Post-divorce retirement planning refers to the process of evaluating and adjusting one's retirement savings, investments, and financial goals following a divorce. Divorce can have a significant impact on both spouses' financial situations, including the assets and income available for retirement. Post-divorce retirement planning is crucial in ensuring that individuals can still achieve their desired retirement lifestyles after their marriages have ended. The process involves assessing one's financial situation, setting new retirement goals, and developing strategies to achieve those goals. This may include reevaluating asset allocation, choosing new retirement accounts, and adjusting contributions to maximize savings. The importance of post-divorce retirement planning cannot be overstated. Divorce often results in significant financial changes, including reduced income, divided assets, and increased expenses. These changes can have a lasting impact on an individual's ability to save for and enjoy a comfortable retirement. By proactively planning for retirement after a divorce, individuals can ensure that they are on track to achieve their financial goals and maintain their desired standard of living during their retirement years. Furthermore, post-divorce retirement planning can help individuals navigate the complex financial and legal issues that often accompany divorce, such as asset division, spousal support, and tax implications. Proper planning can help individuals avoid costly mistakes and make informed decisions that support their long-term financial well-being. Asset division is a critical aspect of the divorce process, as it determines how the couple's shared property and financial assets will be divided between the two parties. This process can have a significant impact on each individual's financial situation and ability to save for retirement. Common assets subject to division include real estate, investments, savings accounts, and retirement accounts. The division of assets can vary depending on the couple's specific circumstances and the laws of the state in which they reside. In some cases, assets may be divided equally. In others, a more equitable distribution based on factors such as the length of the marriage, each spouse's earning capacity, and the needs of any children may be used. Spousal support, also known as alimony or maintenance, is a payment made by one spouse to the other to help maintain their standard of living after the divorce. The amount and duration of spousal support payments can vary greatly depending on factors such as the length of the marriage, the earning capacity of each spouse, and the needs of any children. Spousal support can have a significant impact on both the payer and the recipient's financial situations and ability to save for retirement. For the payer, spousal support payments may reduce the amount of disposable income available for retirement savings. For the recipient, spousal support may provide a critical source of income to help cover living expenses and contribute to retirement savings. Divorce can have various tax implications that can affect an individual's financial situation and retirement planning. For example, the division of assets may result in capital gains taxes, and spousal support payments may be tax-deductible for the payer and taxable income for the recipient. Additionally, changes in filing status from married to single can impact tax brackets and deductions. Understanding the tax implications of divorce is essential for effective post-divorce retirement planning. Individuals should consult with a tax professional to ensure they are aware of the potential tax consequences of their divorce and make informed decisions regarding their financial future. Retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s, IRAs, and pensions, are often subject to division during the divorce process. The specific rules for dividing retirement accounts can vary depending on the type of account and the laws of the state in which the couple resides. In many cases, a Qualified Domestic Relations Order (QDRO) is used to divide retirement accounts without incurring taxes or penalties. The division of retirement accounts can have a significant impact on each spouse's ability to save for retirement. Post-divorce retirement planning should take into account the division of these accounts and the resulting changes to each individual's retirement savings and investment strategies. Social Security benefits can play a significant role in an individual's retirement income strategy. Divorced individuals may be eligible for benefits based on their own earnings record or their former spouse's record, depending on the specific circumstances of their situation. Understanding the rules surrounding Social Security benefits for divorced individuals is crucial for accurate retirement planning. Health care costs can have a significant impact on an individual's retirement savings and income needs. As individuals age, their health care expenses are likely to increase, making it essential to plan for these costs as part of a comprehensive post-divorce retirement plan. This may involve purchasing supplemental insurance, such as Medicare Advantage or Medigap plans, to help cover out-of-pocket expenses. Long-term care insurance can provide coverage for services and support required due to chronic illness, disability, or cognitive impairment. As individuals age, the likelihood of needing long-term care services increases, making it an essential consideration in post-divorce retirement planning. Purchasing long-term care insurance can help protect retirement savings and ensure access to the necessary care in the event of a health crisis. The first step in post-divorce retirement planning is to assess one's current financial situation. This involves taking stock of all assets, liabilities, income, and expenses to understand the overall financial picture. Individuals should also review their credit reports to ensure there are no inaccuracies or outstanding debts associated with their former spouse. Once the financial situation is assessed, individuals can identify any areas that may need attention, such as paying down debt or increasing retirement savings. This information will serve as the foundation for setting new retirement goals and developing a comprehensive post-divorce retirement plan. After assessing their financial situation, individuals should set new retirement goals based on their current circumstances and desired retirement lifestyle. This may involve adjusting the target retirement age, determining the necessary income to maintain their desired standard of living, and estimating how much they will need to save to achieve their goals. Setting realistic and achievable retirement goals is essential for creating a successful post-divorce retirement plan. Individuals should be prepared to make adjustments to their goals as needed based on changes