What Is Retirement Savings?
Retirement savings is a proactive measure that individuals take to secure their financial future by setting aside money during their working years.
This type of savings helps to ensure that people can maintain their desired lifestyle and meet their financial needs in retirement, which is a time when earning potential is typically reduced.
Without adequate retirement savings, individuals may have to rely on government assistance programs or family members for financial support, which can be stressful and limit their ability to enjoy their retirement.
Making regular contributions to retirement savings accounts, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, can help individuals maximize the amount of money they have available for retirement.
Importance of Saving for Retirement
Saving for retirement is essential as it ensures financial security and independence when individuals are no longer earning a regular income from employment.
Adequate retirement savings can provide a steady income stream, cover healthcare expenses, and enable retirees to maintain their desired lifestyle.
Saving for retirement is important because it allows individuals to maintain their standard of living even after they stop working.
Retirement savings can be used to cover expenses such as housing, food, and healthcare, which can be particularly expensive for older individuals.
By saving for retirement, individuals can avoid the stress and uncertainty that can come with relying on government assistance or family members for financial support.
Adequate retirement savings can also provide individuals with the flexibility to pursue hobbies, travel, and other activities that they may not have had time for during their working years.
The earlier individuals start saving for retirement, the more time they have to benefit from compounding interest, which can significantly increase the amount of money they have available for retirement.
Retirement Savings as a Long-Term Financial Goal
Retirement savings is a long-term financial goal, as it typically involves accumulating funds over several decades. A well-planned retirement savings strategy can significantly impact an individual's financial well-being during their retirement years.
Retirement savings is a critical financial goal for individuals because it is often the primary source of income during retirement. As people are living longer and may face higher healthcare costs, saving enough for retirement has become more important than ever before.
Retirement savings typically involves accumulating funds over several decades, and a well-planned retirement savings strategy can significantly impact an individual's financial well-being during their retirement years.
Individuals should start saving for retirement as early as possible to take advantage of compounding interest and maximize their savings potential.
To achieve retirement savings goals, individuals should consider factors such as their current income, desired retirement lifestyle, and retirement age.
They should also take into account any employer-sponsored retirement plans, such as 401(k)s or pension plans, and individual retirement accounts (IRAs).
It is essential for individuals to regularly review and adjust their retirement savings strategy to ensure that they are on track to achieve their financial goals.
This may involve working with a financial advisor or using retirement planning tools to identify potential retirement income gaps and make adjustments to savings contributions and investment strategies.
Retirement Savings Vehicles
Employer-Sponsored Plans
401(k) Plans
A 401(k) plan is a tax-advantaged, employer-sponsored retirement savings plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income towards their retirement. Employers may also offer matching contributions, further enhancing the growth of retirement savings.
403(b) Plans
A 403(b) plan is similar to a 401(k) plan but is designed for employees of tax-exempt organizations, such as schools, hospitals, and religious institutions. These plans also offer tax-deferred growth and the possibility of employer matching contributions.
SIMPLE IRA
A Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) IRA is designed for small businesses with 100 or fewer employees. It allows employees to make pre-tax contributions, and employers are required to make matching or non-elective contributions.
SEP IRA
A Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA is a retirement plan option for self-employed individuals and small business owners. Employers can make tax-deductible contributions on behalf of their employees, and these contributions grow tax-deferred until retirement.
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Traditional IRA
A Traditional IRA is a tax-advantaged retirement account that allows individuals to make pre-tax contributions. The earnings within the account grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals during retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
Roth IRA
A Roth IRA is a retirement account that allows individuals to contribute after-tax income. Although contributions are not tax-deductible, the earnings and qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
Pensions
Pensions are employer-sponsored retirement plans that provide a defined benefit to retirees based on factors such as salary and years of service. While less common today, pensions can be a significant source of retirement income for those who have access to them.
