Benefit Corporations, commonly known as B Corps, are a new type of corporate entity that combines social and environmental responsibility with profitability. These organizations are legally required to consider the impact of their decisions not only on shareholders but also on society and the environment. The primary purpose of B Corps is to create a positive impact on society and the environment, alongside generating profits. They aim to redefine success in business by prioritizing a triple bottom line approach, which focuses on people, planet, and profit. The B Corp movement emerged in 2006 with the founding of B Lab, a nonprofit organization that certifies and supports B Corps. Since then, thousands of companies worldwide have joined the movement, committing to upholding high social, environmental, and accountability standards. B Corps are governed by state laws in the United States, with each state having its specific regulations. Over 30 states have enacted Benefit Corporation legislation, providing a legal framework for these entities. Internationally, several countries have introduced similar legal structures for businesses seeking to align profit with purpose. B Corps differs from traditional corporations by prioritizing social and environmental objectives alongside financial performance. While nonprofits focus on social and environmental missions without seeking profits, B Corps aim to balance profit with purpose, allowing them to attract investment and generate revenues. B Corps must have a material, positive impact on society and the environment. Their charter must include a commitment to these goals, ensuring that social and environmental considerations are factored into decision-making processes. B Corps are required to consider the interests of all stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, the environment, and local communities, in their decision-making processes. B Corps must provide public disclosure of their social and environmental performance, typically through the B Impact Assessment, which measures their impact on stakeholders and the environment. Companies seeking B Corp certification must undergo a rigorous assessment by B Lab, which evaluates their social and environmental performance, legal accountability, and transparency. Certified B Corps must also meet certain legal requirements and pay an annual fee to maintain their certification. B Corps is committed to creating a positive impact on society and the environment, addressing pressing global challenges such as climate change, income inequality, and resource depletion. By adhering to high social and environmental standards, B Corps can enhance their brand reputation, attracting conscious consumers who value ethical and sustainable business practices. B Corps often prioritize employee well-being, offering competitive wages, benefits, and opportunities for growth. This focus on employee welfare can lead to increased engagement, satisfaction, and retention. B Corps can attract impact investors who seek both financial returns and positive social and environmental outcomes, helping them access capital for growth and development. The legal structure of B Corps ensure that its mission and values are protected, even in the face of changes in ownership or management. The certification process for B Corps can be costly and complex, particularly for smaller businesses that may struggle with the requirements and fees associated with B Corp status. Critics argue that the B Corp movement lacks sufficient regulation and oversight, potentially allowing companies to engage in greenwashing or making misleading claims about their social and environmental impact. Although the B Corp movement has grown rapidly, many consumers and investors are still unfamiliar with the concept, limiting market recognition and understanding of the benefits associated with B Corps. B Corps faces the challenge of balancing profit with its social and environmental missions, which can sometimes result in trade-offs and difficult decision-making processes. Outdoor clothing and gear company Patagonia is a well-known B Corp, committed to environmental responsibility and sustainable business practices. The company donates a portion of its profits to environmental causes and encourages its customers to repair and recycle products. Ice cream manufacturer Ben & Jerry's became a certified B Corp in 2012, demonstrating its commitment to social and environmental issues, including climate justice, fair trade, and equitable working conditions. Ethical cosmetics retailer The Body Shop has been a certified B Corp