Your income affects your retirement benefits significantly as both Social Security and private pension benefits are calculated based on your earnings. Higher lifetime earnings result in larger Social Security benefits, while private pensions often base benefits on your final salary and years of service. Fluctuations in income, particularly during your high-earning years, can also impact these benefits. Understanding the relationship between your income and retirement benefits is crucial for effective retirement planning. Social Security Retirement Benefits, managed by the Social Security Administration (SSA), hinges predominantly on an individual's peak 35 years of earnings, which are carefully adjusted for inflation. For those with less than 35 years of documented earnings, the SSA fills in the remaining years with zeros, leading to a potentially lower average, hence, lesser benefits. Private pension plans operate differently, but they are equally connected to one's income. These plans traditionally derive benefits using a calculation that integrates multiple factors. The calculation considers an employee's final salary, length of service, and a specific benefit multiplier, which is predetermined by the pension plan itself. This approach emphasizes the value of long-term, consistent, high-income employment in securing substantial retirement benefits. Your lifetime earnings primarily determine your Social Security benefits. Higher-income over a longer duration means more significant Social Security benefits. Private pension plans often calculates retirement benefits as a percentage of your final salary multiplied by the number of years worked, meaning higher salaries can lead to more substantial benefits. Starting with a higher income early in your career can benefit you when it comes to retirement. Higher early-career earnings can set the stage for larger Social Security benefits and better private pension plans. Mid-career earnings often set the pace for your career trajectory. Maintaining or increasing income during this period contributes positively to retirement benefits. Late-career is when many people earn their highest income. This can significantly affect Social Security benefits and private pension plans since these are based on your top-earning years. Enhancing Education and Skills: Acquiring advanced degrees or professional certifications can help you qualify for higher-paying jobs. In addition, gaining new skills, particularly those in high demand, can also increase your earning potential. Investing in Income-Generating Assets: Purchasing assets such as a real estate for rental income or investing in dividend-yielding stocks can provide additional income streams. Side Hustles or Part-Time Jobs: Engaging in part-time work or a side business aligned with your skills and interests can supplement your regular income. Seeking Promotions or Negotiating Salary: Regularly seeking promotions or salary increases in your current job can lead to a significant boost in income over time. Financial Investments: Proper financial investment strategies can help generate additional income. This includes investing in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or retirement accounts, which can provide considerable returns over the long term. The Social Security system operates by considering an individual's top 35 years of earnings. Consequently, any escalation in your income can directly increase your Social Security benefits, leading to a more financially secure retirement. The mechanism of private pension plans also offers a unique opportunity to amplify your retirement benefits. As these plans base their calculations on your final salary and duration of service, a rise in your income, particularly towards the end of your career, can lead to a considerable increase in your pension payouts. Therefore, income enhancement can prove to be a pivotal strategy for accumulating substantial retirement benefits. Job loss or income reduction can affect your retirement benefits, especially if they occur during your highest-earning years. The SSA uses a formula with "bend points" that benefits lower-income workers. Even if your income is reduced, you may still receive a larger percentage