Annuities
Annuities are financial products offered by insurance companies that provide a guaranteed income stream during retirement. Individuals can purchase annuities using a lump sum or a series of payments, and the income can be immediate or deferred.
Non-retirement Investment Accounts
Non-retirement investment accounts, such as brokerage accounts, can also be used to save for retirement. While these accounts do not offer the same tax advantages as retirement-specific accounts, they provide additional flexibility and access to a wide range of investment options.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are tax-advantaged accounts designed to help individuals save for medical expenses. While primarily used for healthcare costs, any unused funds can be used for retirement expenses after the age of 65.
Real Estate Investments
Real estate investments, such as rental properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs), can provide an additional source of retirement income through rental income or capital appreciation.

Retirement Savings Strategies
Starting Early
Compound Interest
Starting to save for retirement early allows individuals to take advantage of compound interest, which can significantly grow their retirement savings over time
Longer Time Horizon
A longer time horizon enables individuals to benefit from market fluctuations and better manage risks associated with investments.
Starting early also provides more time to recover from any financial setbacks that may occur during their working years.
Consistent Contributions
Paying Yourself First
Paying yourself first involves prioritizing retirement savings by setting aside a specific amount or percentage of income before allocating funds to other expenses. This strategy helps ensure consistent contributions to retirement savings.
Automatic Savings Plans
Automatic savings plans involve setting up recurring transfers from a checking account to a retirement savings account, such as an IRA or 401(k). This approach simplifies the savings process and helps individuals stay committed to their retirement savings goals.
Increasing Contributions Over Time
Annual Raises or Bonuses
Using annual raises or bonuses to increase retirement savings contributions can help individuals build their retirement savings more rapidly, allowing them to reach their financial goals sooner.
Catch-up Contributions for Those Age 50 and Older
Catch-up contributions are additional contributions that individuals aged 50 or older can make to their retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs. This provision helps older individuals boost their retirement savings if they are behind on their savings goals.
Diversification
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation involves distributing investments across various asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash, to reduce risk and potentially increase returns. A well-diversified portfolio can provide more stable returns and better manage market volatility.
Risk Management
Diversification plays a critical role in risk management by reducing the impact of a single asset or investment on the overall portfolio. This approach helps ensure that retirement savings are not excessively exposed to any particular risk.
Factors Influencing Retirement Savings
Life Expectancy
Longer life expectancies increase the need for larger retirement savings, as individuals must support themselves financially for more extended periods.
Inflation
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, making it essential to account for its impact on retirement savings and the cost of living during retirement.
Healthcare Costs
Healthcare costs, particularly for long-term care and prescription medications, can significantly impact retirement savings. Planning for these expenses is crucial to maintaining financial stability in retirement.
Desired Lifestyle in Retirement
Individuals should consider their desired lifestyle during retirement when determining their retirement savings needs. Travel, hobbies, and other leisure activities may require additional savings.
Social Security Benefits
Social Security benefits can be an essential source of retirement income but should not be relied upon as the sole means of financial support. Factoring in Social Security benefits can help individuals determine how much they need to save independently.
Potential Long-Term Care Expenses
Long-term care expenses, such as in-home care or nursing home costs, can quickly deplete retirement savings. Planning for these potential expenses is vital to ensure financial security during retirement.
Retirement Savings Milestones
Suggested Savings by Age
The following table provides a general guideline for suggested retirement savings by age. Individual circumstances and financial goals may vary, so it's essential to consult with a financial advisor to create a personalized plan.
These figures are based on the assumption that the individual starts working at age 25 and aims to retire at 65.
