Retirement savings vehicles are financial instruments and accounts designed to help individuals accumulate funds for retirement. They come in various forms, each with its own set of features, benefits, and drawbacks. Selecting the right retirement savings vehicles is crucial for maximizing returns, minimizing taxes, and ensuring a financially secure retirement. Retirement savings vehicles can be broadly categorized into tax-advantaged and non-tax-advantaged options. They can also be specifically designed for small business owners, self-employed individuals, or tailored to particular investment strategies, such as real estate or annuities. Traditional IRAs are individual retirement accounts that allow eligible individuals to contribute pre-tax income, with taxes deferred until withdrawals are made in retirement. Roth IRAs are individual retirement accounts funded with after-tax income. Contributions are not tax-deductible, but qualified withdrawals are tax-free in retirement. 401(k) plans are employer-sponsored retirement plans that allow employees to make pre-tax contributions. Employers may also offer matching contributions, and taxes on contributions and earnings are deferred until withdrawal. 403(b) plans are similar to 401(k) plans but are designed for employees of tax-exempt organizations, such as schools, hospitals, and non-profit organizations. 457(b) plans are deferred compensation retirement plans for state and local government employees and certain non-governmental organizations. The Thrift Savings Plan is a retirement savings plan for federal employees and members of the uniformed services, including the military. SEP IRAs are retirement plans for small business owners and self-employed individuals that allow employers to make tax-deductible contributions to employees' retirement accounts. SIMPLE IRAs are retirement plans for small businesses that enable both employers and employees to make contributions to employees' retirement accounts. Regular savings accounts are simple, low-risk savings options that can be used for retirement savings but do not offer tax advantages. Certificates of deposit are time-bound, low-risk savings instruments that provide a fixed interest rate in exchange for a predetermined length of time. Money market accounts are interest-bearing savings accounts that offer slightly higher interest rates than regular savings accounts but may have higher minimum balance requirements and withdrawal restrictions. Brokerage accounts are investment accounts that allow individuals to invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and other securities without tax advantages. Solo 401(k) plans are retirement plans designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners without employees, allowing them to make both employee and employer contributions. As mentioned earlier, SEP IRAs are retirement plans for small business owners and self-employed individuals, allowing employers to make tax-deductible contributions to employees' retirement accounts. As mentioned earlier, SIMPLE IRAs are retirement plans for small businesses that enable both employers and employees to make contributions to employees' retirement accounts. Defined benefit plans are employer-sponsored retirement plans that guarantee a specific payout in retirement, typically based on factors such as salary and years of service. HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts designed to help individuals with high-deductible health plans cover medical expenses. While not specifically