A Plan Document is a formal, written document that outlines the rules, regulations, and provisions governing a retirement plan. Retirement plans are established by employers, plan sponsors, or plan administrators to help employees save for retirement. These documents provide crucial information about the plan's design, eligibility criteria, contribution limits, investment options, distribution rules, and other pertinent details. A well-maintained plan document helps ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, protecting the plan sponsor from potential legal or financial consequences. Maintaining a compliant plan document helps plan sponsors avoid penalties and fines resulting from noncompliance with regulatory requirements. A compliant plan document is essential for preserving the plan's tax-qualified status, which provides significant tax benefits to both the plan sponsor and participants. The plan document begins with the plan name and the effective date, which identifies the start date of the plan and its provisions. The plan sponsor, typically the employer, and the plan administrator are responsible for the operation and management of the plan. The plan document should clearly outline their roles, responsibilities, and contact information. Age Criteria: The plan document should specify the age requirement for employees to become eligible to participate in the retirement plan. Service Criteria: The service criteria indicate the length of time an employee must work for the employer before becoming eligible to participate in the plan. Employee Contributions: The plan document should outline the rules governing employee contributions, such as contribution limits, deferral rates, and any applicable catch-up contributions for older participants. Employer Contributions: The employer's contributions to the plan, such as matching contributions or profit-sharing contributions, should be detailed in the plan document, including the formula for calculating these contributions. Rollover Contributions: The plan document should include provisions for accepting rollover contributions from other retirement plans, as well as any limitations or restrictions on such contributions. The plan document should clearly define the vesting schedule, which outlines when participants gain full ownership of their employer's contributions to the plan. The investment options available to plan participants should be detailed in the plan document, along with any restrictions, fees, or other relevant information. Normal Retirement Distributions: The plan document should outline the rules for normal retirement distributions, including the age at which participants can begin receiving benefits and the various payment options available. Early or Late Retirement Distributions: The plan document should provide details about early or late retirement distributions, including any penalties or adjustments that may apply. Required Minimum Distributions: The plan document should include information on required minimum distributions (RMDs), including the age at which RMDs must begin and the formula for calculating the annual distribution amount. The plan document should provide details on plan loans and hardship withdrawals, including eligibility requirements, limitations, and repayment terms. The procedures for amending or terminating the plan should be outlined in the plan document, including any notice requirements or other applicable provisions. IRS Regulations: The plan document should demonstrate compliance with IRS regulations, including those related to contribution limits, vesting schedules, and nondiscrimination testing. ERISA Regulations: The plan document should address compliance with the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA), which governs the administration and management of retirement plans in the United States. Non-discrimination Testing: The plan document should include provisions for conducting nondiscrimination testing to ensure that the plan does not disproportionately benefit highly compensated employees. A well-structured plan document provides clear and comprehensive information about the retirement plan, helping