What Is a Sale of Business Contract?
The sale of a business is a complex and multifaceted transaction that requires a comprehensive and well-drafted contract.
A sale of business contract is a document that outlines in legal terms the conditions of a transaction involving the sale of a business. The contract outlines the obligations of the parties involved, including the buyer and seller, and defines the terms of the sale.
The contract typically includes details regarding the purchase price and payment terms, the assets and liabilities included in the sale, representations and warranties, conditions precedent and subsequent, non-compete and non-solicitation provisions, and liability limitations.
The sale of business contract is the legal foundation upon which the transaction is based, and it defines the rights and obligations of the parties involved.
Without a comprehensive and well-drafted contract, the transaction is at risk of falling apart, and the parties may find themselves in legal disputes.
The sale of business contract helps to mitigate these risks by defining the terms of the transaction in a clear and concise manner. The contract helps to ensure that the parties understand their obligations and that the transaction proceeds smoothly.
Legal Requirements in Sale of Business Contract
Legal requirements in the sale of business contract are crucial in ensuring that the transaction is legal and compliant with applicable laws and regulations.
Due Diligence
This is the process of investigating the business to ensure that the information provided by the seller is accurate and complete. Due diligence includes reviewing financial statements, tax returns, contracts, and other relevant documents.
The due diligence process helps to identify potential risks and liabilities associated with the business and allows the parties to make informed decisions about the transaction.
Disclosure Requirements
The seller is obligated to provide the buyer with complete and accurate information about the business.
This includes disclosing all material facts about the business, including financial information, contracts, and legal disputes. Failure to disclose material information may result in legal liability for the seller.
State-Specific Laws and Regulations
The laws and regulations vary by state and may include requirements for licensing, permits, and other legal documentation.
State laws and regulations may dictate the type of legal entity that can be sold, the requirements for transferring ownership, and the licensing and permit requirements for the business.
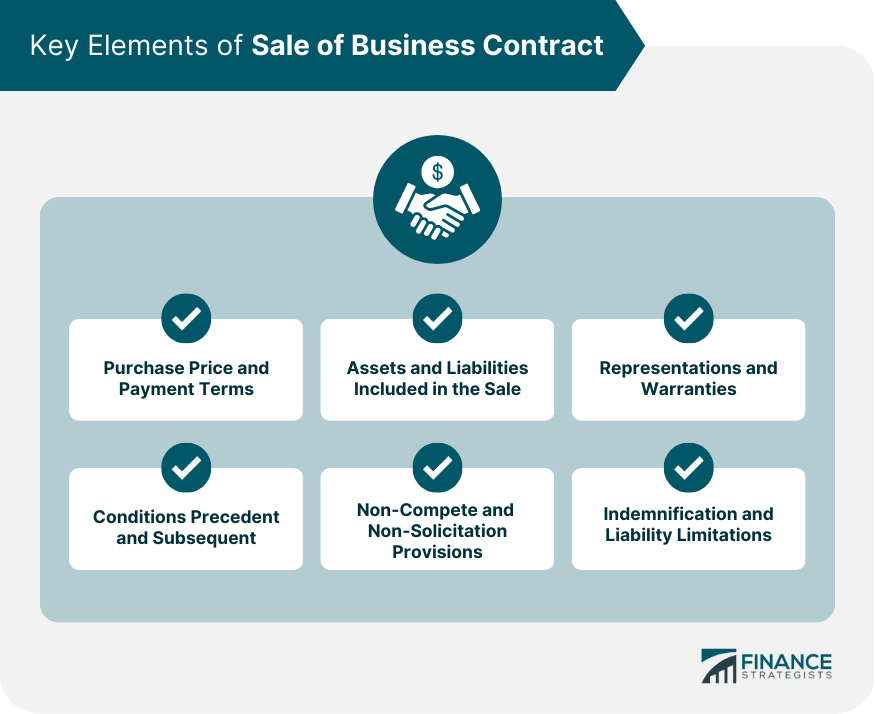
Key Elements of Sale of Business Contract
The key elements of the sale of business contract include the following:
Purchase Price and Payment Terms
The purchase price and payment terms are the most critical elements of the contract. The contract should specify the purchase price and payment terms, including the amount of the down payment, the payment schedule, and the interest rate.
Assets and Liabilities Included in the Sale
The contract should also specify the assets and liabilities included in the sale. This includes tangible assets such as inventory, equipment, and real estate, as well as intangible assets such as goodwill and intellectual property.
Representations and Warranties
The seller provides representations and warranties to the buyer regarding the condition of the business, financial statements, contracts, and other relevant information. The buyer relies on these representations and warranties when deciding to purchase the business.
Conditions Precedent and Subsequent
Conditions precedent are events that must occur before the contract becomes effective, such as obtaining financing or regulatory approval. Conditions subsequent are events that must occur after the contract becomes effective, such as the successful transfer of licenses or permits.