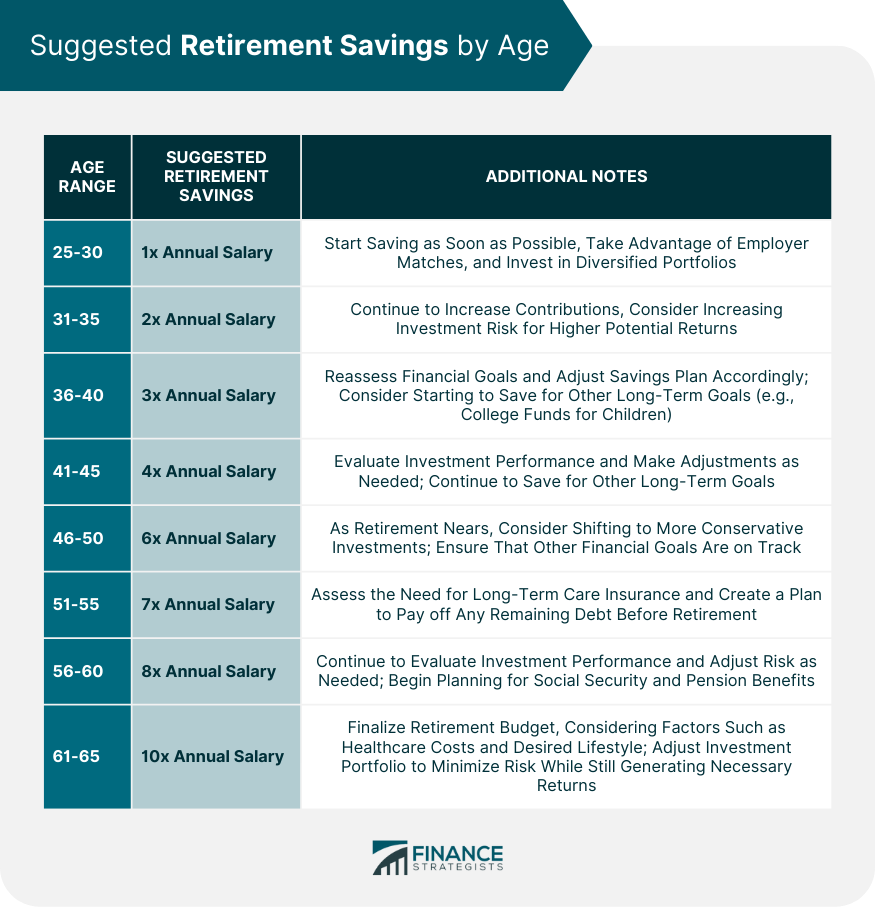
Financial experts often recommend specific retirement savings milestones based on age, such as having a certain multiple of annual income saved by specific ages. These recommendations can serve as a useful starting point for individual retirement savings goals.
Retirement Savings Benchmarks
Retirement savings benchmarks provide general guidelines for the amount individuals should have saved at various stages of their life. These benchmarks can help individuals track their progress and adjust their savings strategies as needed.
Retirement savings benchmarks provide a useful reference point for individuals to gauge their retirement savings progress and plan accordingly.
These benchmarks are typically based on factors such as age, income, and expected retirement expenses.
Benchmarks may also take into account factors such as Social Security benefits and pension plans to provide a more accurate picture of an individual's retirement savings needs.
By using retirement savings benchmarks, individuals can get a better sense of whether they are on track to achieve their retirement goals, and make adjustments to their savings strategies as needed.
It is important to note that while retirement savings benchmarks can be helpful, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution, and individuals should consult with a financial advisor to develop a retirement savings plan that is tailored to their needs and circumstances.
Adjusting Savings Goals Based on Individual Circumstances
Individual circumstances, such as income, expenses, and lifestyle preferences, should be considered when setting retirement savings goals. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these goals can help ensure that individuals stay on track to achieve their desired retirement lifestyle.
Retirement Withdrawal Strategies
The 4% Rule
The 4% rule is a commonly used withdrawal strategy that suggests retirees can withdraw 4% of their portfolio value in the first year of retirement and adjust the withdrawal amount annually for inflation.
This approach aims to provide a sustainable income stream throughout retirement while minimizing the risk of depleting savings.