since 2019, emphasizing cruelty-free products, sustainable sourcing, and community trade partnerships to promote social and environmental well-being. Women's clothing brand Eileen Fisher is a B Corp dedicated to sustainable and ethical fashion, using organic and recycled materials in its products and supporting fair labor practices throughout its supply chain. Eyewear company Warby Parker is a B Corp that combines fashion with social impact, providing affordable glasses to consumers while also donating a pair to someone in need for every pair sold. The B Corp movement is expected to continue expanding globally, as more companies recognize the benefits of combining profit with purpose and seek to adopt sustainable business practices. Governments and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the importance of B Corps, introducing new regulations and incentives to support their growth and development. B Corps are likely to collaborate more closely with other stakeholders, including traditional corporations, nonprofits, and governments, in addressing global challenges and promoting sustainable development. As the B Corp movement grows, its principles are expected to become more widely adopted in mainstream business practices, influencing corporate culture and decision-making processes across various industries. B Corps plays a crucial role in driving sustainable and inclusive growth, demonstrating that businesses can be a force for good by prioritizing social and environmental objectives alongside financial performance. As the business landscape continues to evolve, B Corps faces both opportunities and challenges in promoting its mission and values. By addressing these challenges and embracing new opportunities, B Corps can help create a more sustainable, equitable, and prosperous future for all.Definition of Benefit Corporations (B Corps)
Purpose and Goals of B Corps
Emergence and Growth of the B Corp Movement
Legal Framework of B Corps
Legislation and Regulations Governing B Corps
Comparison to Traditional Corporations and Nonprofits
Key Legal Requirements for B Corps
Purpose
Accountability
Transparency
Certification Process for B Corps
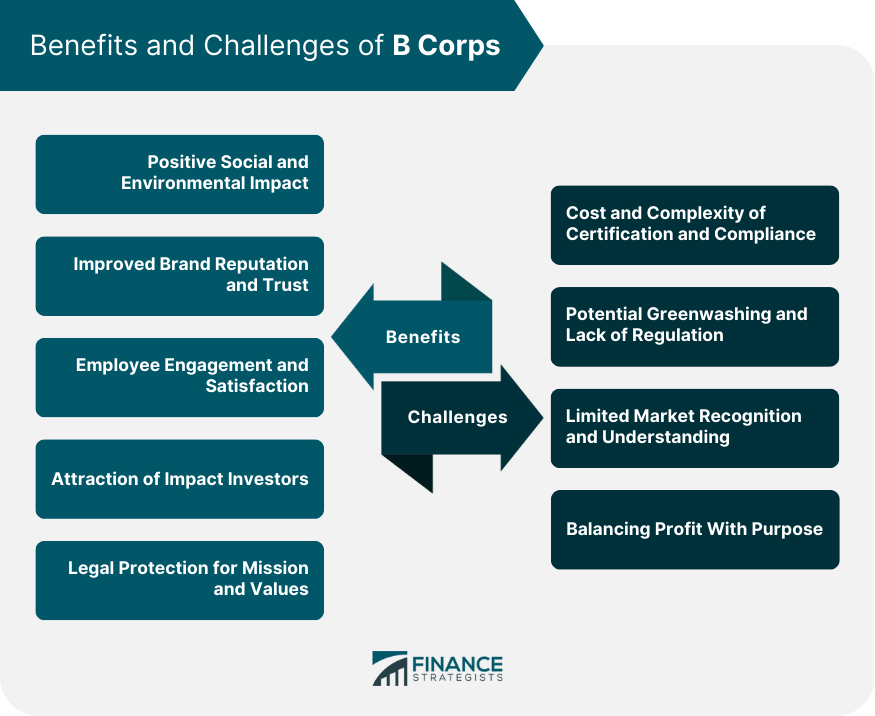
Benefits of B Corps
Positive Social and Environmental Impact
Improved Brand Reputation and Consumer Trust
Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
Attraction of Impact Investors
Legal Protection for Long-Term Mission and Values
Challenges and Criticisms of B Corps
Cost and Complexity of Certification and Compliance
Potential Greenwashing and Lack of Regulation
Limited Market Recognition and Understanding
Balancing Profit With Purpose
Case Studies of Successful B Corps
Patagonia
Ben & Jerry's
The Body Shop
Eileen Fisher
Warby Parker
The Future of B Corps
Expansion of B Corp Movement Globally
Policy and Regulatory Changes Supporting B Corps
Collaboration Between B Corps and Other Stakeholders
Integration of B Corp Principles in Mainstream Business Practices
Conclusion
Benefit Corporations (B Corps) FAQs
Benefit Corporations (B Corps) are businesses that prioritize social and environmental responsibility alongside profitability. Unlike traditional corporations, which focus primarily on shareholder returns, B Corps legally commit to considering the impact of their decisions on society, the environment, and all stakeholders.
B Corps become certified through a rigorous assessment conducted by the nonprofit organization B Lab. The process evaluates a company's social and environmental performance, legal accountability, and transparency. Companies must meet specific legal requirements and pay an annual fee to maintain their B Corp certification.
Benefits of becoming a B Corp include creating a positive social and environmental impact, improving brand reputation and consumer trust, increasing employee engagement and satisfaction, attracting impact investors, and providing legal protection for long-term mission and values.
Common criticisms and challenges faced by B Corps include the cost and complexity of certification and compliance, potential greenwashing and lack of regulation, limited market recognition and understanding, and balancing profit with social and environmental missions.
B Corps contribute to sustainable and inclusive growth by prioritizing social and environmental objectives alongside financial performance. By adopting a triple bottom line approach focused on people, planet, and profit, B Corps can drive positive change and demonstrate that businesses can be a force for good in society.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