participants understand their benefits and make informed decisions about their retirement savings. The plan document serves as a roadmap for participants to achieve their retirement goals, outlining the various contribution options, investment choices, and distribution strategies available to them. A clear and comprehensive plan document facilitates effective communication between the plan sponsor, participants, and service providers, ensuring that all parties understand their roles and responsibilities in the retirement plan. Plan sponsors should review and update the plan document regularly to ensure that it remains current and accurately reflects the plan's provisions and objectives. Changes in legislation may necessitate amendments to the plan document. Plan sponsors should monitor regulatory changes and update the plan document as needed to maintain compliance. As the plan sponsor's objectives evolve, or as plan design changes are implemented, the plan document should be updated to reflect these modifications, ensuring that participants are well-informed about their retirement plan. A well-structured retirement plan document plays a vital role in the effective administration and management of a retirement plan. It serves as a legal foundation and operational guide, outlining key components such as eligibility requirements, contribution types, vesting schedules, investment options, distribution rules, and compliance guidelines. By regularly reviewing and updating the plan document to address legislative changes and modifications in plan design or sponsor objectives, plan sponsors can maintain compliance with legal and regulatory requirements and preserve the plan's tax-qualified status. A clear and comprehensive plan document facilitates communication between plan sponsors, participants, and service providers, ultimately contributing to a successful retirement planning experience for all parties involved.Definition of Retirement Plan Document
Importance of Plan Document Compliance
Ensuring Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Avoiding Penalties and Fines
Maintaining the Tax-Qualified Status of the Plan
Components of a Retirement Plan Document
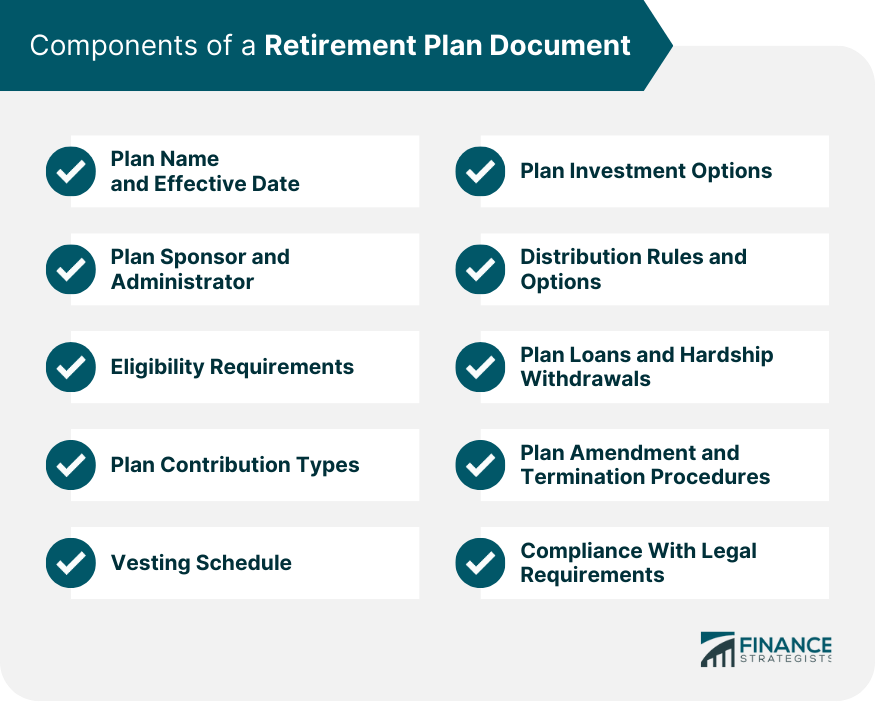
Plan Name and Effective Date
Plan Sponsor and Administrator Information
Eligibility Requirements
Plan Contribution Types
Vesting Schedule
Plan Investment Options
Distribution Rules and Options
Plan Loans and Hardship Withdrawals
Plan Amendment and Termination Procedures
Compliance With Legal Requirements
Role of Plan Documents
Ensuring Clarity and Understanding of the Plan
Establishing a Roadmap for Retirement Goals
Facilitating Communication Between Plan Sponsor, Participants, and Service Providers
Keeping the Plan Document Up-To-Date
Reviewing and Updating the Plan Document Regularly
Amending the Plan Document Due to Changes in Legislation
Updating the Plan Document to Reflect Changes in Plan Design or Sponsor Objectives
Conclusion
Plan Document FAQs
A retirement plan document serves as the legal foundation and operational guide for the plan sponsor, administrator, and participants, outlining the plan provisions, eligibility requirements, and compliance guidelines.
While there is no set frequency for reviewing and updating a plan document, it is advisable to review it regularly, at least annually, to ensure its accuracy, compliance with regulations, and alignment with plan sponsor objectives.
Key components of a retirement plan document include eligibility requirements, contribution types, vesting schedules, investment options, distribution rules, plan loans, hardship withdrawals, and compliance with legal requirements.
Changes in legislation may necessitate amendments to the plan document to maintain compliance with new laws and regulations, protect the plan's tax-qualified status, and avoid penalties or fines.
Maintaining a compliant plan document is essential for preserving the plan's tax-qualified status, avoiding penalties and fines, and ensuring that the retirement plan is effectively administered and managed according to applicable laws and regulations.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