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) are mandatory withdrawals from certain tax-deferred retirement accounts, such as Traditional IRAs and 401(k)s, starting at age 72.
RMDs help ensure that individuals withdraw and pay taxes on the funds they have saved during their working years.
Tax-Efficient Withdrawal Strategies
Tax-efficient withdrawal strategies involve withdrawing funds from various retirement accounts in a specific order to minimize tax liabilities.
For example, retirees might withdraw from taxable accounts first, followed by tax-deferred accounts and finally tax-free accounts like Roth IRAs.
Annuity Payouts
Annuity payouts provide a steady income stream during retirement, either for a specified period or for the remainder of the individual's life. Annuities can help provide financial stability and predictability in retirement, especially for those concerned about outliving their savings.
Sequence of Returns Risk
Sequence of returns risk refers to the potential impact of market fluctuations on a retirement portfolio during the withdrawal phase.
Poor market performance early in retirement can have a lasting impact on the sustainability of retirement income. Managing sequence of returns risk may involve adjusting withdrawal rates or using a dynamic withdrawal strategy based on market conditions.
Role of Financial Advisors in Retirement Savings
Personalized Retirement Planning
Financial advisors can provide personalized retirement planning services, taking into account individual circumstances, goals, and risk tolerance.
By developing tailored retirement savings strategies, advisors help individuals maximize their chances of achieving their desired retirement lifestyle.
Portfolio Management
Financial advisors can assist with portfolio management, including asset allocation, diversification, and rebalancing, to ensure retirement savings are invested appropriately based on individual risk tolerance and financial goals.
Tax Planning Strategies
Advisors can recommend tax planning strategies to help individuals minimize their tax liabilities during both the accumulation and withdrawal phases of retirement savings, ultimately increasing the longevity of their retirement funds.
Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustments
Regularly reviewing and adjusting retirement savings strategies is crucial to ensuring financial success in retirement.
Financial advisors can provide ongoing monitoring and recommendations for adjustments based on changes in individual circumstances or market conditions.
Conclusion
Importance of Proactive Retirement Savings
Proactively saving for retirement is essential for achieving financial security and independence during one's retirement years.
By starting early, contributing consistently, and implementing a well-diversified investment strategy, individuals can build a substantial nest egg to support their desired lifestyle in retirement.
Developing a Comprehensive Retirement Savings Strategy
Developing a comprehensive retirement savings strategy involves considering various factors, including life expectancy, inflation, healthcare costs, and individual lifestyle preferences.
By taking these factors into account and utilizing a range of retirement savings vehicles, individuals can create a robust and flexible plan to achieve their financial goals.
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting Retirement Savings Goals and Strategies
Regularly reviewing and adjusting retirement savings goals and strategies is critical to staying on track and adapting to changing circumstances.
Working with a financial advisor can provide valuable guidance and support in navigating the complexities of retirement savings and ensuring long-term financial success.
Retirement Savings FAQs
Retirement savings refer to the funds that individuals set aside to support themselves financially during retirement. These savings may be held in various investment vehicles, such as 401(k)s, IRAs, or other retirement accounts.
The amount individuals should save for retirement depends on their financial situation, lifestyle, and retirement goals. As a general rule of thumb, financial experts recommend saving at least 10-15% of one's income annually for retirement.
It is recommended to start saving for retirement as early as possible to take advantage of compound interest and maximize the growth of retirement savings. The earlier one starts saving, the more time their savings will have to grow.
If individuals do not save enough for retirement, they may face financial difficulties during retirement and may not be able to support their desired lifestyle. They may need to rely on Social Security or other sources of income, which may not be sufficient to cover all of their expenses.
Some retirement savings strategies include contributing to tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, diversifying investments, maximizing employer matches, and regularly reviewing and adjusting retirement goals and savings plans. Consulting with a financial advisor can also help individuals create a personalized retirement savings plan.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











