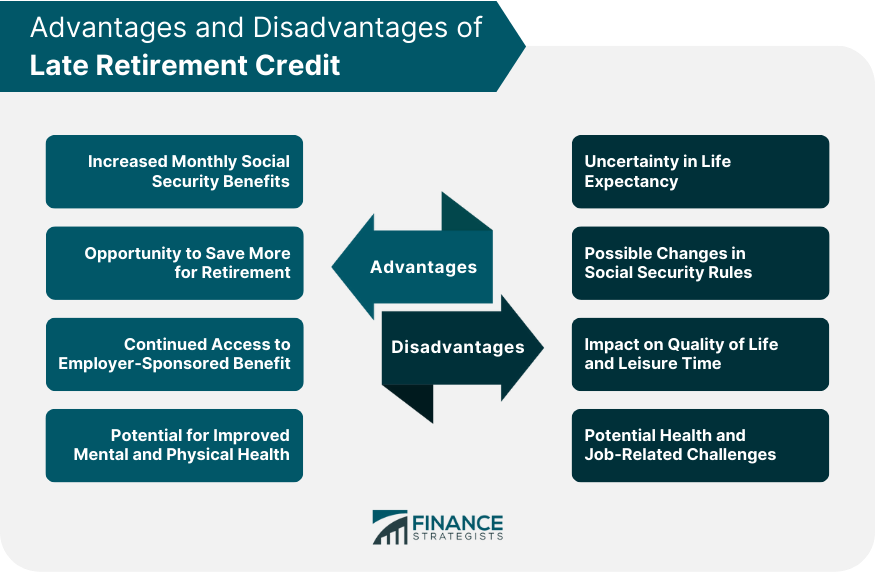
Late Retirement Credit (LRC) is a financial incentive provided by the Social Security Administration for individuals who choose to delay claiming their Social Security benefits beyond their Full Retirement Age (FRA). LRCs increase the amount of monthly Social Security benefits a person receives as a reward for postponing retirement. The credit percentage depends on the individual's birth year and the age at which they claim Social Security benefits. By understanding and strategically utilizing LRC, retirees can enhance their retirement income and improve their financial security during their retirement years. Understanding the Social Security Administration's rules and regulations is crucial to maximizing your benefits. Full Retirement Age is the age at which you can receive your full Social Security benefits, which differs based on your birth year. If you delay retirement beyond FRA, you can earn late retirement credits that boost your monthly benefits. These credits can increase your benefits by approximately 8% every year you delay retirement until age 70. After age 70, no additional LRCs are accrued. Knowing the rules and regulations, you can make informed decisions about your retirement planning and potentially increase your benefits. When considering delaying retirement to take advantage of late retirement credits, it's important to consider personal factors. One such factor is your financial situation, as it can determine whether delaying retirement is a feasible option. Your overall health is another crucial factor, as it can impact your ability to work longer and take advantage of LRCs. The availability of job opportunities in your field is also important, as it can influence your decision to work beyond your full retirement age. Finally, the presence of other retirement income sources can affect the need to rely on LRCs. By weighing these personal factors, you can decide whether delaying retirement and earning LRCs is the right choice for you. Determining the credit percentage for Late Retirement Credit depends on two key factors: the individual's year of birth and the age at which they start claiming Social Security benefits. The birth year defines the credit percentage, as it is used to establish the full retirement age. The age at which a person claims Social Security benefits also influences the LRC percentage. Delaying retirement beyond the full retirement age can result in an increased credit percentage, leading to higher monthly benefits. The impact of LRC on monthly Social Security benefits is crucial for anyone planning their retirement income. To better understand the increase in monthly payments resulting from LRC, comparing your benefits before and after applying is essential. You can assess the difference in your monthly Social Security income by doing so. Delaying retirement can also have a significant impact on your Social Security benefits, potentially resulting in a higher monthly income during retirement. This delay can offer increased financial security and stability. As a result, it's essential to consider the potential benefits of delaying retirement and the impact it can have on your overall retirement income planning. Increased Monthly Social Security Benefits: LRCs can significantly boost your monthly Social Security payments, ensuring a more comfortable retirement. Opportunity to Save More for Retirement: Working longer allows you to save more for your retirement years, potentially improving your financial security. Continued Access to Employer-Sponsored Benefits: Delaying retirement can enable you to access valuable employer-sponsored benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Potential for Improved Mental and Physical Health: Staying engaged in the workforce may improve mental and physical well-being. Uncertainty in Life Expectancy: Life expectancy can be unpredictable, making it difficult to determine when to claim Social Security benefits. Possible Changes in Social Security Rules: Future changes in Social Security regulations may impact the benefits of LRC. Impact on Quality of Life and Leisure Time: Working longer may reduce the time available for leisure activities and impact your overall quality of life. Potential Health and Job-Related Challenges: Prolonged employment may pose health risks and job-related challenges, particularly