You can apply for FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) even if you did not file taxes. The FAFSA form requires information about your financial situation to determine eligibility for financial aid. If you weren’t required to file taxes because your income was below the IRS filing threshold, you can indicate that on the FAFSA form. You'll need to answer "Not going to file" when prompted about your tax return status. Ensure you have all relevant financial records, such as W-2s or other income statements, to accurately report your income and assets. However, if you were required to file taxes and didn't, it's essential to address that situation promptly, as the Department of Education may request verification of your financial data. Always ensure the accuracy of information provided to avoid potential issues later on. Financial aid is a significant factor for many students pursuing higher education. The FAFSA, or Free Application for Federal Student Aid, often uses tax returns to determine eligibility and the amount of financial aid. Tax returns provide a clear picture of a student's or their family's financial status, ensuring that financial aid is distributed fairly and goes to those most in need. It gives institutions a standardized, verified document that represents an individual's or family's financial status for the past year. There are various reasons an individual might not file a tax return. Understanding these reasons is crucial when approaching FAFSA. Some students or their parents might have incomes below the threshold required for filing taxes. For these individuals, the tax-filing obligation doesn't exist, but they still need to communicate their financial status on the FAFSA. Income sources such as certain types of disability payments or child support aren't always taxable. Those who primarily receive non-taxable income might not file taxes but are still eligible for financial aid. Some people, such as dependents or non-working students, might not have any income, hence no reason to file taxes. Their financial aid needs might still be significant. The straightforward answer is yes. However, the specifics depend on the reasons and circumstances surrounding the lack of a tax return. It's essential to differentiate between those not required to file taxes and those evading their tax obligations. The former group can apply for FAFSA without issues, while the latter might face challenges or legal consequences. Even without a tax return, the FAFSA process remains relatively straightforward if you know the steps. The IRS Data Retrieval Tool allows students and parents to link to the IRS database and transfer information directly into the FAFSA. Non-filers can use this tool to indicate they didn't file. The FAFSA form has specific sections where applicants can mention that they didn't file taxes. This ensures clarity and transparency in the application. Sometimes, schools or the Department of Education might request further documentation or an explanation about why you didn't file taxes. This step is to ensure that all information on the FAFSA form is accurate and honest. If you haven't yet filed your taxes but plan to, you can select the "Will File" status on the FAFSA. This lets institutions know that you'll provide tax details once they're available. While it might seem like an unnecessary chore, there are advantages to filing taxes, even if you're not obligated. Tax credits, like the American Opportunity Credit, can provide substantial savings for eligible students, reducing the cost of education. Once you've filed taxes, future FAFSA applications become more straightforward. The system can retrieve your information seamlessly, reducing the effort needed to reapply. Having a tax record can be beneficial beyond just the FAFSA. It's often required for things like loan applications or housing agreements. While the process might seem straightforward, there can be complications, especially if schools decide to verify your information. Schools can request a non-filing verification letter from the IRS. This letter confirms that you didn't file and weren't legally required to for that year. Verification is a process where your school ensures that all data submitted is accurate. During verification, always respond promptly to requests for information, and ensure all provided data is truthful. Joining the ranks of those who have filed taxes, even if not obligated, can offer unexpected benefits. A tax return can sometimes unlock financial products or services that would otherwise remain inaccessible. This includes certain types of loans or financial instruments tailored to individuals with verified income. By showcasing a comprehensive financial picture through a tax return, some entities might offer dividends or profit-sharing opportunities. These can enhance your overall financial health. Building a financial history, even when not required, fosters trust in various financial institutions. A tax return is a clear communication tool. It shows your financial status transparently, allowing institutions to trust the data you provide. Filing taxes voluntarily can indicate financial responsibility. This can foster trust with banks, lenders, and educational institutions, benefiting you in the long run. For budding entrepreneurs, understanding finances, including taxes and FAFSA, can provide a solid foundation for future ventures. Startups often have unique financial situations. Grasping the nuances of tax filing and financial aid can position entrepreneurs for success. As businesses evolve, so do their financial needs. A clear understanding of taxes and financial aid ensures businesses get appropriate support at every stage. Being financially literate, and understanding the importance of taxes and the intricacies of FAFSA, can be empowering. Various organizations offer financial literacy programs. These can enhance your understanding of taxes, FAFSA, and more. Beyond traditional financial literacy, targeted workshops can delve into specific areas like tax breaks for students, maximizing financial aid, and optimizing financial health. Navigating the financial landscape of higher education requires clarity, especially concerning FAFSA and tax obligations. While it's possible to apply for FAFSA without having filed taxes, understanding the nuances—like the distinction between not being required to file and avoiding tax obligations—is essential. The benefits of filing taxes, even when not mandated, extend beyond merely simplifying the FAFSA process; they can open doors to tax credits and financial products, and foster trust with financial institutions. Furthermore, a solid grasp of these financial principles can be beneficial for potential entrepreneurs, positioning them for future success. With numerous resources available, including financial literacy programs and tailored workshops, individuals can arm themselves with knowledge, ensuring they make informed decisions regarding their education and financial well-being.Can You Apply for FAFSA if You Did Not File Taxes?
