The endowment spending policy is a set of rules and guidelines determining how the institution will spend its funds. The policy aims to strike a balance between the needs of the present and the needs of future generations, ensuring intergenerational equity and long-term financial sustainability. Endowment funds are crucial financial resources for institutions such as universities, hospitals, and nonprofit organizations. These funds provide a stable source of income to support the institution's mission and long-term objectives. Different institutions adopt various endowment spending policies depending on their specific needs, goals, and financial situations. These policies generally fall into three main categories: payout rate policies, total return policies, and inflation-adjusted policies. The fixed percentage policy is a straightforward approach that involves setting a predetermined percentage of the endowment fund to be spent annually. This percentage is typically between 4% and 5.5% of the fund's total value. The advantage of this method is its simplicity and predictability; however, it may not adequately address fluctuations in market conditions or inflation rates. The moving average policy calculates the payout rate based on a multi-year average of the endowment's market value. This method provides a more stable and predictable spending rate that is less susceptible to short-term market fluctuations. However, prolonged periods of low investment returns or high inflation can still affect the moving average policy. The historical spending rule is a widely used total return policy. This approach considers the endowment's investment returns (capital gains, dividends, and interest) and the inflation rate when determining the spending rate. The policy typically targets a spending rate of around 5% while ensuring that the endowment's value grows at least at the rate of inflation. The historical spending rule has been credited with helping institutions like Yale University achieve significant endowment growth, but it may not be suitable for all organizations. The hybrid spending rule is a variation of the total return policy that combines elements of the fixed percentage and historical spending rules. This approach sets a spending rate based on a percentage of the endowment's market value and a percentage of the endowment's investment returns. The hybrid spending rule aims to provide stability and flexibility, allowing institutions to adapt to changing market conditions and financial needs. The inflation-adjusted policy seeks to maintain the purchasing power of the endowment fund by adjusting the spending rate to account for inflation. This approach ensures that the fund's value remains constant in real terms, safeguarding the institution's ability to support its mission and objectives over time. The inflation-adjusted policy requires regular monitoring of inflation rates and may be more complex to implement than other endowment spending policies. Deciding on an appropriate endowment spending policy involves considering various factors that influence the institution's financial health and long-term sustainability. Some of the key factors that impact the choice of spending policy include: The performance of the endowment's investments plays a significant role in determining the spending policy. Higher investment returns enable institutions to allocate more funds to their programs and operations while still maintaining the endowment's principal value. Institutions must carefully monitor their investment portfolios and ensure a diverse mix of assets to achieve consistent returns. Inflation can erode the purchasing power of an endowment fund over time, affecting the institution's ability to support its mission and objectives. Endowment spending policies should account for inflation to ensure that the endowment's value remains constant in real terms and that the institution can continue to meet its financial needs. The size of the endowment can influence the choice of spending policy. Larger