of your pre-retirement earnings than a high-income earner. If you experience income fluctuation or reduction, consider financial planning tools, professional guidance, or even part-time work to mitigate potential negative impacts on retirement benefits. A good retirement plan can help you understand how your current income will affect your future retirement benefits and help strategize accordingly. A financial advisor can provide valuable guidance, help you understand complex retirement benefits, and assist you in maximizing your retirement income. There are many tools and resources available for retirement planning, from online calculators to financial planning services. Leveraging these can ensure a more secure retirement. Understanding the profound connection between your income and retirement benefits paves the way for effective retirement planning. The significance of your earnings is highlighted in both Social Security and private pension benefits calculations, emphasizing the value of consistent high income. Whether you are in the early, mid, or late stages of your career, each phase contributes to the potential retirement benefits you can accrue. Actively employing strategies such as enhancing your skills, investing wisely, or even negotiating your salary can maximize these benefits. Meanwhile, strategies for mitigating the effects of income fluctuation or job loss help safeguard your future. Harnessing the expertise of a financial advisor, along with various financial planning tools, will aid in strategically navigating your income to secure a comfortable retirement. By mastering this interplay between income and retirement benefits, you can ensure a prosperous and worry-free post-career life.Income and Retirement Benefits: Overview
Calculating Retirement Benefits
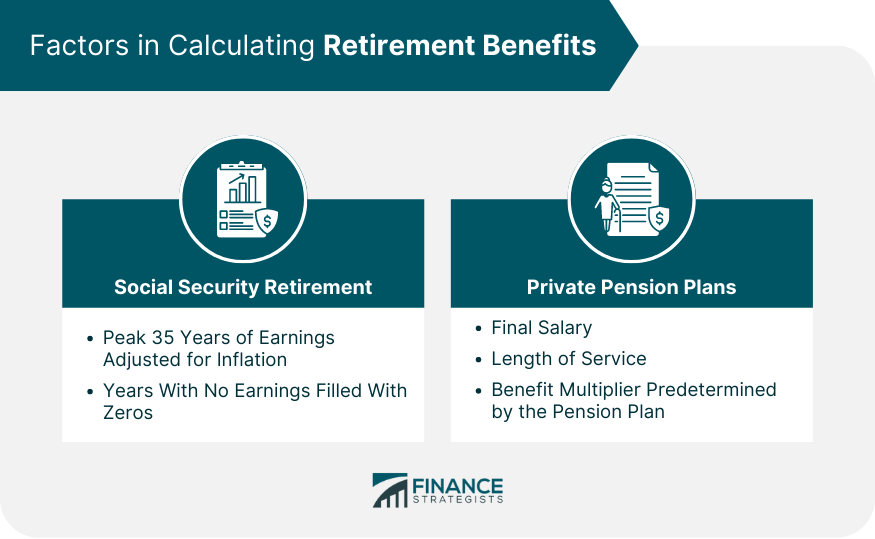
Social Security Retirement Benefits
Private Pension Plans
Role of Income in Calculations
Influence of Lifetime Earnings on Social Security Benefits
Basis of Private Pension Plans on Salary
Income Considerations Throughout Your Career
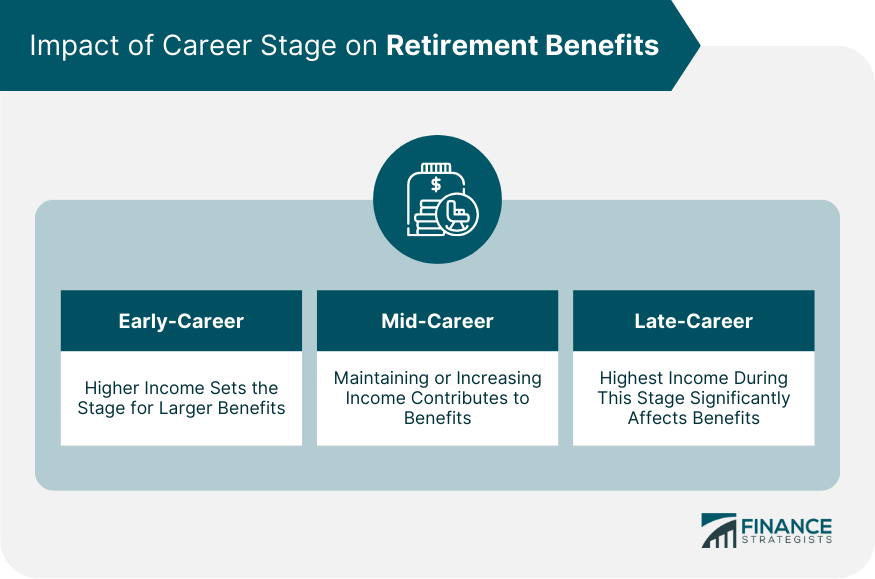
How Early-Career Income Affects Retirement Benefits
Impact of Mid-Career Earnings on Retirement Benefits
How Late-Career Income Affects Retirement Benefits
Increasing Your Income and Maximizing Retirement Benefits
Strategies for Boosting Income
Implications of Increased Income on Retirement Benefits
Maximizing Social Security Benefits Through Income Enhancement
Augmenting Private Pension Payouts Through Increased Income
Consequences of Fluctuating or Reduced Income on Retirement Benefits
Impact of Job Loss or Income Reduction
Role of Social Security Administration's "Bend Points"
Strategies to Mitigate Potential Negative Impacts
Planning and Strategizing for Retirement
Importance of Financial Planning for Retirement
How a Financial Advisor Can Help
Tools and Resources for Retirement Planning
Conclusion
How Your Income Affects Your Retirement Benefits FAQs
Your Social Security retirement benefits are calculated based on your 35 highest earning years. The higher your income during these years, the greater your Social Security benefits will be.
Yes, fluctuations in your income can affect your retirement benefits. A significant decrease, for instance, during your high-earning years, may reduce your Social Security benefits.
Increasing your income, particularly during your high-earning years, can result in higher Social Security benefits and larger private pension payouts. This is because these benefits are calculated based on your income over your career.
Your income in retirement, including withdrawals from retirement accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs, could push you into a higher tax bracket, which affects the net amount of benefits you receive. Understanding your potential tax situation in retirement can help you plan more effectively.
Strategies include boosting your income by enhancing your education or investing in income-generating assets and working with a financial advisor to understand how your income affects your retirement benefits. Using financial planning tools and resources can also be beneficial.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