FAFSA and Tax Returns: General Expectation
Why Tax Information Is Typically Required
Reasons for Not Filing Taxes
Income Below the IRS Requirement
Non-taxable Income Sources
Specific Life Circumstances

Can You Apply for FAFSA Without Filing Taxes?
Distinction Between Not Required to File vs Avoiding Tax Obligations
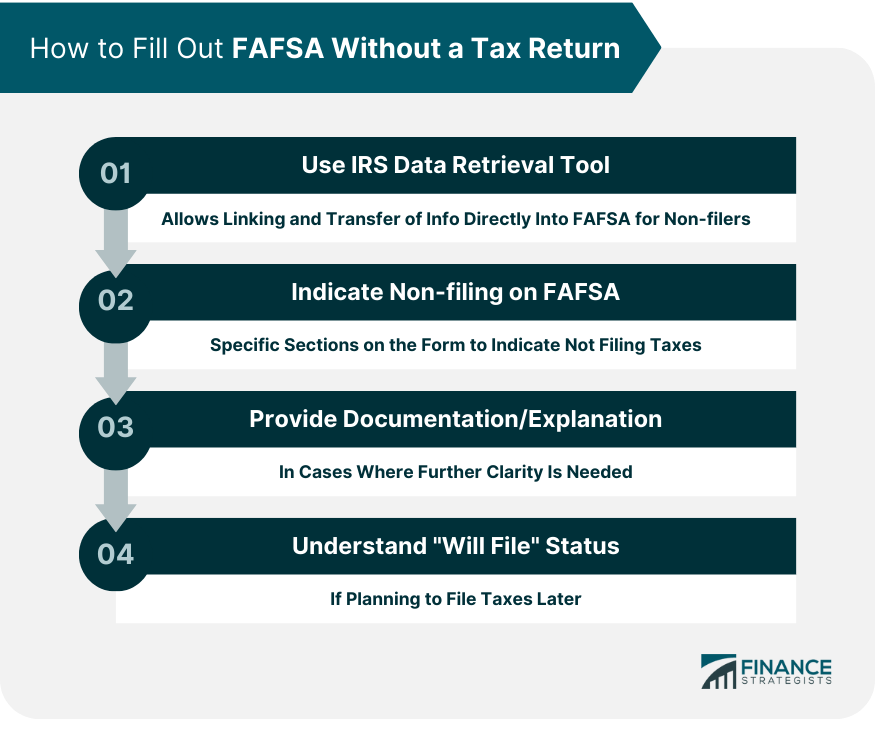
How to Fill Out FAFSA Without a Tax Return
Use the IRS Data Retrieval Tool for Non-filers
Indicate on the FAFSA Form That You Did Not File
Provide Documentation or Written Explanation if Needed
Understand the "Will File" Status on FAFSA
Benefits of Filing Taxes Even If Not Required
Potential Eligibility for Tax Credits
Easier FAFSA Application Process in Subsequent Years
Financial Records for Other Potential Needs
Potential Complications and Verification
Schools Might Ask For Confirmation or Proof of Non-filing Status
Process of Verification and How to Navigate It
Membership Advantages
Access to Other Financial Products and Services
Potential for Dividends and Profit-Sharing
Transparency and Trust
Clear Communication and Disclosure
Building Trust Through Community Involvement and Ethical Practices
Support for Startups and New Businesses
Understanding the Potential of Startups
Tailored Solutions for Businesses at Different Growth Stages
Financial Education and Workshops
Access to Financial Literacy Programs
Workshops Tailored for Individual Needs
Conclusion
Can You Apply for FAFSA if You Did Not File Taxes? FAQs
Yes, individuals with income below the IRS requirement can apply for FAFSA, even if they did not file taxes. They will need to indicate their non-filing status on the application.
If you did not file taxes, you might be asked to provide a non-filing verification letter from the IRS or other relevant documentation to confirm your financial status.
For those who did not file taxes, FAFSA will rely on the provided financial information, such as income statements or benefits, to determine eligibility and aid amount.
No, it's not mandatory. However, the IRS Data Retrieval Tool can be used by non-filers to indicate they didn't file and streamline the application process.
While it's possible to apply for FAFSA without filing taxes, some schools might request additional verification or proof of non-filing status. It's essential to be prepared with the necessary documentation.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