in their financial situation or other factors that may impact their retirement planning. With a clear understanding of their financial situation and retirement goals, individuals can choose the appropriate retirement accounts to help them achieve their objectives. This may involve opening a new account, such as an individual retirement account (IRA) or a Roth IRA, or rolling over existing accounts from their previous marriage. When choosing a retirement account, individuals should consider factors such as their income, tax situation, and investment preferences. They should also be aware of any contribution limits and eligibility requirements associated with different types of retirement accounts. To achieve their retirement goals, individuals should aim to maximize their contributions to their retirement accounts. This may involve increasing contributions to an employer-sponsored plan, such as a 401(k) or 403(b), or making regular contributions to an IRA or Roth IRA. Maximizing contributions can help individuals take advantage of tax benefits and compound interest, allowing their retirement savings to grow more quickly over time. Additionally, some employers may offer matching contributions, providing an additional incentive to contribute to retirement accounts. Estate planning is an important aspect of post-divorce retirement planning, as it ensures that an individual's assets and wishes are protected and carried out after their death. Following a divorce, it is essential to review and update estate planning documents, such as wills, trusts, and beneficiary designations, to reflect the new circumstances and ensure that assets are distributed according to the individual's wishes. Estate planning may also involve designating a power of attorney and creating a living will or health care proxy to ensure that an individual's medical and financial decisions are managed according to their preferences in the event of incapacitation. Effective budgeting and expense management are crucial for achieving financial goals and maintaining a comfortable retirement lifestyle. Following a divorce, individuals should create a new budget that reflects their current income and expenses, as well as their retirement savings goals. Regularly tracking and adjusting spending can help individuals stay on track and ensure they are living within their means. Debt can have a significant impact on an individual's ability to save for retirement and achieve their financial goals. Post-divorce retirement planning should include a strategy for managing and reducing debt, such as paying off high-interest debt first or consolidating debt to lower interest rates. By reducing debt, individuals can free up more income for retirement savings and other financial priorities. As previously mentioned, maximizing contributions to retirement accounts is essential for achieving post-divorce retirement goals. This may involve increasing contributions to employer-sponsored plans or making regular contributions to IRAs or Roth IRAs. Individuals should also consider taking advantage of catch-up contributions if they are age 50 or older to boost their retirement savings. A well-diversified investment portfolio can help individuals manage risk and achieve their retirement goals. Following a divorce, individuals should review and adjust their investment strategy to ensure it aligns with their new financial situation and retirement objectives. This may involve diversifying across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to spread risk and optimize potential returns. Retirement income planning involves determining how an individual will generate income during their retirement years. This may include drawing from retirement accounts, receiving Social Security benefits, or generating income from other investments or part-time work. A comprehensive post-divorce retirement plan should consider various sources of income and develop a strategy for managing and maximizing these income streams. As discussed earlier, planning for health care and long-term care costs is a critical aspect of post-divorce retirement planning. This may involve purchasing supplemental insurance, such as Medicare Advantage or Medigap plans, or long-term care insurance to help cover out-of-pocket expenses and protect retirement savings. Updating estate planning documents and ensuring that assets and wishes are protected after a divorce is crucial for effective post-divorce retirement planning. Individuals should work with an estate planning attorney to review and revise their wills, trusts, and beneficiary designations as needed. Consulting with financial professionals, such as financial planners, accountants, and attorneys, can provide valuable guidance and expertise when navigating the complexities of post-divorce retirement planning. These professionals can help individuals develop a comprehensive retirement plan that addresses their unique financial needs and goals. Retirement planning is an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustments. Following a divorce, individuals should commit to regularly reviewing and updating their retirement plan to ensure it remains aligned with their financial goals and circumstances. This may involve adjusting investment strategies, revising retirement goals, or seeking additional guidance from financial professionals as needed. Post-divorce retirement planning is essential for individuals to navigate the financial changes that follow a divorce and ensure they remain on track to achieve their desired retirement lifestyle. This process involves assessing one's financial situation, setting new retirement goals, choosing appropriate retirement accounts, and developing strategies to maximize contributions and manage expenses. Given the complexity of financial and legal issues that often accompany divorce, it is crucial for individuals to seek the advice of financial professionals, such as financial planners, accountants, and attorneys. These experts can provide valuable guidance and support in developing a comprehensive post-divorce retirement plan that addresses an individual's unique financial needs and goals. Divorce can be a challenging and emotional experience, but it is important for individuals to prioritize their financial well-being and retirement planning during this time. By proactively addressing financial considerations, such as asset division, spousal support, and tax implications, individuals can avoid costly mistakes and make informed decisions that support their long-term financial security. Ultimately, a successful post-divorce retirement plan requires ongoing review and adjustments to account for changes in financial circumstances and goals. By staying committed to their retirement planning and seeking the guidance of financial professionals, individuals can navigate the challenges of divorce and secure a comfortable and financially stable retirement.What Is Post-Divorce Retirement Planning?