designed for retirement, they can serve as an additional savings vehicle in certain situations. HSAs offer triple tax advantages: contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and qualified withdrawals for medical expenses are tax-free. Funds in an HSA can be invested, and after age 65, withdrawals for non-medical expenses are subject to income tax but not penalties. HSAs can only be used by individuals with high-deductible health plans, and contribution limits apply. Additionally, HSA funds should primarily be used for medical expenses, with retirement savings as a secondary purpose. Fixed annuities are insurance contracts that provide a guaranteed fixed income stream for a specified period or for life, in exchange for an upfront premium payment. Variable annuities are insurance contracts that allow individuals to invest in a range of investment options, with the annuity payout dependent on the performance of the investments. Indexed annuities are insurance contracts that provide returns based on the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, with a guaranteed minimum return. Annuities can provide a guaranteed income stream in retirement, reducing the risk of outliving one's savings. However, they can also have high fees, complex terms, and limited flexibility, making them less suitable for some individuals. Investing in rental properties can provide a steady stream of income during retirement, along with potential appreciation in property value over time. Additionally, real estate often acts as a hedge against inflation, as property values and rental income typically rise with inflation, helping to preserve the purchasing power of your retirement savings. Real Estate Investment Trusts are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate. Investing in REITs allows individuals to gain exposure to the real estate market through a diversified portfolio of properties. Real estate crowdfunding platforms enable individuals to invest in real estate projects, either through debt or equity, with a relatively small initial investment. Real estate investments can provide diversification, passive income, and potential appreciation. However, they also come with risks, such as illiquidity, market fluctuations, and management responsibilities. Individuals should consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon when selecting retirement savings vehicles. Diversifying retirement savings across multiple vehicles can help manage risk and improve the likelihood of achieving retirement goals. Individuals should consider the tax implications of their chosen retirement savings vehicles, including tax advantages and potential future tax liabilities. Understanding the fees and expenses associated with various retirement savings vehicles is essential for making informed decisions and maximizing returns. Selecting suitable retirement savings vehicles is crucial for ensuring a secure and comfortable retirement. By carefully considering individual needs, goals, and risk tolerance, individuals can choose the right combination of savings vehicles to achieve their retirement objectives. Diversification and informed decision-making play a critical role in managing risks and ensuring a successful retirement savings strategy. Regular evaluation and adjustments to one's retirement savings plan can help keep individuals on track and adapt to changing circumstances. A secure financial future requires ongoing attention and effort. To maximize the potential of retirement savings, it is important to stay informed about available savings vehicles, tax implications, and fees associated with each option. By leveraging a mix of tax-advantaged and non-tax-advantaged retirement savings vehicles, individuals can create a well-rounded and resilient retirement plan that addresses their unique needs and aspirations. Ultimately, a thoughtful and proactive approach to retirement savings can pave the way for a fulfilling and financially stable retirement.What Are Retirement Savings Vehicles?
