Retirement age is the age at which an individual stops working and begins to receive financial support from their pension, savings, or social security benefits. Factors influencing retirement age can range from personal preferences to financial circumstances and overall health. Retirement planning is crucial for ensuring a comfortable and fulfilling life after leaving the workforce. Retirement ages vary significantly across different countries. For instance, in the United States, the current retirement age is 66 for full social security benefits, while in Australia, the age pension eligibility age is 65-67. The retirement age can be influenced by various factors, including demographics, cultural values, and economic conditions. Many countries have adjusted their retirement ages in recent years, primarily due to increases in life expectancy and concerns about the sustainability of pension systems. For example, some European countries have gradually increased their retirement ages to reduce the financial burden on pension systems. Cultural and economic factors play a significant role in determining retirement age. In some countries, it is common for people to continue working past the official retirement age due to strong work ethics or financial necessity. In contrast, in other nations, early retirement may be encouraged to make way for younger generations in the workforce. A crucial factor influencing retirement age is an individual's financial security. Pensions and retirement savings, such as 401(k) plans and individual retirement accounts (IRAs), can significantly impact when a person decides to retire. Social security benefits often play a vital role in determining retirement age. The age at which a person can receive full social security benefits varies across countries and may influence when an individual chooses to retire. The cost of living in retirement is another significant factor. Individuals must consider their anticipated expenses, such as housing, utilities, and healthcare when determining their retirement age. Physical health can significantly impact retirement age decisions. Individuals with poor health or chronic medical conditions may need to retire earlier than planned. Mental health is another crucial factor in determining retirement age. Prolonged work-related stress can lead to burnout or other mental health issues, prompting some individuals to retire early. Increases in life expectancy have influenced retirement age decisions, as individuals may need to work longer to ensure financial security throughout their retirement years. Some individuals may choose to work beyond the traditional retirement age because they enjoy their careers or feel a sense of purpose in continuing to contribute to their professions. Retirement can offer an opportunity for individuals to pursue hobbies and interests that they may not have had time for while working. Personal interests may influence an individual's decision to retire early or continue working. Family and social connections can also play a role in retirement age decisions. Retiring early may provide more time to spend with loved ones or to care for aging family members. Early retirement allows individuals more leisure time to pursue hobbies, travel, or spend time with family and friends. Retiring early can reduce work-related stress and the potential for burnout. Early retirement provides individuals the opportunity to focus on personal interests and passions, leading to a more fulfilling and enjoyable retirement experience. Early retirement may result in reduced financial resources, as individuals have less time to accumulate savings and may receive lower social security or pension benefits. Leaving the workforce earlier than anticipated can lead to a loss of social connections, as individuals may have fewer opportunities to interact with colleagues or professional networks. Research has shown that staying engaged in mentally stimulating activities, such as work, can help maintain cognitive abilities. Early retirement may lead to a decline in cognitive function due to reduced mental engagement. Working beyond the traditional retirement age can result in increased financial security, as individuals have more time to save for retirement and may receive higher social security or pension benefits. Delayed retirement can help maintain social connections and provide opportunities for continued engagement with colleagues and professional networks. Working longer can provide a sense of purpose and accomplishment as individuals continue to contribute to their professions and achieve career milestones. Delaying retirement may result in burnout or work-related stress, particularly for individuals in high-pressure or physically demanding careers. Continuing to work beyond the traditional retirement age may exacerbate health concerns or lead to new health issues due to the physical and mental demands of the workplace. Delayed retirement may result in less time for leisure activities, personal interests, and spending time with loved ones. Individuals should begin by evaluating their personal goals and needs, such as desired lifestyle, travel plans, and potential healthcare costs, to determine their optimal retirement age. Creating a financial plan is essential for ensuring a comfortable retirement. Individuals should consider their retirement savings and investment strategies, including contributions to retirement accounts and diversification of investments. A detailed budget can help individuals anticipate retirement expenses and adjust their savings goals accordingly. This budget should account for housing, utilities, healthcare, and other anticipated costs. Healthcare costs can significantly impact retirement planning. Individuals should research and plan for potential healthcare expenses, such as long-term care, prescription medications, and supplemental insurance coverage. Retirement offers an opportunity to explore new hobbies and interests. Individuals should consider engaging in activities that promote mental, physical, and emotional well-being. Maintaining strong social connections is crucial during retirement. Individuals should cultivate friendships and relationships with family members, join clubs or organizations, or volunteer in their communities to stay socially engaged. Some individuals may choose to relocate or downsize during retirement to reduce expenses, be closer to family, or enjoy a different climate or lifestyle. Careful consideration should be given to the financial and emotional implications of such a decision. Determining the optimal retirement age is a multifaceted decision that depends on a variety of factors, such as financial security, health, and personal preferences. With retirement ages varying across different countries, it is essential to consider the specific context when making retirement decisions. Early retirement offers benefits such as more leisure time and reduced stress, while delayed retirement can provide increased financial security and continued social engagement. Proper planning, which includes assessing personal goals, developing a financial plan, and preparing for lifestyle changes, is crucial for ensuring a comfortable and fulfilling retirement experience. As the global population continues to age and pension systems face sustainability challenges, understanding the various factors influencing retirement age decisions remains a pertinent topic for individuals and policymakers alike.What Is Retirement Age?