Non-Compete and Non-Solicitation Provisions
These provisions prevent the seller from competing with the buyer or soliciting the buyer's customers for a specified period after the sale.
Indemnification and Liability Limitations
Indemnification provisions define the responsibilities of each party in case of a breach of the contract or other legal issues that arise after the sale.
Liability limitations are provisions that limit the liability of the parties involved in the transaction. These provisions help to protect the parties from legal claims that may arise after the sale.
Drafting Sale of Business Contract
It is important to follow best practices when drafting a sale of business contract for maximum protection:
Understand the Needs of the Parties Involved
The contract should reflect the needs and expectations of both the buyer and the seller and should be structured to ensure that both parties are protected.
It should address issues such as the purchase price, payment terms, assets and liabilities included in the sale, and representations and warranties.
Also, the contract should include provisions for conditions precedent and subsequent, non-compete and non-solicitation provisions, and indemnification and liability limitations.
Structure the Contract for Maximum Protection
The contract should be structured to ensure that the parties are protected from potential risks and liabilities.
This includes defining the scope of the transaction, outlining the purchase price and payment terms, specifying the assets and liabilities included in the sale.
The provisions for representations and warranties, conditions precedent and subsequent, and indemnification and liability limitations should be included.
The contract should also be written in clear and concise language to ensure that both parties understand their obligations and responsibilities.
Avoid Common Pitfalls and Mistakes
Common pitfalls include failing to perform adequate due diligence, failing to disclose material information, and failing to include important provisions in the contract.
To avoid these pitfalls, it is important to work with an experienced attorney who can help ensure that the contract is comprehensive, well-drafted, and compliant with all applicable laws and regulations.
Negotiate and Compromise Effectively
It is important to understand the needs and expectations of the parties involved and to identify common goals and interests. It is also important to be prepared and to have a clear understanding of the terms and conditions of the contract.
During negotiations, it is important to remain open-minded, flexible, and willing to explore alternative solutions.
Effective negotiation and compromise can help to reduce the risk of disputes and can help to ensure that both parties are satisfied with the outcome of the transaction.
Closing the Sale of Business Contract
Closing the sale of a business involves a series of important steps:
Review the Closing Checklist
The checklist should include items such as the completion of due diligence, the satisfaction of all conditions precedent, the transfer of ownership of assets, and the execution of all necessary documents.
It should be prepared well in advance of the closing date and should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure that all necessary steps are taken.
Properly Execute and Deliver the Contract
The contract should be executed in accordance with the terms and conditions outlined in the contract. The delivery of the contract should be made in a timely and efficient manner to ensure that the transaction proceeds smoothly.
Accomplish Post-closing Obligations
There should be provisions for post-closing obligations, such as the transfer of licenses or permits, the payment of taxes, and the handling of outstanding debts or liabilities. The parties involved should work together to ensure that all post-closing obligations are fulfilled.
Prepare Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Dispute resolution mechanisms are also important in closing the sale of business contract. The contract should include provisions for dispute resolution, such as mediation or arbitration, to ensure that any disputes that arise are resolved fairly.

Final Thoughts
A sale of business contract is a critical document that outlines the terms and conditions of a business transaction.
Understanding the legal requirements, key elements, and best practices for drafting and closing a sale of business contract is crucial for ensuring that the transaction is successful and that both parties are protected.
Legal requirements such as the due diligence process, disclosure requirements, and state-specific laws and regulations must be carefully considered when drafting a sale of business contract.
Key elements include the purchase price and payment terms, assets and liabilities included in the sale, representations and warranties, conditions precedent and subsequent, non-compete and non-solicitation provisions, and indemnification and liability limitations.
Drafting a comprehensive sale of business contract requires an understanding of the needs of the parties involved, structuring the contract for maximum protection, and avoiding common pitfalls and mistakes.
It is also important to seek tax services when closing a sale of business contract to ensure that both parties understand the tax implications of the transaction and to minimize tax liabilities. This ensures that the transaction proceeds smoothly and that both parties are protected.
Sale of Business Contract FAQs
A sale of business contract is a legal agreement that outlines the terms and conditions of a business transaction, including the purchase price, payment terms, assets and liabilities included in the sale, and representations and warranties.
The key elements of a sale of business contract include the purchase price and payment terms, assets and liabilities included in the sale, representations and warranties, conditions precedent and subsequent, non-compete and non-solicitation provisions, and indemnification and liability limitations.
Common mistakes to avoid when drafting a sale of business contract include failing to perform adequate due diligence, failing to disclose material information, and failing to include important provisions in the contract.
Effective negotiation and compromise are important in closing a sale of business contract because they can help to reduce the risk of disputes and can help to ensure that both parties are satisfied with the outcome of the transaction.
It is important to seek tax services when closing a sale of business contract to ensure that both parties understand the tax implications of the transaction and to minimize tax liabilities. Working with an experienced attorney and tax professional can help to ensure that the transaction proceeds smoothly and that both parties are protected.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