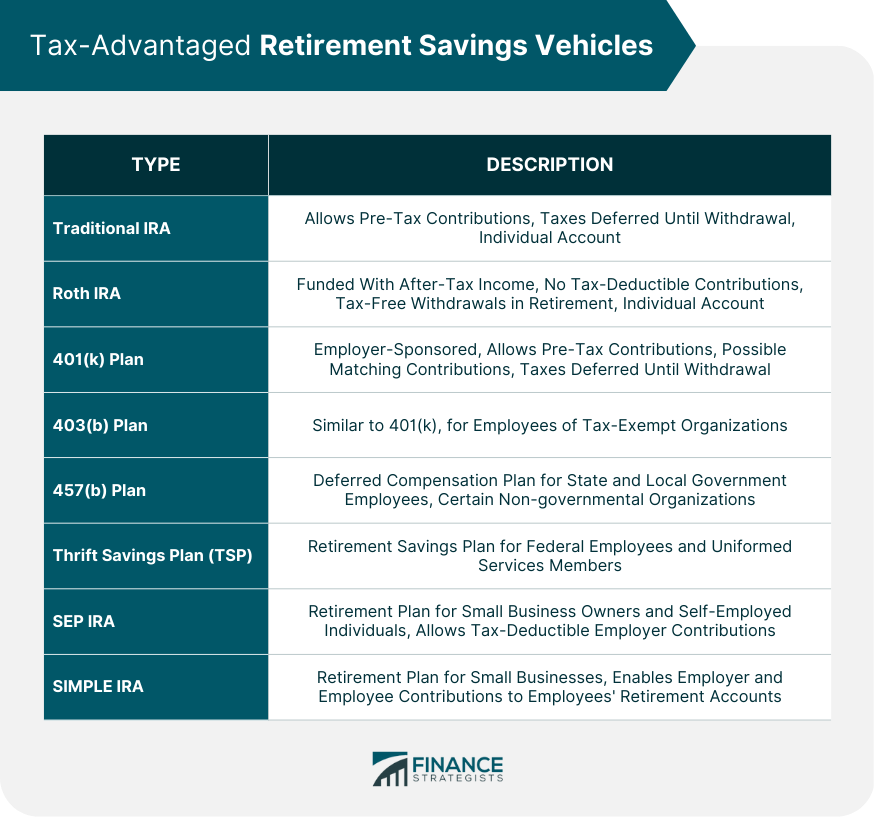
Tax-Advantaged Retirement Savings Vehicles
Traditional Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs)
Roth IRAs
401(k) Plans
403(b) Plans
457(b) Plans
Thrift Savings Plan (TSP)
Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRAs
Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) IRAs
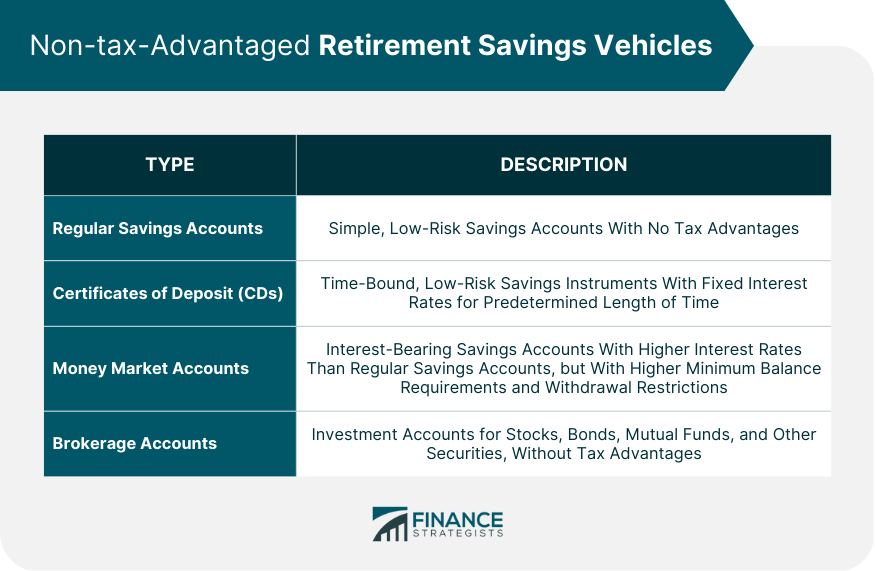
Non-tax-Advantaged Retirement Savings Vehicles
Regular Savings Accounts
Certificates of Deposit (CDs)
This is because CDs offer predictable returns and are insured by the FDIC up to certain limits, making them a safe investment choice. When interest rates are favorable, the fixed returns from CDs can significantly enhance the stability and growth of your retirement portfolio.Money Market Accounts
Brokerage Accounts
Retirement Savings Vehicles for Small Business Owners and Self-Employed Individuals
Solo 401(k) Plans
SEP IRAs
SIMPLE IRAs
Defined Benefit Plans
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Retirement
Overview of HSAs
Benefits of Using HSAs for Retirement Savings
Limitations and Considerations
Annuities as a Retirement Savings Vehicle
Fixed Annuities
Variable Annuities
Indexed Annuities
Benefits and Drawbacks of Annuities
Real Estate as a Retirement Savings Vehicle
Rental Properties
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Real Estate Crowdfunding
Benefits and Risks of Investing in Real Estate for Retirement
Choosing the Right Retirement Savings Vehicle
Assessing Individual Needs and Goals
Diversification and Risk Management
Tax Considerations
Fees and Expenses
Conclusion
Retirement Savings Vehicles FAQs
Retirement savings vehicles are accounts or plans that allow individuals to save money specifically for retirement. Examples include 401(k)s, IRAs, Roth IRAs, and pension plans.
A 401(k) is a retirement savings plan offered by employers that allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income to a retirement account. Employers may also offer matching contributions or other incentives for employee contributions.
An Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is a retirement savings account that individuals can open and manage on their own. Contributions to traditional IRAs are tax-deductible, while contributions to Roth IRAs are not tax-deductible but can be withdrawn tax-free in retirement.
A pension plan is a retirement savings plan in which an employer sets aside funds on behalf of employees, which are invested and then paid out as retirement income. Pension plans are less common today, but still exist in some industries such as government or union jobs.
Yes, there are other retirement savings vehicles, such as annuities, taxable investment accounts, and health savings accounts (HSAs) that can be used to save for retirement. It's important to work with a financial advisor to determine which retirement savings vehicles are appropriate for your specific financial situation and retirement goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