in physically demanding professions. Estimating Retirement Income Needs: Properly assessing your financial needs during retirement can help determine if LRCs benefit you. Evaluating Other Sources of Income: Consider your other income sources when deciding whether to pursue LRCs. Part-time or flexible work arrangements allow you to continue earning income while gradually transitioning into retirement. Social Security Calculators: Online tools can help you estimate the impact of LRC on your benefits. Financial Advisors: Consulting with financial professionals can provide tailored advice on maximizing LRC. Retirement Planning Seminars: Attending seminars can provide valuable insights and strategies for maximizing LRC. Thresholds for Taxation: LRC may impact the taxation of your Social Security benefits depending on your total income. Strategies for Minimizing Taxes on Benefits: Tax planning can help you minimize the taxes on your Social Security benefits. Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): Working longer may affect the timing and amount of RMDs from retirement accounts. Traditional and Roth IRAs: LRCs can affect managing your IRA accounts. 401(k) and Other Employer-Sponsored Plans: The decision to delay retirement can impact your employer-sponsored retirement plans. Late Retirement Credit is a financial incentive provided by the Social Security Administration that rewards individuals who delay claiming their Social Security benefits beyond their Full Retirement Age. Factors such as understanding the Social Security Administration's rules and regulations, personal financial situations, and health considerations influence the decision to delay retirement and earn LRC. Calculating the credit percentage based on birth year and age at claiming Social Security benefits helps individuals assess the impact on their monthly Social Security payments. There are several advantages to earning LRC, including increased monthly Social Security benefits, the opportunity to save more for retirement, continued access to employer-sponsored benefits, and potential improvements in mental and physical health. However, there are also disadvantages to consider, such as uncertainty in life expectancy, potential changes in Social Security rules, the impact on quality of life and leisure time, and potential health and job-related challenges. To maximize LRC, individuals can assess their personal financial situation, consider part-time or flexible work arrangements, utilize financial planning tools and resources, and understand the impact of LRC on taxes and other retirement income sources.What Is Late Retirement Credit?
Factors Influencing the Late Retirement Credit
Social Security Administration Rules and Regulations
Personal Factors
Calculation of Late Retirement Credit
Determining the Credit Percentage
Impact on Monthly Social Security Benefits
Advantages and Disadvantages of Late Retirement Credit
Advantages
Disadvantages
Strategies for Maximizing Late Retirement Credit
Assessing Personal Financial Situation
Considering Part-Time or Flexible Work Arrangements
Utilizing Financial Planning Tools and Resources

Late Retirement Credit and Taxes
Impact on Social Security Benefit Taxation
Potential Impact on Other Retirement Income Sources
Conclusion
Late Retirement Credit FAQs
Late retirement credits (LRC) are additional credits that are added to your Social Security benefits if you delay receiving them beyond your full retirement age.
You can start earning late retirement credits once you reach your full retirement age, which varies based on your birth year. For those born after 1960, the full retirement age is 67.
Every year you delay claiming Social Security benefits beyond your full retirement age, your benefits will increase by approximately 8% up until age 70.
The decision to delay retirement and earn late retirement credits should be based on your individual financial situation and goals. However, delaying retirement can result in a higher monthly Social Security benefit, providing increased financial security during retirement.
No, late retirement credits can only be earned if you delay receiving Social Security benefits beyond your full retirement age. Once you start receiving benefits, they will not increase due to any additional credits earned.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