Retirement Age Around the World
Comparison of Retirement Ages by Country
Trends in Retirement Age Adjustments
Impact of Cultural and Economic Factors on Retirement Age
Factors Affecting Retirement Age Decisions
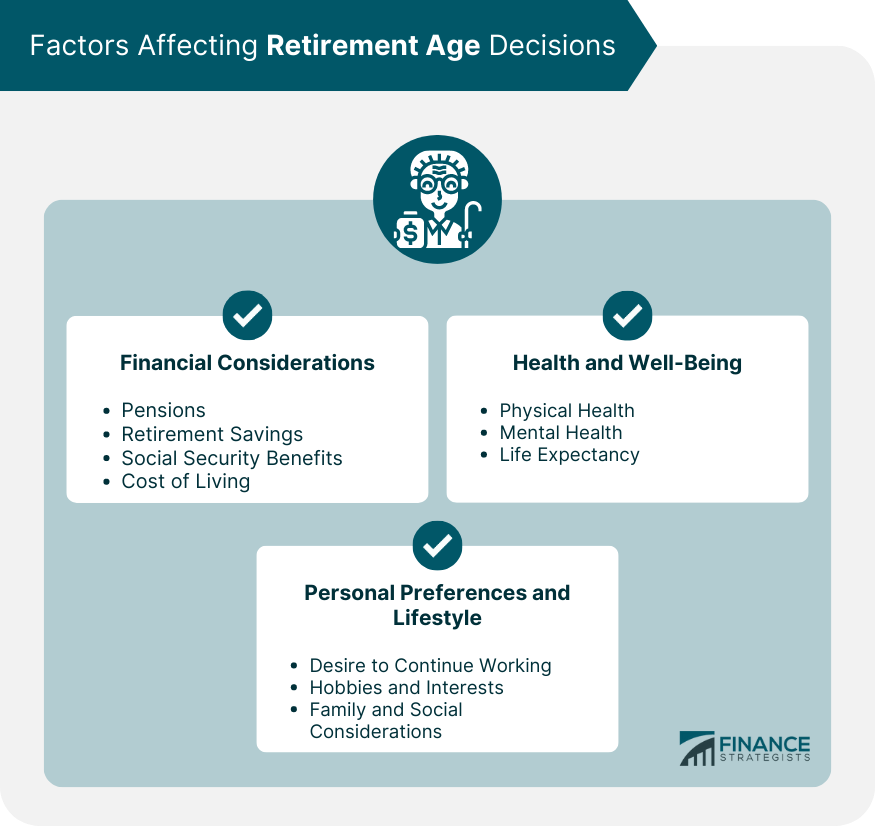
Financial Considerations
Pensions and Retirement Savings
Social Security Benefits
Cost of Living
Health and Well-Being
Physical Health
Mental Health
Life Expectancy
Personal Preferences and Lifestyle
Desire to Continue Working
Hobbies and Interests
Family and Social Considerations
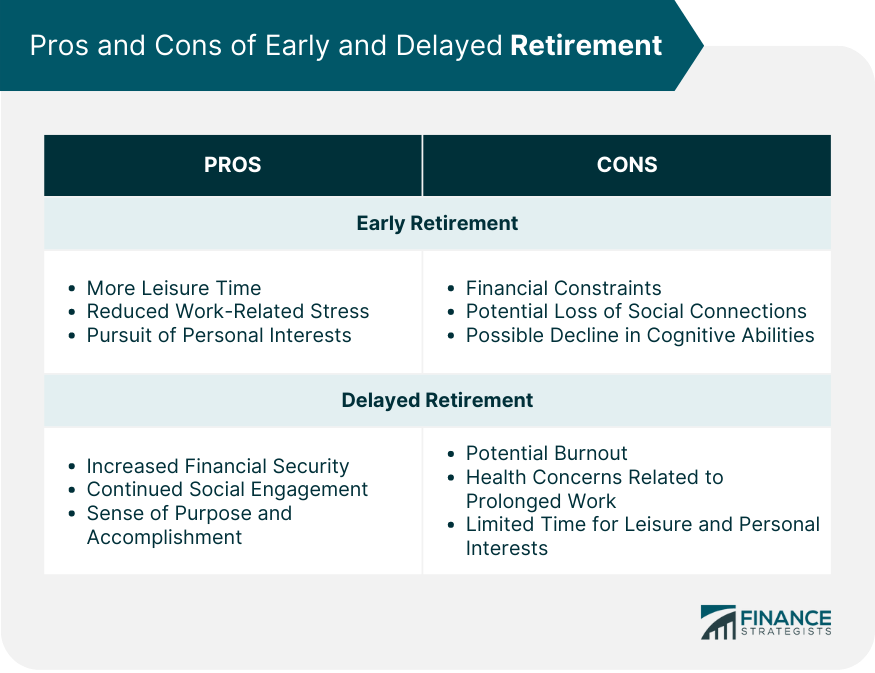
Pros and Cons of Early Retirement
Pros
More Leisure Time
Reduced Work-Related Stress
Pursuit of Personal Interests
Cons
Financial Constraints
Potential Loss of Social Connections
Possible Decline in Cognitive Abilities
Pros and Cons of Delayed Retirement
Pros
Increased Financial Security
Continued Social Engagement
Sense of Purpose and Accomplishment
Cons
Potential Burnout
Health Concerns Related to Prolonged Work
Limited Time for Leisure and Personal Interests
Planning for Retirement
Assessing Personal Goals and Needs
Developing a Financial Plan
Retirement Savings and Investment Strategies
Budgeting for Retirement Expenses
Managing Healthcare Costs
Preparing for Lifestyle Changes
Developing New Hobbies and Interests
Strengthening Social Networks
Considering Relocation or Downsizing
Conclusion
Retirement Age FAQs
The retirement age varies across countries due to differences in demographics, cultural values, and economic conditions. Some countries have higher retirement ages, such as Australia at 65-67, while others, like the United States, have a retirement age of 66 for full social security benefits.
Factors that influence retirement age decisions include financial considerations (pensions, retirement savings, social security benefits, and cost of living), health and well-being (physical health, mental health, and life expectancy), and personal preferences and lifestyle (desire to continue working, hobbies and interests, and family and social considerations).
Early retirement offers advantages such as more leisure time, reduced work-related stress, and the opportunity to pursue personal interests. However, it may also result in financial constraints, potential loss of social connections, and a possible decline in cognitive abilities due to reduced mental engagement.
Delaying retirement can lead to increased financial security, continued social engagement, and a sense of purpose and accomplishment. However, it may also result in potential burnout, health concerns related to prolonged work, and limited time for leisure and personal interests.
Individuals can plan for their retirement age by assessing personal goals and needs, developing a financial plan that includes retirement savings and investment strategies, budgeting for retirement expenses, and managing healthcare costs. Additionally, preparing for lifestyle changes, such as developing new hobbies, strengthening social networks, and considering relocation or downsizing, can help ensure a comfortable and fulfilling retirement.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











