What Is the Pensions Protection Fund (PPF)?
The Pensions Protection Fund is a statutory fund established to protect the pension benefits of members belonging to eligible defined benefit pension schemes in the event of an employer's insolvency.
The primary objective of PPF is to ensure that members continue to receive a portion of their pension benefits, even when their pension scheme's sponsoring employer is unable to fulfill its financial obligations.
PPF Eligibility and Coverage
Types of Pension Schemes Covered
PPF covers defined benefit (DB) pension schemes, including final salary and career average schemes. It does not cover defined contribution (DC) pension schemes, as their benefits are dependent on individual investment performance and contributions.
Qualifying Criteria for Pension Schemes
To qualify for PPF protection, a pension scheme must be a registered DB scheme in the United Kingdom, and its sponsoring employer must be insolvent. Additionally, the scheme must have insufficient assets to provide benefits at least equal to the PPF compensation levels.
PPF Protection Limits
PPF protection is subject to limits, including a cap on the maximum compensation payable to individual members. The cap varies depending on a member's age and is adjusted annually for inflation.
PPF Compensation Levels
PPF compensation levels depend on whether a member has reached their scheme's normal pension age. For those below the normal pension age, PPF provides 90% of their accrued pension benefits, subject to the aforementioned cap.
Members who have reached their scheme's normal pension age receive 100% of their pension benefits, with no cap applied.
PPF Funding and Financial Sustainability
Sources of PPF Funding
The PPF is primarily funded through three sources:
Annual Levies on Eligible Pension Schemes: All eligible DB pension schemes pay an annual levy to PPF, which is determined based on the scheme's risk of insolvency and the level of underfunding.
Recoveries from Insolvent Employers: PPF recovers assets from insolvent employers to partially offset compensation payments.
Investment Returns: PPF invests its assets to generate returns that support its financial stability and long-term funding objectives.

PPF Investment Strategy
The PPF adopts a diversified investment strategy, investing in a mix of assets, including equities, bonds, property, and other alternative investments. This approach aims to balance risk and return, ensuring the fund's financial sustainability.
Financial Sustainability and Risk Management
PPF maintains a strong focus on financial sustainability and risk management. It uses sophisticated models to monitor and manage risks, and it continually reviews its investment strategy to optimize long-term funding.
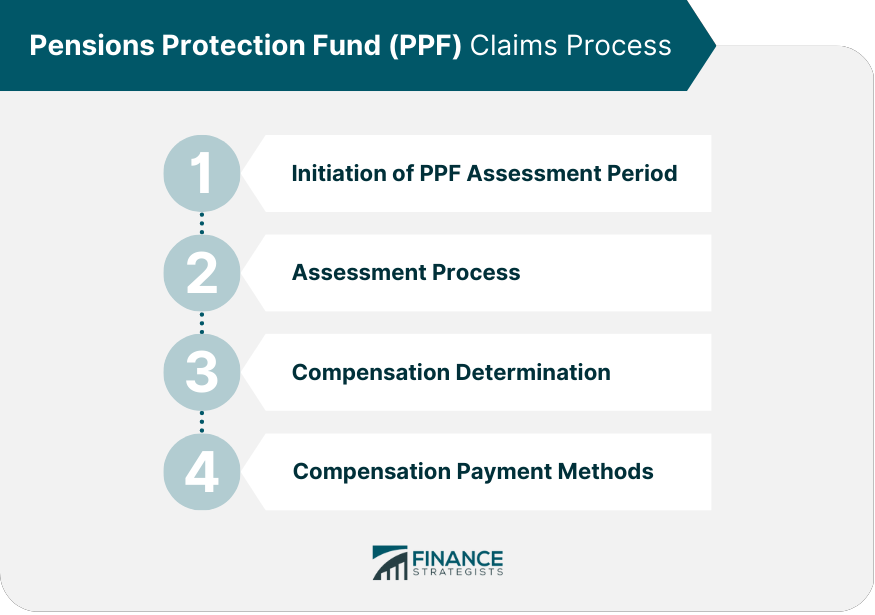
PPF Claims Process
Initiation of PPF Assessment Period
The PPF assessment period begins when a pension scheme's sponsoring employer becomes insolvent, and the scheme enters PPF assessment. During this period, PPF evaluates the scheme's assets, liabilities, and funding position.
PPF Assessment Process
The assessment process typically takes up to two years. During this time, the pension scheme's assets and liabilities are valued, and PPF determines whether the scheme meets the eligibility criteria for PPF protection.
PPF Compensation Determination
If the pension scheme is eligible, PPF calculates the compensation for each member based on their age, pension benefits accrued, and the applicable compensation cap.
PPF Compensation Payment Methods
Once PPF compensation is determined, members receive their compensation in the form of a pension, either directly from PPF or through an insurance company that has taken on the responsibility of paying the pension.
PPF Governance and Regulation
PPF Board Structure and Responsibilities
The PPF is governed by a board consisting of a Chair, Chief Executive Officer, and other non-executive directors. The board is responsible for setting the strategic direction, overseeing the management of the fund, and ensuring compliance with applicable regulations.
Regulatory Oversight and Accountability
PPF operates under the oversight of the Department for Work and Pensions (DWP) and is accountable to Parliament. Additionally, PPF works closely with The Pensions Regulator (TPR) to ensure that pension schemes comply with the required funding standards and other regulations.
Interaction With the Pensions Regulator
PPF and TPR collaborate to protect pension scheme members and maintain the stability of the pensions landscape. They share information, intelligence, and resources to identify and address potential risks to pension schemes and their members.
PPF and Pension Scheme Members
Impact of PPF on Pension Scheme Members
PPF plays a critical role in providing financial security to pension scheme members when their sponsoring employer becomes insolvent. By ensuring that members receive a portion of their pension benefits, PPF helps prevent significant financial hardship for affected individuals.
