limit to a Roth IRA for anyone below the age of 50 is $7,000 in 2024. This limit was $6,500 in 2023. For anyone aged 50 and above, a catch-up contribution of $1,000 is allowed. This limit remains unchanged since 2019. Thus, this group’s total Roth IRA contribution for 2024 is $8,000. There are many benefits to increasing your Roth IRA contribution limit. The most obvious one is that you will be able to save more money for retirement. Another benefit is the possibility of paying less taxes. The amount of tax you pay on Roth contributions depends on how much you are earning now. Salary and income usually go up as you get older. Thus, it might be wiser to invest more in a Roth IRA when you are making less money and in a lower tax bracket. Both yearly and monthly contributions to a Roth IRA can be practical, depending on how your income and expense cycle works. Regardless of the frequency you choose, the most important thing is to be consistent in your contributions. If you have accidentally contributed more than the limit in a given year, you should withdraw any excess contributions as a "corrective distribution." This distribution will include both your excess contributions and any income on them. Failure to do this will result in a 6% tax penalty on the excess amount, charged for every year that it remains in the account. You can contribute to a Roth IRA if you are earning an income and you meet certain requirements. These conditions include filing status and modified adjusted gross income (MAGI). If you have an annual income on the higher end of your category, your contribution limit may be reduced. If you are single, head of household, or married though filing separately and did not live with your spouse at any time during the year, your maximum income limit for Roth IRA in 2024 is $161,000. If your annual income is greater than $146,000 but less than $161,000, your contribution limit may be reduced. If you and your spouse are filing jointly or you are a qualifying widow(er), your Roth IRA income limit for 2024 is $230,000. If your annual income is between $230,000 to $240,000, your contribution limit may be reduced. If you are married, filing separately, and you lived with your spouse at any time during the year, your Roth IRA income limit for 2024 is $10,000. If your annual income is less than $10,000, your contribution limit may be reduced. If you are not eligible for a Roth IRA due to income, you can explore other alternatives such as setting up a backdoor Roth IRA. There are rules you must observe if you are considering withdrawing funds from your Roth IRA. For instance, regardless of when a withdrawal is made, you must abide by the five-year rule. The five-year rule states that withdrawal of earnings without penalties is allowed provided that you are at least 59 ½ years old and it has been at least five years since your first contribution. There are also rules specifically covering withdrawal before retirement and withdrawal after retirement. If you are looking for a retirement savings account that offers some flexibility on withdrawals, a Roth IRA might be a good option for you. With Roth IRAs, you can withdraw your contributions even before retirement without incurring a penalty. This difference gives it a big advantage over a traditional IRA. Generally, the earnings in a Roth IRA cannot be withdrawn penalty-free until you reach the age of 59 1/2. However there are some exceptions, which include: A Roth IRA also provides more flexibility for withdrawals after retirement. Unlike other retirement savings accounts, there is no minimum required distribution for Roth IRAs. This means that you are not required to withdraw a certain amount yearly when you reach retirement age. Instead, you can keep growing your money tax-free until you are ready to withdraw it. There are other rules pertaining to eligibility and contribution for Roth IRA. With a traditional IRA, you are required to stop making contributions when you reach the age of 70.5, but Roth IRAs have no such rule. Thus, you can continue making contributions to your Roth IRA for as long as you live. This makes it a valuable asset for those who want to build up wealth to transfer to their heirs. Due to the contribution and income limits involved in a Roth IRA, some people open up other retirement accounts and contribute to all of them in the same year. Below are some common combinations: You may be able to contribute to both a Roth and a traditional IRA if you meet the income limits, but your combined contributions for both cannot exceed $6,500. It is also possible to have both a 401(k) and a Roth IRA. Since 401(k) plans have separate contribution limits from IRAs, you may contribute up to the maximum for each type. For instance, in 2024, if you are under the age of 50, you may contribute up to $23,000 in a 401(k) and up to $7,000 in a Roth IRA. With the options stated above, you can maximize the amount of money in your tax-advantaged retirement savings accounts. A Roth IRA is an attractive retirement savings option because contributions are made with after-tax dollars, and all qualifying withdrawals are tax-free. The Roth IRA contribution limit for 2024 is $7,000, with an additional catch-up contribution of $1,000 for individuals who are aged 50 and above. There are also income limits that Roth IRA owners need to take note of. These income limits vary according to your filing status and modified adjusted gross income (MAGI). If you are looking for a retirement savings account that offers some flexibility on withdrawals, a Roth IRA might be a good option for you. With Roth IRAs, you can withdraw your contributions even before retirement without incurring a penalty. However, there are separate rules for withdrawing earnings. One of them is the five-year rule which states that withdrawal of earnings without taxes or penalties is allowed provided that you are at least 59 1/2 years old and it has been at least five years since your first contribution. You can contribute to other retirement savings accounts such as a traditional IRA or 401(k) in the same year as your Roth IRA. However, these accounts have their own contribution limits that you need to take note of as well.What Is a Roth IRA?
Roth IRA Contribution Limit for 2024
Benefits of Increasing Your Contribution
When Is the Best Time of the Year to Contribute to Your IRA?
What to Do When You Have Over-Contributed
Roth IRA Income Limit for 2024
Single, Head of Household and Married Filing Separately (Did Not Live With a Spouse in 2024)
Married Filing Jointly and Qualifying Widow(er)
Married Filing Separately (Did Live With a Spouse in 2024)
Roth IRA Withdrawal Rules
Roth IRA Withdrawal Before Retirement
Roth IRA Withdrawal After Retirement
Other Rules Related to Eligibility and Contribution for Roth IRA
Roth IRAs and Age Limits
Contributing to Multiple Retirement Accounts in the Same Year
Roth IRA and Traditional IRA
Roth IRA and 401(k)
The Bottom Line
Roth IRA Contribution Limit FAQs
No, you don't have to contribute every month. You can make Roth IRA contributions anytime during the year. However, keep in mind that the sooner you make your contribution, the more time your money has to grow.
If you are under 50, you can contribute $7,000 per year to your Roth IRA or $583 per month. If you are over 50, you can contribute $8,000 per year or $667 per month. There is no monthly limit, only the annual limit.
The five-year rule states that the withdrawal of earnings without taxes or penalties is allowed provided that you are at least 59 1/2 years old and it has been at least five years since your first contribution.
If you no longer qualify for a Roth IRA because you have exceeded the income limit, you can make after-tax contributions to a Roth 401(k) instead.
If you have contributed too much to your Roth IRA, there are a few ways to fix the problem. You can withdraw the excess money, recharacterize your Roth IRA as a traditional IRA, or carry over the excess contribution to next year's Roth. Until this situation is remedied, you will be subject to a 6% tax penalty every year.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











