Social Security is a government program that provides financial assistance to retired workers, disabled individuals, and their families. It is funded through payroll taxes and aims to provide a safety net for citizens during their retirement years. Planning for Social Security is essential to ensure a comfortable retirement. Proper planning helps individuals make informed decisions regarding when to claim benefits, maximize their monthly payments, and better integrate Social Security into their overall retirement strategy. Social Security is a crucial component of retirement planning. It serves as a reliable source of income for retirees, supplementing other sources like personal savings, pensions, and investments, to help maintain a desired standard of living. The Social Security program was established in 1935 to provide financial assistance to elderly citizens during the Great Depression. Today, it continues to support millions of Americans by offering a steady income source during retirement, as well as benefits for disabled individuals and survivors. Retirement benefits are the primary function of Social Security. They provide a monthly income to eligible workers who have reached the required retirement age and have earned enough work credits throughout their careers. Disability benefits offer financial support to workers who have become disabled and can no longer work. These benefits aim to provide a safety net for individuals facing long-term disabilities and help them maintain their financial stability. Survivor benefits are designed to provide financial assistance to the families of deceased workers. These benefits can be claimed by eligible spouses, children, and sometimes parents, helping to support families who have lost a primary breadwinner. Spousal benefits are available to the spouse of a Social Security beneficiary, even if they have not earned enough credits themselves. These benefits are typically equal to 50% of the higher-earning spouse's primary insurance amount (PIA) and can be claimed as early as 62, but will be reduced if claimed before the spouse's FRA. Work credits are the basis for determining eligibility for Social Security benefits. Workers earn credits by paying Social Security taxes on their income, with a maximum of four credits earned per year. The number of required credits varies based on the type of benefit being claimed. Age requirements play a significant role in determining eligibility for retirement benefits. The full retirement age varies depending on the birth year but generally falls between 66 and 67 years old. Early retirement can be claimed at 62, but this results in reduced monthly benefits. Disability benefits have specific requirements that must be met. Claimants must have a medically determinable physical or mental impairment that prevents them from working and is expected to last at least one year or result in death. They must also have earned sufficient work credits based on their age. Full retirement age (FRA) is the age at which an individual can claim their full Social Security benefits without any reduction. Claiming benefits at FRA is a common strategy that ensures retirees receive their maximum monthly payments without penalty. Claiming Social Security benefits early, at age 62, results in a permanently reduced monthly payment. However, this strategy may be suitable for individuals who need immediate income or have a shorter life expectancy, as it allows them to start receiving benefits sooner. Delaying the start of Social Security benefits beyond FRA results in an increased monthly payment. This strategy can be beneficial for those who can afford to wait and want to maximize their lifetime benefits, especially if they have a longer life expectancy. Spousal benefits are available to the spouses of eligible workers, providing up to 50% of the worker's primary insurance amount. To qualify, the spouse must be at least 62 years old or caring for a child under 16 from the marriage. Understanding eligibility requirements for spousal benefits is essential for couples looking to optimize their combined Social Security income during retirement. To maximize spousal benefits, it's crucial to understand the various claiming strategies available. Couples should consider factors such as age, work history, and life expectancy to determine the best approach to optimize their combined benefits and secure a stable retirement income. Survivor benefits are available to the surviving spouse, children, and sometimes parents of a deceased worker. To be eligible, the surviving spouse must be at least 60 years old, or 50 if disabled, or any age if caring for a child under 16. Children who are disabled and incapable of self-support remain eligible if the disability occurred before age 18 or before 22 if a full-time student. Maximizing survivor benefits involves making informed decisions