Year's Maximum Pensionable Earnings (YMPE) is a vital concept in the Canadian pension system, specifically the Canada Pension Plan (CPP). It establishes the maximum earnings on which CPP contributions are based and impacts pension benefits upon retirement. YMPE has evolved since the CPP's inception in 1966, with annual adjustments reflecting wage and salary changes. It plays a crucial role in retirement planning by setting contribution limits and determining the maximum CPP benefit individuals can receive. YMPE also affects other CPP benefits like disability and survivor benefits. Its annual updates ensure the CPP remains relevant and adequately funded. YMPE's increase over time aligns with economic growth and wage inflation in Canada, further highlighting its significance in Canadian retirement planning. YMPE is integral to the functioning of the CPP. The CPP is a contributory, earnings-related social insurance program. This means the benefits one receives are directly tied to how much and how long one has paid into the plan. The YMPE sets the maximum limit for these contributions, and therefore, the maximum pensionable earnings. In retirement planning, understanding YMPE is crucial. The CPP forms a significant portion of many Canadians' retirement income, and the amount they can expect to receive is influenced by their contributions, which are capped by the YMPE. Thus, individuals earning more than the YMPE in a given year should factor this into their retirement savings strategies. Apart from the CPP, YMPE also impacts other retirement income sources such as employer-sponsored pension plans. Many of these plans use the YMPE to determine their contributions or benefits structure. For example, a plan might stipulate different contribution rates or accrual rates for earnings below and above the YMPE. The calculation of the YMPE is legislated under the Canada Pension Plan Act. It's determined based on increases in the average wage in Canada. Each year, Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC) reviews the average industrial wage (AIW) and adjusts the YMPE accordingly. The primary factor influencing the YMPE is the change in the AIW. If wages increase on average, the YMPE will increase too. Other economic factors such as inflation and changes in employment rates can indirectly influence the YMPE by affecting average wages. The AIW is a vital determinant of the YMPE. The AIW is calculated by Statistics Canada and reflects the average wage earned by Canadians in a given year. The YMPE for the following year is set at a rate tied to the increase in the AIW, ensuring that the YMPE keeps pace with wage growth. The YMPE sets a cap on the earnings on which CPP contributions are calculated. Both employees and employers are required to contribute a set percentage of an employee's gross income to the CPP, up to the YMPE limit. Earnings above the YMPE are not subject to CPP contributions. The CPP contribution rate for employees and employers is determined as a percentage of the employee's earnings, up to the YMPE. For 2024, this rate is set at 5.95%, meaning that both the employee and the employer would each contribute 5.95% of the employee's earnings up to the YMPE. Self-employed individuals are responsible for paying both portions, equating to a contribution rate of 11.9%. For self-employed individuals, understanding the YMPE is particularly crucial. They are responsible for paying both the employee and employer portions of CPP contributions. Therefore, a self-employed individual's contributions are effectively double those of an employed individual, up to the YMPE limit. The YMPE plays a crucial role in determining