The maximum social security benefit is for individuals who, for at least 35 years of working, had earnings equal to or greater than Social Security's maximum taxable income. In 2024, a person's taxable income cannot exceed $168,600. The maximum benefit varies each year due to the annual adjustment based on changes in the national wage level. The current maximum monthly benefit is $3,822 for someone who files at full retirement age (FRA) of 66. However, the maximum payment for individuals who qualify and wait until 70 is $4,873. For those born in 1960 or later, FRA is age 67. For those born between 1943 and 1954, FRA is age 66, and so on. For more information on FRA, please see the table below. You can get more money from your retirement if you wait until you reach your full retirement age. Social Security is a component of nearly every retirement program for American workers. It offers qualified retirees and their families replacement income. Knowing how the system works and how much you will receive when you retire is essential. The percentage of your pre-retirement earnings that Social Security replaces is based on your greatest 35 years of earnings. Higher lifetime earnings will translate to higher benefits. Suppose you stopped working for a while and had minimal wages. In that case, your benefit is reduced as opposed to those who continuously work. Your benefits depend on how much you earn and when you begin receiving benefits. Social Security retirement benefit is distinct from disability benefits, family benefits, and supplemental security income (SSI). In these cases, Social Security benefits are also paid to disabled people, spouses, children, and survivors. The initial criteria to qualify for Social Security is for you to have 40 work credits which translates to a working experience of 10 years. You must earn the maximum taxable income for Social Security for 35 years to get the maximum benefit. To estimate your Social Security benefits, the 35 years you made the most money are added together. All salaries are adjusted for inflation, multiplying wages from prior years by a factor based on the years earned. This calculation approximates purchasing power based on the present worth of the dollar. The Average Indexed Monthly Earnings (AIME) are calculated by dividing the total indexed wages by 420. The value of 420 is 35 years, expressed in months. If you worked less than 35 years, a zero is indicated for the years you were not employed. Additional variables that determine the benefit amount include the year in which benefits are first collected and whether or not full retirement age has been attained. It also counts whether or not you continue to work while collecting benefits. Here are the steps you must take to maximize your Social Security benefit: Social Security uses the average of your 35 highest-paid inflation-adjusted years to determine your benefits. To obtain the maximum Social Security benefit, you must contribute the maximum amount, which changes annually depending on the national average salary index, over this period. Social Security payments are available beginning at age 62. If you wish to receive the maximum benefits, hold off on receiving the benefits and opt to wait until age 70. You will get the largest possible monthly check. Based on your birth year, if your full retirement age is 67 and you decide to collect your Social Security benefits at 62, your benefits will be reduced by up to 30%. Truly maximizing your pay would require you to work until you are 70. If your full retirement age is 66, and you continue to work, your monthly payment will grow by approximately 0.7% every month or 8% annually. This means they will be 32% higher than if you began receiving them at age 66. This scale is not comprehensive but is used to show how early or delayed withdrawal of Social Security benefits affects beneficiaries. The optimal period to begin receiving Social Security payments depends on a number of variables: Your cash flow is one of the primary factors you should consider when deciding when to start taking Social Security benefits. If you do not have other sources of retirement income, this may prompt you to withdraw your benefits. If your expenses are relatively high, you may start taking benefits sooner rather than later. If you are still working, you may want to wait to take Social Security benefits. Your benefits will be reduced if you take them before reaching full retirement age. Being employed allows you to continue to grow your benefits. Having money saved in additional retirement funds can supplement your Social Security benefits, which may allow you to hold off until later before collecting the benefits. Life expectancy is another critical factor when deciding when to start taking Social Security benefits. If you expect to live longer, wait for a while before taking benefits to receive larger payments for a more extended period. Some individuals are required to pay income taxes on their Social Security payments. This is typically the case only if you have considerable extra income in addition to your benefits. These extra revenues include salaries, self-employment, interest, dividends, and other taxable resources that must be reported on your tax return. According to Internal Revenue Service (IRS) regulations, you will have to pay taxes on your Social Security income under the following conditions: Income Tax Rules for Social Security Benefits For those married who file a separate tax return, your Social Security benefits will be subject to taxation as well. The most straightforward approach to avoid paying income tax on your Social Security payments is to maintain your total combined income below the tax limits. Below are ways you can follow: Move Assets Into an IRA Put assets that generate income into your IRA, where their interest or dividends will not be counted as income immediately. Withdraw Before Retirement It may be advantageous to delay receiving Social Security and withdraw from conventional retirement funds. Your monthly benefit payment will be higher if you wait until you reach full retirement age. Invest in an Annuity Purchase a qualified longevity annuity contract (QLAC). This delayed annuity is paid for with a qualified retirement plan or an IRA. QLAC offers monthly payments for life and is protected against stock market declines. So long as the annuity meets IRS standards, it is free from Required Minimum Distributions (RMD) laws until distributions commence after the stated annuity starting date. Below are some ways married couples can best claim and maximize their Social Security benefits: Delay Both Spouses' Benefits Delaying both spouses' benefits until age 70 can provide the most significant possible lifetime benefits for a married couple. Delay Higher-Earning Spouses' Benefits It generally makes sense to use a split strategy, which means that the higher-earning spouse waits to claim benefits. The higher-earning spouse will receive a more significant benefit amount, which will grow over time, resulting in a more significant total cash. When a higher-earning spouse delays collecting Social Security, the survivor benefits of the lower-earning spouse also increase. In 2024, the highest Social Security payout is $4,873 per month or $58,476 annually. However, most people are unlikely to have any probability of attaining such an amount. To estimate your Social Security benefits, the 35 years you made the most money are added together and adjusted for inflation. Your average indexed monthly earnings are calculated by dividing the total indexed wages by 420 months. Earn maximum income for 35 years, delay collecting benefits until 70, and consider working until 70 to get the maximum Social Security benefits. Your Social Security benefits can have tax consequences if they exceed the total income threshold. Take advantage of other tax-free retirement accounts. The timing is crucial in these transactions, and things can become very complicated. Do not hesitate to reach out to a retirement planning advisor.What Is the Maximum Social Security Benefit?
Have questions about Social Security Benefits? Click here.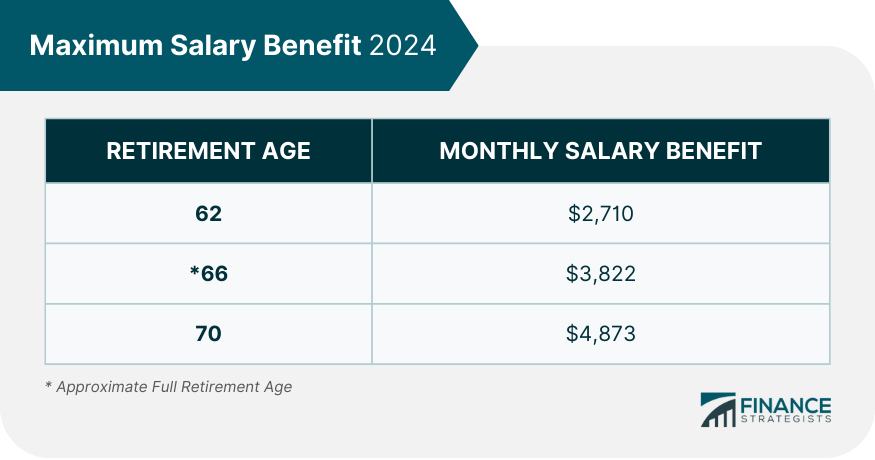