based on the surviving spouse's age, the deceased worker's benefit amount, and other available benefits. Timing is crucial, as waiting until full retirement age to claim survivor benefits can result in higher monthly payments. Social Security benefits may be subject to federal income tax, depending on an individual's total income. If the combined income exceeds certain thresholds, up to 85% of the benefits could be taxable. Proper tax planning can help minimize the tax impact on Social Security income. Some states also tax Social Security benefits, while others do not. Retirees should be aware of their state's tax policies and consider the potential tax implications when planning their retirement and Social Security claiming strategies. Implementing tax-efficient withdrawal strategies can help reduce the tax burden on Social Security benefits. This may involve strategically drawing from taxable, tax-deferred, and tax-free accounts to minimize the impact on combined income and keep Social Security benefits below taxable thresholds. Roth conversions involve transferring funds from a tax-deferred retirement account, such as a traditional IRA, to a Roth IRA. This can help reduce future taxable income and minimize the taxation of Social Security benefits, as Roth distributions are generally tax-free. Estimating Social Security income is an essential step in retirement planning. Individuals can use their Social Security statement or online tools to project their future benefits, helping them create a comprehensive financial plan for retirement. Pensions are a valuable source of retirement income for some workers. Integrating pension income with Social Security benefits helps retirees create a diversified income stream, providing more financial stability and security during retirement. Retirement savings accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, are essential components of a well-rounded retirement plan. Balancing withdrawals from these accounts with Social Security income can help ensure a sustainable income throughout retirement. Part-time work during retirement can supplement Social Security benefits and other income sources, helping retirees maintain their desired lifestyle. It's important to consider the potential impact of earned income on Social Security benefits and taxes. Social Security may undergo legislative changes in the future to address its long-term solvency. Retirees should stay informed about potential reforms and be prepared to adjust their retirement plans accordingly to maintain financial stability. Longevity risk, or the risk of outliving one's retirement savings, is a concern for many retirees. By incorporating Social Security planning strategies that maximize lifetime benefits, retirees can help mitigate this risk and ensure a more financially secure retirement. The Social Security Administration (SSA) website is an invaluable resource for individuals seeking information about their benefits, eligibility, and claiming strategies. The website provides detailed guides, tools, and resources to help users better understand and plan for their Social Security benefits. Online benefit calculators, such as the SSA's Retirement Estimator, can help individuals estimate their future Social Security income. These tools provide personalized estimates based on work history and claiming strategies, allowing users to make more informed decisions about their retirement planning. Financial advisors and planners can offer personalized guidance on Social Security planning, helping clients navigate complex rules and regulations. Working with a professional can ensure that individuals make well-informed decisions that align with their overall retirement goals and financial situation. Social Security provides financial assistance to retired workers, disabled individuals, and their families. Planning for Social Security is essential to ensure a comfortable retirement. Understanding Social Security basics, eligibility criteria, and planning strategies like determining the optimal age to claim benefits, maximizing spousal and survivor benefits, and minimizing tax liability can help retirees make informed decisions. It's important to balance Social Security benefits with other retirement income sources like pensions, retirement savings accounts, and part-time work, and adjust retirement plans for potential changes to Social Security. Tools and resources for Social Security planning like the SSA website, online benefit calculators, and financial advisors can offer personalized guidance to help individuals make well-informed decisions that align with their overall retirement goals and financial situation. Professional guidance can help navigate the intricacies of Social Security and ensure that retirees are well-prepared to enjoy a comfortable and financially secure retirement.What Is Social Security Planning?