Importance of Post-Divorce Retirement Planning
Considerations During Post-Divorce Retirement Planning
Asset Division
Spousal Support
Tax Implications
Retirement Accounts
Social Security BenefitsHealth Care Costs
Long-Term Care Insurance
How to Perform a Post-Divorce Retirement Planning
Assess Your Financial Situation
Set Retirement Goals
Choose a Retirement Account
Maximize Contributions
Plan for Your Estate

Strategies for Post-Divorce Retirement Planning
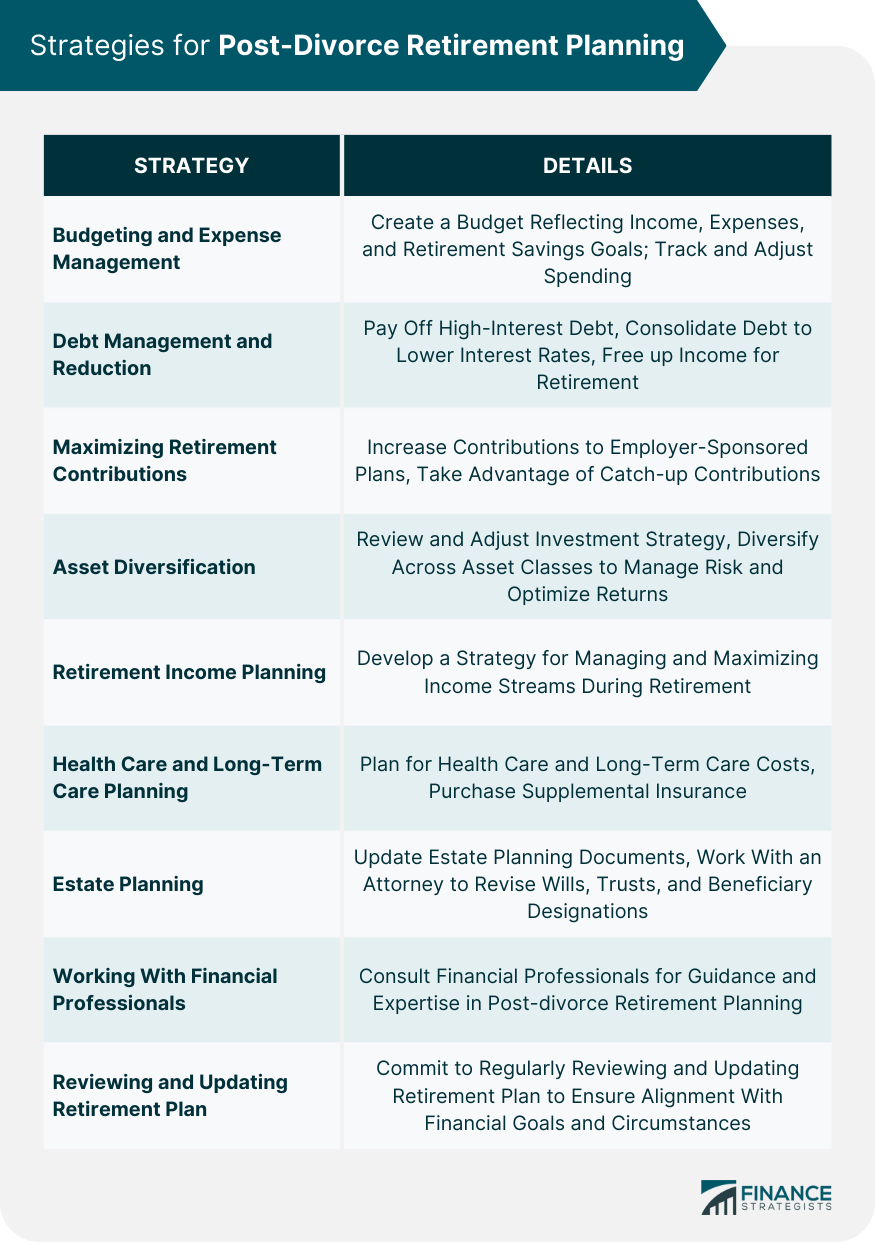
Budgeting and Expense Management
Debt Management and Reduction
Maximizing Retirement Contributions
Asset Diversification
Retirement Income Planning
Health Care and Long-Term Care Planning
Estate Planning
Working With Financial Professionals
Reviewing and Updating Retirement Plan Regularly
Bottom Line
Post-Divorce Retirement Planning FAQs
Post-divorce retirement planning involves making financial arrangements to support your retirement after a divorce.
The key financial considerations include asset division, spousal support, tax implications, and retirement accounts.
Assess your financial situation, set retirement goals, choose a retirement account, maximize contributions, and consider factors like Social Security benefits, health care costs, and long-term care insurance.
Yes, it is advisable to work with financial advisors, attorneys, accountants, and other professionals to ensure your post-divorce retirement plan is well-informed and robust.
Yes, post-divorce retirement planning is crucial to ensure your financial security in retirement and to protect your assets after a divorce.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