How Social Security Benefits Are Calculated
How to Get the Maximum Social Security Benefit
Earn Maximum Taxable Income for at Least 35 Years
Choose to Receive Social Security Benefits at Age 70
Work Until You Reach Age 70

Factors to Consider on When to Start Taking Social Security Benefits
Current Income
Employment Status
Other Available Retirement Funds
Life Expectancy
Income Taxes And Social Security Benefits

Avoiding Taxes on Social Security Benefits
How Married Couples Can Best Claim Social Security Benefits
The Bottom Line
Maximum Social Security Benefit FAQs
The maximum Social Security benefit payable in 2024 is $4,873 per month.
To qualify for the maximum Social Security benefit, you must have earned 35 years of maximum Social Security wage credits and reached full retirement age (66 to 67 depending on your year of birth).
Yes, up to 85% of the Maximum Social Security benefit may be subject to federal income tax.
No, the maximum Social Security benefit does not increase with age. It remains fixed for your retirement year.
The maximum Social Security benefit is calculated based on your average indexed monthly earnings (AIME) and the primary insurance amount (PIA). Your highest 35 years of earnings are indexed to the current wage base in order to calculate your AIME, then your PIA is calculated based on a formula set by law. The maximum benefit is calculated by applying the bend points of the PIA formula.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