Understanding Social Security Basics
History and Purpose of Social Security
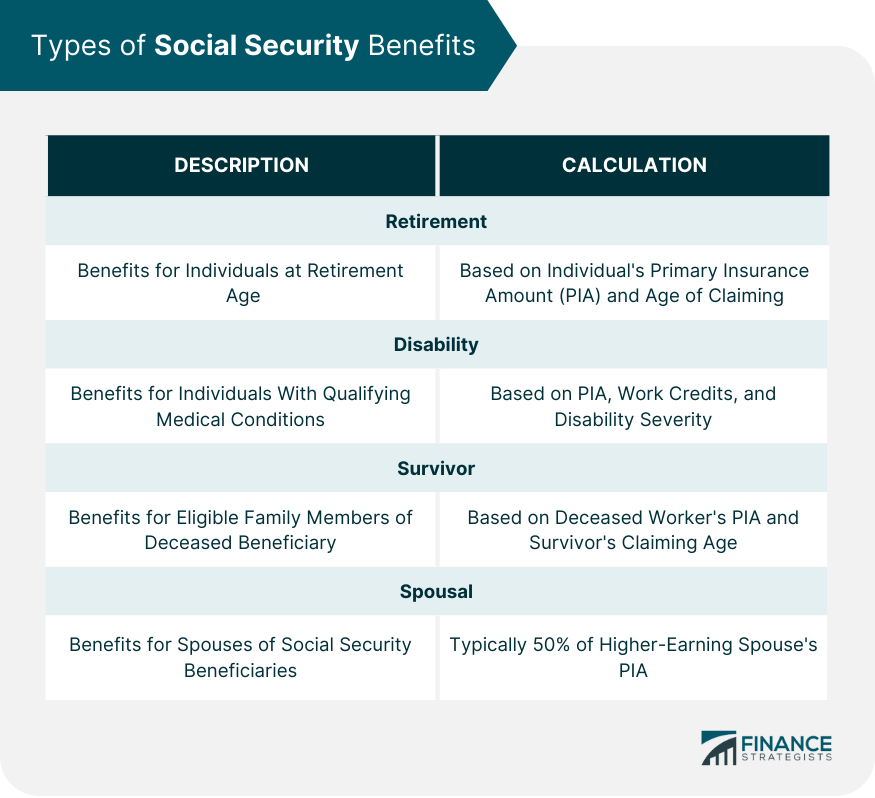
Types of Social Security Benefits
Retirement Benefits
Disability Benefits
Survivor Benefits
Spousal Benefits
Eligibility Criteria
Work Credits
Age Requirements
Disability Requirements
Social Security Planning Strategies
Determining the Optimal Age to Claim Benefits
Full Retirement Age
Early Retirement
Delayed Retirement
Spousal Benefits and Strategies
Spousal Benefits Eligibility
Maximizing Spousal Benefits
Survivor Benefits and Strategies
Eligibility and Claiming Survivor Benefits
Maximizing Survivor Benefits
Social Security and Taxes
Taxation of Social Security Benefits
Federal Income Tax
State Income Tax
Strategies to Minimize Tax Liability
Tax-Efficient Withdrawal Strategies
Roth Conversions

How to Integrate Social Security into Your Retirement Plan
Estimate Social Security Income
Balance Social Security with Other Retirement Income Sources
Pensions
Retirement Savings Accounts
Part-Time Work
Adjust Your Retirement Plan for Potential Changes to Social Security
Legislative Changes
Longevity Risk

Tools and Resources for Social Security Planning
Social Security Administration Website
Online Social Security Benefit Calculators
Financial Advisors and Planners
Final Thoughts
Social Security Planning FAQs
Social Security planning is crucial for a successful retirement as it helps individuals make informed decisions about when to claim benefits, maximize their monthly payments, and integrate Social Security with other income sources, ensuring a stable and comfortable retirement.
Social Security planning involves evaluating factors such as your full retirement age, the potential advantages of early or delayed retirement, and your individual financial needs and life expectancy. This helps you determine the best age to start claiming benefits to maximize your lifetime income.
Yes, there are several tools and resources for Social Security planning, including the Social Security Administration website, online benefit calculators, and professional financial advisors and planners who can offer personalized guidance and advice.
Social Security planning helps minimize tax liability by implementing tax-efficient withdrawal strategies from various retirement accounts and considering options such as Roth conversions. This can help reduce the impact of taxes on your Social Security benefits and overall retirement income.
Social Security planning takes into account potential legislative changes and longevity risk, allowing retirees to adjust their plans accordingly. Staying informed about potential reforms and incorporating strategies that maximize lifetime benefits can help ensure financial stability during retirement.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