endowments may be able to support more aggressive spending policies, while smaller endowments may need to adopt more conservative approaches to preserve their principal value. Each institution has its unique goals, priorities, and financial needs. The endowment spending policy should align with the institution's mission and strategic objectives, ensuring that the endowment effectively supports the programs and operations that are most critical to the institution's success. Institutions must also consider legal and regulatory requirements when determining their endowment spending policies. In the United States, for example, the Uniform Prudent Management of Institutional Funds Act (UPMIFA) provides guidelines for nonprofit organizations to manage and spend their endowment funds prudently. One of the main challenges in designing an endowment spending policy is striking the right balance between meeting the institution's immediate financial needs and preserving the endowment's long-term sustainability. Institutions must carefully consider the trade-offs between spending more to support their current programs and operations and ensuring that the endowment continues to generate income for future generations. Intergenerational equity refers to the principle of providing equal benefits and opportunities to both current and future generations. In the context of endowment spending, this means ensuring that the endowment fund continues to support the institution's mission and objectives over time without disproportionately favoring one generation over another. Achieving intergenerational equity can be challenging, particularly in periods of economic uncertainty or fluctuating investment returns. Endowment spending policies must be adaptable to changing economic conditions, such as fluctuations in investment returns or inflation rates. Rigid spending policies may not provide the flexibility needed for institutions to respond effectively to these challenges, potentially putting their financial stability at risk. Institutions should regularly review and adjust their spending policies to remain responsive to evolving economic conditions. It is essential for institutions to align their endowment spending with their mission and strategic objectives. This can be challenging, particularly in times of financial strain when institutions may be tempted to prioritize short-term needs over their long-term goals. A well-designed spending policy should support the institution's core mission and values while ensuring its long-term financial sustainability. Institutions should develop a clear and comprehensive endowment spending policy framework that outlines the goals, objectives, and principles that guide their spending decisions. This framework should be aligned with the institution's mission and strategic priorities and provide a roadmap for managing the endowment fund effectively. Endowment spending policies should be regularly reviewed and adjusted to ensure they remain responsive to changing economic conditions and the institution's evolving financial needs. This may involve reevaluating the spending rate, adjusting the investment portfolio, or updating the policy framework to better align with the institution's mission and objectives. Institutions should be transparent about their endowment spending policies and provide regular updates on the endowment's performance and spending decisions. This transparency can help build trust with stakeholders, including donors, beneficiaries, and the broader community, and ensure that the institution is held accountable for its spending decisions. Institutions should engage with their stakeholders, including donors, beneficiaries, and the broader community, to inform the development and implementation of their endowment spending policies. This collaboration can help ensure that the policy reflects the institution's and its stakeholders' needs and priorities and fosters a sense of shared ownership and commitment to the endowment's success. A diversified