the CPP retirement pension amount. The maximum CPP retirement pension is based on the average YMPEs during the years of highest earnings, up to the YMPE limit for each year. Therefore, individuals with earnings consistently at or above the YMPE during their working years will receive the maximum CPP retirement pension. Beyond retirement pensions, the YMPE also impacts other CPP benefits. For instance, CPP disability benefits are based on a flat-rate portion and an earnings-related portion derived from the pensionable earnings up to the YMPE. Similarly, CPP survivor benefits depend on the deceased contributor's pensionable earnings up to the YMPE. Consider an individual who has consistently earned at or above the YMPE throughout their working life. They would be eligible for the maximum CPP retirement benefit. However, if another individual earned less than the YMPE in some years, their CPP retirement benefit would be proportionally less. These examples underscore the importance of understanding the YMPE when planning for retirement. The YMPE is updated annually to keep pace with changes in the average wages in Canada. This ensures the CPP remains relevant, adequately funded, and continues to provide significant support to retirees. The YMPE update is legislated under the Canada Pension Plan Act, which mandates the adjustment based on the rise in the average wage. Inflation indirectly impacts the YMPE by affecting wage growth. As the cost of living rises, wages typically increase to compensate. This wage growth, in turn, leads to an increase in the YMPE. Thus, the YMPE helps maintain the purchasing power of CPP benefits in an inflationary environment. Historically, the YMPE has shown a consistent upward trend, reflecting wage growth and economic expansion in Canada. For instance, the YMPE in 1987 was CAD 25,900, and by 2023 it had increased to CAD 66,600. This growth underscores the dynamic nature of the YMPE and its responsiveness to economic conditions. Understanding the YMPE is vital in retirement savings strategies. For individuals earning above the YMPE, it's crucial to consider other savings vehicles for income beyond the maximum CPP benefit. These may include RRSPs, TFSAs, and non-registered investment accounts. The YMPE directly impacts how much individuals can expect to receive from CPP in retirement, which should be a significant consideration in financial planning. By understanding the YMPE and its implications, individuals can better forecast their CPP retirement income and plan their savings accordingly. For those nearing the YMPE limit, it's essential to factor in the YMPE when calculating CPP contributions and benefits. Additional retirement savings strategies should be considered to supplement income in retirement, given that CPP contributions and benefits are capped. Just like employees, employers are required to contribute to the CPP up to the YMPE limit. Therefore, employers need to be aware of the current YMPE when calculating their CPP contributions. Employers also need to consider the YMPE when designing and administering employee benefit plans, especially defined benefit pension plans, which often integrate their benefits with the CPP. Employers must ensure they are in compliance with the CPP legislation, including accurately calculating and remitting CPP contributions based on the YMPE. Failure to comply can result in penalties and interest on late or deficient payments. Some critics argue that the YMPE is too low and does not adequately reflect the need for higher-income earners to save for retirement. They suggest a higher YMPE would allow for greater CPP benefits. Potential reforms to the