Rights and Protections for Members
PPF offers several rights and protections for pension scheme members, including the right to receive compensation if their pension scheme becomes eligible for PPF protection and the right to appeal decisions related to their compensation.
Communication and Support for Members
PPF is committed to providing clear, timely, and accurate information to pension scheme members. It offers various communication channels and support services to help members understand their rights, benefits, and the claims process.
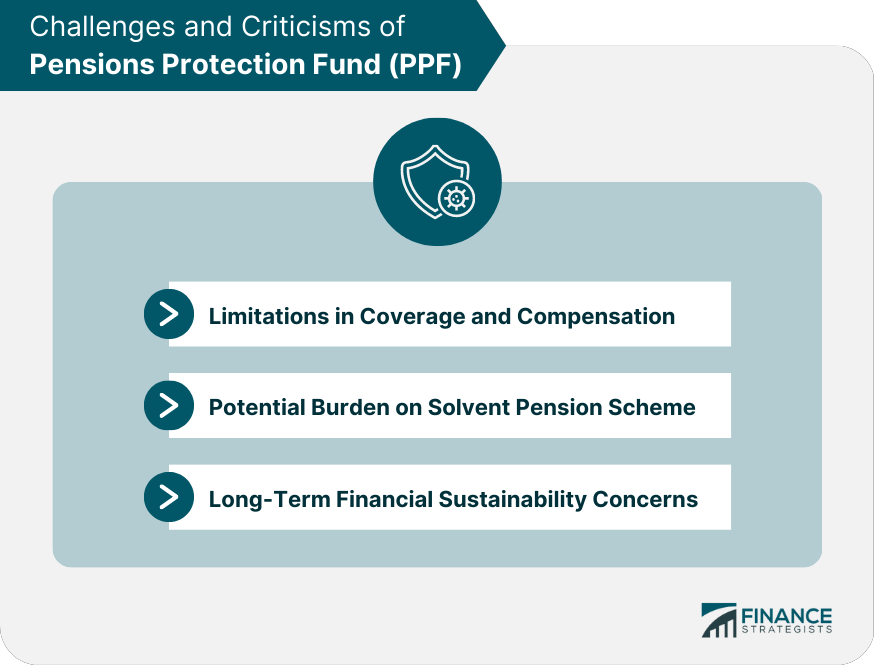
Challenges and Criticisms of PPF
Limitations in Coverage and Compensation
Despite its critical role in protecting pension scheme members, PPF has faced criticism for its limitations in coverage and compensation.
For example, the compensation cap can result in significant reductions in pension benefits for some members, particularly those with higher accrued benefits.
Potential Burden on Solvent Pension Schemes
The annual levy on eligible pension schemes has been criticized for potentially placing a financial burden on solvent pension schemes, which may have to increase contributions to meet their PPF levy obligations.
Long-Term Financial Sustainability Concerns
As the number of defined benefit pension schemes declines and the population ages, concerns have been raised about PPF's long-term financial sustainability. Ensuring that PPF remains adequately funded to meet its obligations will be an ongoing challenge.
International Comparisons and Best Practices
Comparison of PPF With Similar Pension Protection Schemes Worldwide
PPF can be compared to other pension protection schemes in countries such as the United States, Germany, and Sweden. These comparisons can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and efficiency of different approaches to pension protection.
Lessons Learned From Other Pension Protection Systems
Studying other pension protection schemes can help identify best practices and potential improvements for PPF, ensuring that it remains a robust and effective safety net for pension scheme members.
Best Practices for Pension Protection
Some best practices for pension protection include maintaining strong regulatory oversight, implementing risk-based levies, fostering collaboration between pension protection funds and regulators, and adopting diversified investment strategies.
Conclusion
The Pensions Protection Fund plays a crucial role in safeguarding the pension benefits of members belonging to eligible defined benefit pension schemes in the event of employer insolvency.
By providing financial security to affected members, PPF helps prevent significant financial hardship and ensures a safety net for the pension system.
The PPF faces ongoing challenges, such as limitations in coverage and compensation, the potential burden on solvent pension schemes, and concerns about long-term financial sustainability.
To address these challenges, it is essential to maintain vigilance and adapt to the changing pension landscape, drawing on best practices from other pension protection schemes and incorporating technological advancements to optimize operations and risk management.
As demographic changes and evolving economic conditions continue to impact the pension system, the PPF must be prepared to adapt and reform to maintain its effectiveness and ensure the protection of pension scheme members.
By doing so, the PPF will continue to fulfill its vital role in providing financial security to those affected by employer insolvency.
Pensions Protection Fund (PPF) FAQs
The Pensions Protection Fund (PPF) is a UK government-backed compensation fund that was established in 2005 to provide a safety net for members of defined benefit pension schemes in the event of their employer becoming insolvent.
The Pensions Protection Fund is funded through a levy on eligible pension schemes. The levy is calculated based on the risk of the scheme becoming insolvent and the amount of assets held by the scheme.
Members of eligible defined benefit pension schemes can receive compensation from the Pensions Protection Fund if their employer becomes insolvent and the scheme cannot meet its pension obligations. The compensation amount is based on a statutory formula and is subject to a cap.
If your employer goes bust and you are a member of a defined benefit pension scheme, the Pensions Protection Fund may provide compensation to you. The amount of compensation is based on a statutory formula and is subject to a cap.
Yes, the Pensions Protection Fund is backed by the UK government and is considered a secure source of compensation for members of eligible defined benefit pension schemes in the event of their employer becoming insolvent. However, the amount of compensation provided by the Pensions Protection Fund is subject to certain limits and caps.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