investment portfolio can help institutions achieve more consistent investment returns and reduce the risk associated with market fluctuations. Institutions should work with investment professionals to develop diverse assets that align with their risk tolerance, investment objectives, and spending policy goals. An effective endowment spending policy is critical for institutions to balance their short-term financial needs with their long-term sustainability. Institutions can develop a policy that aligns with their mission and ensures intergenerational equity by considering factors such as investment returns, inflation rates, endowment size, and institutional objectives. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the policy, engaging with stakeholders, and diversifying investment portfolios are essential best practices for institutions to achieve long-term success with their endowment funds. Institutions are encouraged to seek professional tax planning services to further optimize endowment management and maximize the potential benefits of endowment spending policies. Expert tax planning can help identify tax-efficient strategies for endowment management, ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and provide valuable insights into the potential impact of tax policies on endowment spending decisions. With professional guidance, institutions can more effectively navigate the complexities of endowment spending policies and enhance their long-term financial sustainability.What Are Endowment Spending Policies
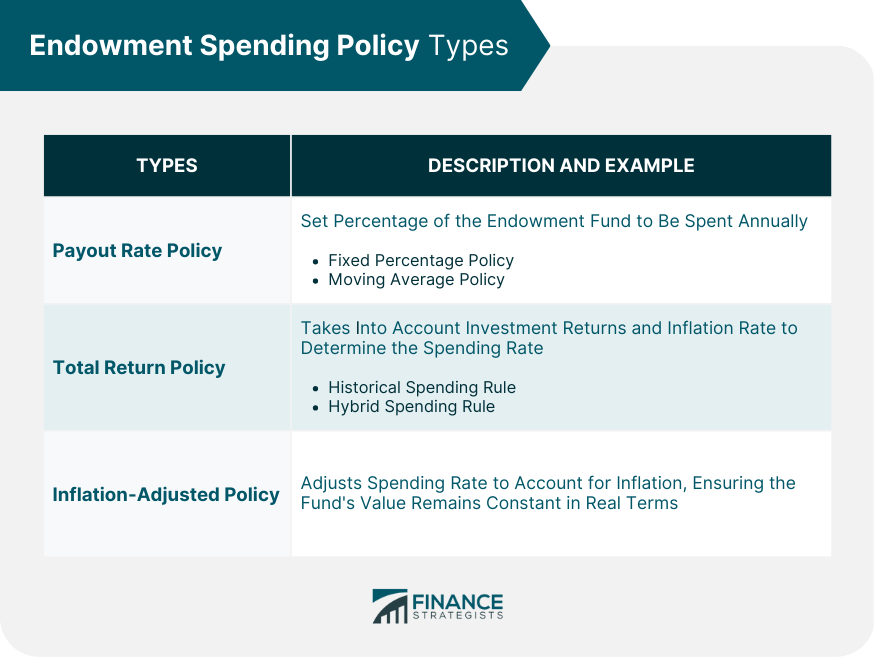
Types of Endowment Spending Policies
Payout Rate Policy
Fixed Percentage Policy
Moving Average Policy
Total Return Policy
Historical Spending Rule
Hybrid Spending Rule
Inflation-Adjusted Policy
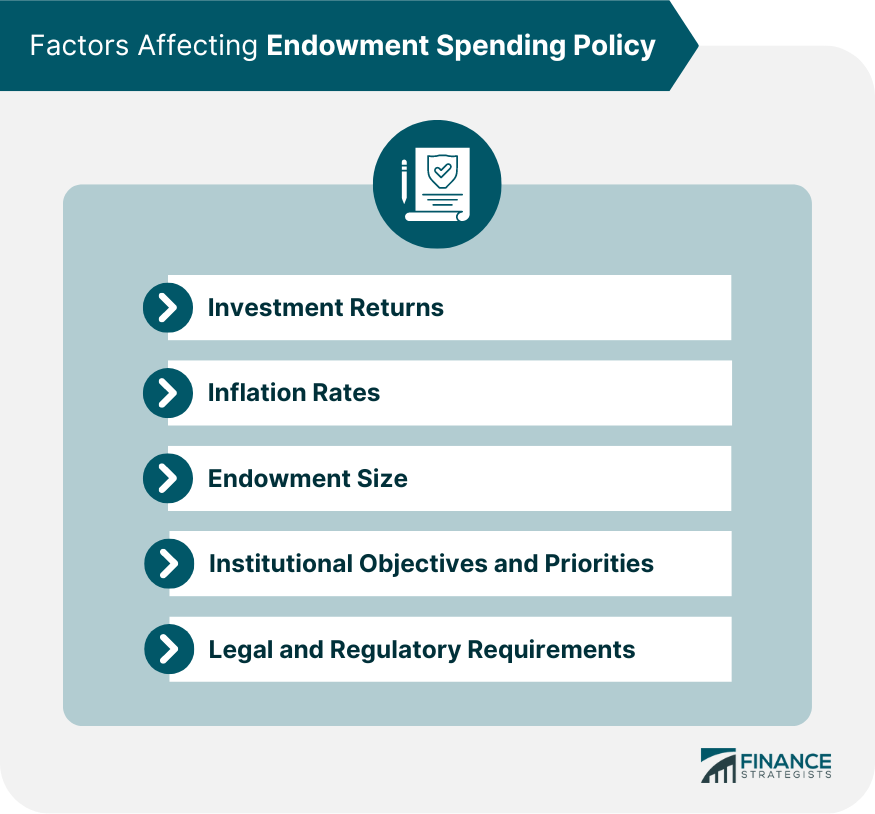
Factors Affecting Endowment Spending Policy
Investment Returns
Inflation Rates
Endowment Size
Institutional Objectives and Priorities
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Challenges in Endowment Spending Policy
Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals
Ensuring Intergenerational Equity
Responding to Changing Economic Conditions
Aligning Spending With Institutional Mission
Best Practices in Endowment Spending Policy
Establishing a Clear Policy Framework
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting the Policy
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Collaborating With Stakeholders
Diversifying Investment Portfolios

Final Thoughts
Endowment Spending Policies FAQs
Endowment spending policies are a set of rules and guidelines that institutions, such as universities and nonprofit organizations, use to determine how they will spend their endowment funds. These policies aim to balance the needs of the present with those of future generations while ensuring long-term financial sustainability and intergenerational equity.
There are three main categories of endowment spending policies: payout rate policies, total return policies, and inflation-adjusted policies. Payout rate policies can be either fixed percentage policies or moving average policies. Total return policies can be either historical spending rules or hybrid spending rules.
Several factors can impact an institution's choice of endowment spending policy, including investment returns, inflation rates, endowment size, institutional objectives and priorities, and legal and regulatory requirements.
One of the main challenges is balancing short-term and long-term goals, ensuring intergenerational equity, responding to changing economic conditions, and aligning spending with the institutional mission.
Institutions should establish a clear policy framework, regularly review and adjust the policy, ensure transparency and accountability, collaborate with stakeholders, and diversify investment portfolios. Seeking professional tax planning services can also help optimize endowment management and enhance long-term financial sustainability.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