YMPE could include raising the YMPE limit or changing the formula used to calculate the YMPE. Such changes would need careful consideration, given their potential impact on CPP funding and benefit levels. When compared to similar systems in other countries, the YMPE is often seen as relatively low. For instance, the U.S. Social Security system's equivalent to the YMPE is significantly higher, leading to debates about whether Canada's YMPE should be increased. The Year's Maximum Pensionable Earnings plays a vital role in the Canadian pension system, directly impacting the Canada Pension Plan contributions and retirement benefits. The YMPE is adjusted annually, reflecting changes in the average wages across Canada. Its cap determines both the maximum contributions from employees and employers towards CPP and the maximum potential CPP benefit. For self-employed individuals, understanding the YMPE is particularly important as they contribute both the employee and employer portions. Additionally, the YMPE affects disability and survivor benefits, as well as retirement savings strategies, with earnings beyond the YMPE needing alternative savings vehicles. Finally, the YMPE is subject to ongoing debate regarding its adequacy for higher-income earners and its comparisons with equivalent systems in other countries. It's essential for individuals and employers to stay updated on YMPE adjustments for accurate CPP contributions and retirement planning.What Are Year's Maximum Pensionable Earnings (YMPE)?
Understanding the Concepts Behind YMPE
Relationship Between YMPE and Canada Pension Plan (CPP)
How YMPE Affects Retirement Planning
YMPE and Other Retirement Income Sources
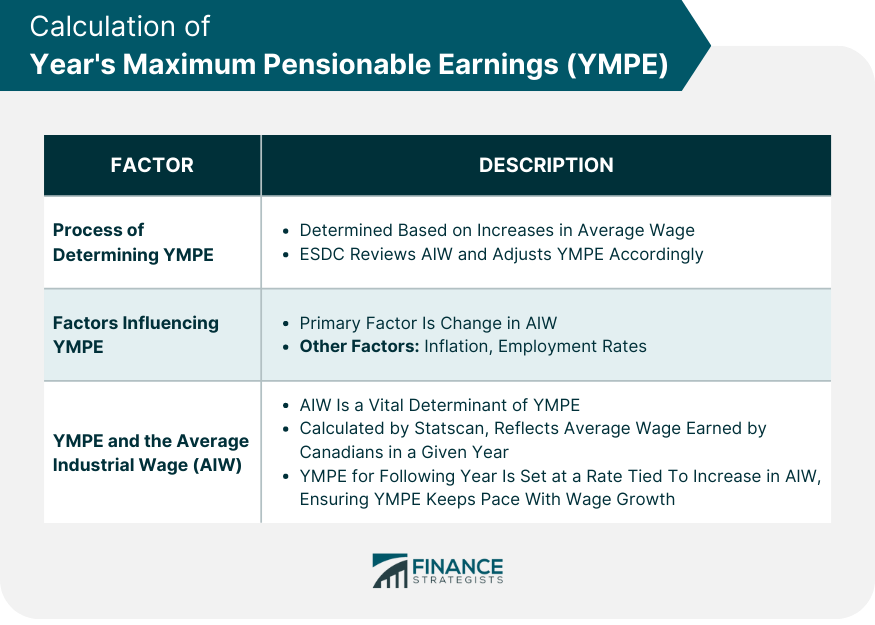
Calculation of YMPE
Process of Determining YMPE
Factors Influencing YMPE
YMPE and the Average Industrial Wage (AIW)
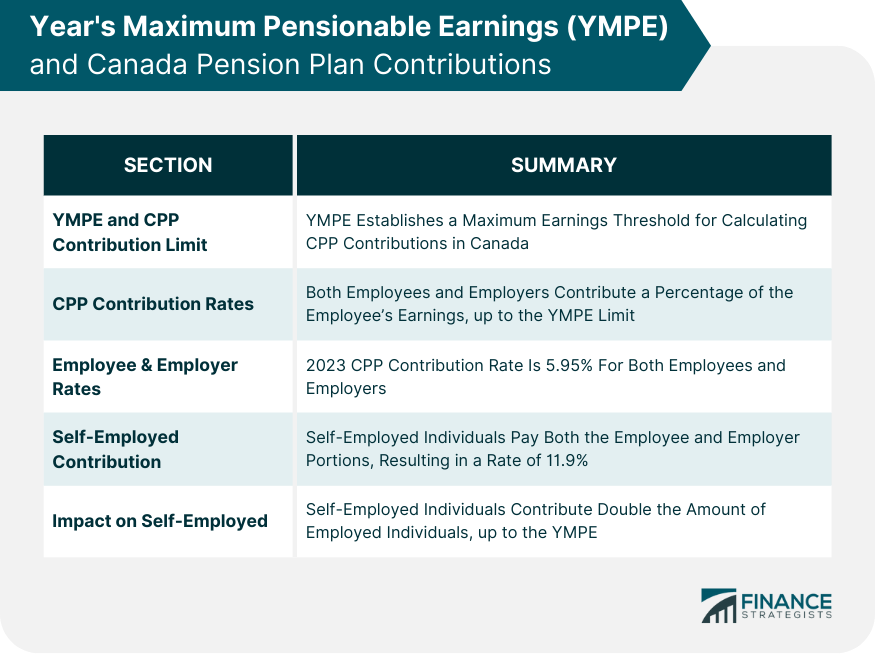
YMPE and Canada Pension Plan Contributions
How YMPE Limits CPP Contributions
Calculation of CPP Contribution Rates Based on YMPE
Impact of YMPE on Self-Employed Individuals' CPP Contributions
YMPE and Benefit Calculation
How YMPE Affects CPP Retirement Benefits
YMPE's Role in Disability and Survivor Benefits Calculation
Case Examples: YMPE and Benefit Calculation
YMPE Adjustments and Updates
Annual Update
Impact of Inflation
Historical Trends
YMPE in Retirement Planning
Incorporating YMPE Into Retirement Savings Strategies
YMPE's Impact on Financial Planning for Retirement
Advice for Individuals Nearing the YMPE Limit
YMPE and Employer Considerations
How YMPE Affects Employers' Payroll Contributions
YMPE and Employee Benefit Plans
Compliance Issues Related to YMPE for Employers
Controversies and Criticisms of YMPE
Debate Over the Adequacy of YMPE
Potential Reforms to YMPE
Comparisons of YMPE to Pensionable Earnings Ceilings in Other Countries
Final Thoughts
Year's Maximum Pensionable Earnings (YMPE) FAQs
The Year's Maximum Pensionable Earnings (YMPE) is the maximum amount of income on which CPP contributions are based each year.
The YMPE is calculated based on the average industrial wage (AIW) in Canada. It is adjusted annually to account for wage growth.
Yes, the YMPE directly influences the amount of CPP retirement benefits an individual will receive. The maximum CPP benefit is based on the YMPE.
Self-employed individuals are responsible for paying both the employee and employer portions of CPP contributions, up to the YMPE limit.
Some critics argue that the YMPE is too low and does not reflect the needs of higher-income earners. There are ongoing debates about potential reforms to increase the YMPE.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











